
Meta-advertising refers to a hybrid form of advertising, where the advertiser advertises for an advertisement. [1] [2] It can also be used for advertisements about advertising agencies. [3]

Meta-advertising refers to a hybrid form of advertising, where the advertiser advertises for an advertisement. [1] [2] It can also be used for advertisements about advertising agencies. [3]
The most common definition of meta-advertising is an ad about an ad. This form of advertising was popular with Super Bowl advertising during the 2000s. Super Bowl ads and spots cost far more than regular ads. [4] In American culture, the Super Bowl ads became highly anticipated. This often leads the companies to air ads encouraging viewers to watch the companies' upcoming Super Bowl ads, a form of meta-advertising. [5]
Advertising about advertisements is a form of viral advertising, whereby advertisers seek to garner attention for their ad and therefore product. [6] [7]
Other examples include advertisements in one form of media, advertising for an ad in another medium. This could include a radio ad saying "Look in your Sunday paper for a free coupon."
The term meta-advertising can also refer to advertisers advertising for themselves. This could include an advertisement for an ad agency. [8]
Meta-advertising can also include ads which advertise for advertising. This is common with billboards, such as a billboard that says "A thousand people will pass by this billboard today. To advertise here call..."

Advertising is the practice and techniques employed to bring attention to a product or service. Advertising aims to put a product or service in the spotlight in hopes of drawing it attention from consumers. It is typically used to promote a specific good or service, but there are wide range of uses, the most common being the commercial advertisement.
Advertising in video games is the integration of advertising into video games to promote products, organizations, or viewpoints.
Pop-up ads or pop-ups are forms of online advertising on the World Wide Web. A pop-up is a graphical user interface (GUI) display area, usually a small window, that suddenly appears in the foreground of the visual interface. The pop-up window containing an advertisement is usually generated by JavaScript that uses cross-site scripting (XSS), sometimes with a secondary payload that uses Adobe Flash. They can also be generated by other vulnerabilities/security holes in browser security.

Classified advertising is a form of advertising, particularly common in newspapers, online and other periodicals, which may be sold or distributed free of charge. Classified advertisements are much cheaper than larger display advertisements used by businesses, although display advertising is more widespread. They were also commonly called "want" ads, starting in 1763, and are sometimes called small ads in Britain.
Google AdSense is a program run by Google through which website publishers in the Google Network of content sites serve text, images, video, or interactive media advertisements that are targeted to the site content and audience. These advertisements are administered, sorted, and maintained by Google. They can generate revenue on either a per-click or per-impression basis. Google beta-tested a cost-per-action service, but discontinued it in October 2008 in favor of a DoubleClick offering. In Q1 2014, Google earned US$3.4 billion, or 22% of total revenue, through Google AdSense. AdSense is a participant in the AdChoices program, so AdSense ads typically include the triangle-shaped AdChoices icon. This program also operates on HTTP cookies. In 2021, over 38.3 million websites use AdSense.

In bus advertising, buses and their related infrastructure is a medium commonly used by advertisers to reach the public with their message. Usually, this takes the form of promoting commercial brands, but can also be used for public campaign messages. Buses may also be used as part of a political or promotional campaign, or as a tool in a commercial enterprise.
Pay-per-click (PPC) is an internet advertising model used to drive traffic to websites, in which an advertiser pays a publisher when the ad is clicked.
Out-of-home (OOH) advertising, also called outdoor advertising, outdoor media, and out-of-home media, is advertising experienced outside of the home. This includes billboards, wallscapes, and posters seen while "on the go". It also includes place-based media seen in places such as convenience stores, medical centers, salons, and other brick-and-mortar venues. OOH advertising formats fall into four main categories: billboards, street furniture, transit, and alternative.
An online advertising network or ad network is a company that connects advertisers to websites that want to host advertisements. The key function of an ad network is an aggregation of ad supply from publishers and matching it with the advertiser's demand. The phrase "ad network" by itself is media-neutral in the sense that there can be a "Television Ad Network" or a "Print Ad Network", but is increasingly used to mean "online ad network" as the effect of aggregation of publisher ad space and sale to advertisers is most commonly seen in the online space. The fundamental difference between traditional media ad networks and online ad networks is that online ad networks use a central ad server to deliver advertisements to consumers, which enables targeting, tracking and reporting of impressions in ways not possible with analog media alternatives.
Online advertising, also known as online marketing, Internet advertising, digital advertising or web advertising, is a form of marketing and advertising that uses the Internet to promote products and services to audiences and platform users. Online advertising includes email marketing, search engine marketing (SEM), social media marketing, many types of display advertising, and mobile advertising. Advertisements are increasingly being delivered via automated software systems operating across multiple websites, media services and platforms, known as programmatic advertising.
Direct response television (DRTV) is any television advertising that asks consumers to respond directly to the company — usually either by calling a toll-free telephone number, sending an SMS message, or by visiting a web site. This is a form of direct response marketing.

Super Bowl commercials, colloquially known as Super Bowl ads, are high-profile television commercials featured in the U.S. television broadcast of the Super Bowl, the championship game of the National Football League (NFL). Super Bowl commercials have become a cultural phenomenon of their own alongside the game itself, as many viewers only watch the game to see the commercials. Many Super Bowl advertisements have become well known because of their cinematographic quality, unpredictability, surreal humor, and use of special effects. The use of celebrity cameos has also been common in Super Bowl ads. Some commercials airing during, or proposed to air during the game, have also attracted controversy due to the nature of their content.

Ad creep is the "creep" of advertising into previously ad-free spaces.
In-game advertising (IGA) is advertising in electronic games. IGA differs from advergames, which refers to games specifically made to advertise a product. The IGA industry is large and growing.
Apple Inc. has had many notable advertisements since the 1980s. The "1984" Super Bowl commercial introduced the original Macintosh mimicking imagery from George Orwell's 1984. The 1990s Think Different campaign linked Apple to famous social figures such as John Lennon and Mahatma Gandhi, while also introducing "Think Different" as a new slogan for the company. Other popular advertising campaigns include the 2000s "iPod People", the 2002 Switch campaign, and most recently the Get a Mac campaign which ran from 2006 to 2009.
Media buying refers to the procurement of advertising on mediums such as a television, newspapers, commercial radio, magazines, websites, mobile apps, over-the-top media services, out-of-home advertising etc. It also includes price negotiation and the appropriate placement of ads based on research to reach the right audiences considering the product, service and message being advertised. A media buyer is tasked to perform such activities.
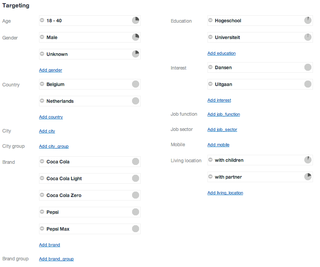
Targeted advertising is a form of advertising, including online advertising, that is directed towards an audience with certain traits, based on the product or person the advertiser is promoting.
Social network advertising, also known as social media targeting, is a group of terms used to describe forms of online advertising and digital marketing focusing on social networking services. A significant aspect of this type of advertising is that advertisers can take advantage of users' demographic information, psychographics, and other data points to target their ads.
Super Bowl XXXIV featured 14 advertisements from 14 different dot-com companies, each of which paid an average of $2.2 million per spot. In addition, five companies that were founded before the dot-com bubble also ran tech-related ads, and 2 before game ads, for a total of 21 different dot-com ads. These ads amounted to nearly 20 percent of the 61 spots available, and $44 million in advertising. In addition to ads which ran during the game, several companies also purchased pre-game ads, most of which are lesser known. All of the publicly held companies which advertised saw their stocks slump after the game as the dot-com bubble began to rapidly deflate.
Major annual or one-time televised mega-events can draw large viewership and significant interest from regional, national, and international advertisers. Advertisers strategically unveil major marketing campaigns in conjunction with televised mega-events and create memorable advertising content with high entertainment value. Some mega-event advertising, such as during the Super Bowl, even attracts a subset of viewers interested primarily in the advertising content. This type of advertisement is an increasingly common television phenomenon as televised mega-events become more popular and available globally.