The Nuremberg Code is a set of ethical research principles for human experimentation created by the court in U.S. v Brandt, one of the Subsequent Nuremberg trials that were held after the Second World War.
Bioethics is both a field of study and professional practice, interested in ethical issues related to health, including those emerging from advances in biology, medicine, and technologies. It proposes the discussion about moral discernment in society and it is often related to medical policy and practice, but also to broader questions as environment, well-being and public health. Bioethics is concerned with the ethical questions that arise in the relationships among life sciences, biotechnology, medicine, politics, law, theology and philosophy. It includes the study of values relating to primary care, other branches of medicine, ethical education in science, animal, and environmental ethics, and public health.
Medical ethics is an applied branch of ethics which analyzes the practice of clinical medicine and related scientific research. Medical ethics is based on a set of values that professionals can refer to in the case of any confusion or conflict. These values include the respect for autonomy, non-maleficence, beneficence, and justice. Such tenets may allow doctors, care providers, and families to create a treatment plan and work towards the same common goal. It is important to note that these four values are not ranked in order of importance or relevance and that they all encompass values pertaining to medical ethics. However, a conflict may arise leading to the need for hierarchy in an ethical system, such that some moral elements overrule others with the purpose of applying the best moral judgement to a difficult medical situation. Medical ethics is particularly relevant in decisions regarding involuntary treatment and involuntary commitment.

Arthur L. Caplan is an American ethicist and professor of bioethics at New York University Grossman School of Medicine.
The Declaration of Helsinki is a set of ethical principles regarding human experimentation developed originally in 1964 for the medical community by the World Medical Association (WMA). It is widely regarded as the cornerstone document on human research ethics.

Jonathan Max Mann was an American physician who was an administrator for the World Health Organization, and spearheaded early AIDS research in the 1980s.
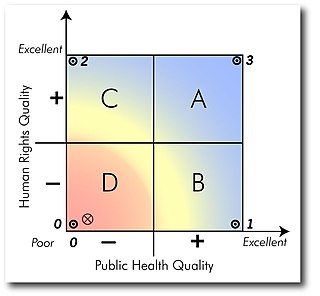
The Four-Step Impact Assessment is an academic framework initiated and published by Jonathan Mann and colleagues at the François-Xavier Bagnoud Center for Health and Human Rights at the Harvard School of Public Health. The assessment takes into account the negotiation of objectives between human rights and public health. Such an approach takes into account a measure of each discipline's respective overlap to expose infringement of goals. Such infringement or confluence can be mapped out in what Mann and colleagues proposed in a 2 by 2 table, as illustrated below.
George J. Annas is the William Fairfield Warren Distinguished Professor and Director of the Center for Health Law, Ethics & Human Rights at the Boston University School of Public Health, School of Medicine, and School of Law.
Jonathan D. Moreno is an American philosopher and historian who specializes in the intersection of bioethics, culture, science, and national security, and has published seminal works on the history, sociology and politics of biology and medicine. He is an elected member of the National Academy of Medicine.
Ruth Macklin is an American philosopher and retired professor of bioethics.

I. Glenn Cohen is a Professor of Law at Harvard Law School. He is also the director of Harvard Law School's Petrie-Flom Center for Health Law Policy, Biotechnology, and Bioethics.
Ellen Wright Clayton is an American Rosalind E. Franklin Professor of genetics and chairwoman of the Institute of Medicine Board at the Population Health and Public Health Practice who became a 2013 recipient of the David Rall Medal.
Penny Wise Budoff was an American physician. She was a family practitioner, and a clinical associate professor of family medicine at the State University of New York at Stony Brook. She is known for her research, which established that menstrual cramping is a physical phenomenon rather than a psychological one. She wrote two books on women's health.
Conflict of interest in the health care industry occurs when the primary goal of protecting and increasing the health of patients comes into conflict with any other secondary goal, especially personal gain to healthcare professionals, and increasing revenue to a healthcare organization from selling health care products and services. The public and private sectors of the medical-industrial complex have various conflicts of interest which are specific to these entities.

Françoise Elvina BaylisFISC is a Canadian bioethicist whose work is at the intersection of applied ethics, health policy, and practice. The focus of her research is on issues of women's health and assisted reproductive technologies, but her research and publication record also extend to such topics as research involving humans, gene editing, novel genetic technologies, public health, the role of bioethics consultants, and neuroethics. Baylis' interest in the impact of bioethics on health and public policy as well as her commitment to citizen engagement]and participatory democracy sees her engage with print, radio, television, and other online publications.
Edward C. Halperin, is the chancellor and CEO of New York Medical College (NYMC) where he is also a professor of radiation medicine, pediatrics and history. He also serves as the Miriam Popack Chair in Biomedical Ethics and director of the Hirth and Samowitz Center for Medical Humanities and Holocaust Studies at NYMC, director of bioethics in the School of Health Sciences and Practice at NYMC, as well as provost for biomedical affairs for the Touro College and University System, a position he has held since 2012.

Fitzhugh Mullan was an American physician, writer, educator, and social activist. He participated in the founding of the Student Health Organization, the National Coalition for Cancer Survivorship, Seed Global Health, and the Beyond Flexner Alliance. Mullan was a professor of Health Policy and Management and of Pediatrics at the George Washington University and the George Washington University Health Workforce Institute, now renamed the Fitzhugh Mullan Institute for Health Workforce Equity. He was an elected member of the National Academy of Medicine.
Amy Lauren Fairchild is an American historian who is a professor at Syracuse University. She is co-director of the World Health Organization Collaborating Center for Bioethics.

Kathy Lynn Hudson is an American microbiologist specializing in science policy. She was the deputy director for science, outreach, and policy at the National Institutes of Health from October 2010 to January 2017. Hudson assisted in the creation and launch of All of Us, the BRAIN initiative, and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences. She founded the Genetics and Public Policy Center at Johns Hopkins University in 2002. Hudson is an advocate for women in science.
Jessica Wilen Berg is an American attorney and specialist in Public Health (MPH), currently serving as co-Dean at Case Western Reserve University School of Law, the first female co-Dean or Dean in the law school's 129-year history. She is also Tom J.E. and Bette Lou Walker Professor of Law,Professor in the Departments of Bioethics, and of Population and Quantitative Health Sciences at the CWRU School of Medicine. She is a reference book author in the area of informed consent. Her scholarly opinion is often reported by institutions and media on ethical aspects iof innovative biomedical procedures.






