
A lathe is a machine tool that rotates a workpiece about an axis of rotation to perform various operations such as cutting, sanding, knurling, drilling, deformation, facing, and turning, with tools that are applied to the workpiece to create an object with symmetry about that axis.

Henry Maudslay was an English machine tool innovator, tool and die maker, and inventor. He is considered a founding father of machine tool technology. His inventions were an important foundation for the Industrial Revolution.

A machine tool is a machine for handling or machining metal or other rigid materials, usually by cutting, boring, grinding, shearing, or other forms of deformations. Machine tools employ some sort of tool that does the cutting or shaping. All machine tools have some means of constraining the workpiece and provide a guided movement of the parts of the machine. Thus, the relative movement between the workpiece and the cutting tool is controlled or constrained by the machine to at least some extent, rather than being entirely "offhand" or "freehand". It is a power-driven metal cutting machine which assists in managing the needed relative motion between cutting tool and the job that changes the size and shape of the job material.

Metalworking is the process of shaping and reshaping metals to create useful objects, parts, assemblies, and large scale structures. As a term it covers a wide and diverse range of processes, skills, and tools for producing objects on every scale: from huge ships, buildings, and bridges down to precise engine parts and delicate jewelry.

A machinist is a tradesperson or trained professional who operates machine tools, and has the ability to set up tools such as milling machines, grinders, lathes, and drilling machines.
A reamer is a type of rotary cutting tool used in metalworking. Precision reamers are designed to enlarge the size of a previously formed hole by a small amount but with a high degree of accuracy to leave smooth sides. There are also non-precision reamers which are used for more basic enlargement of holes or for removing burrs. The process of enlarging the hole is called reaming. There are many different types of reamer and they may be designed for use as a hand tool or in a machine tool, such as a milling machine or drill press.

A grinding machine, often shortened to grinder, is a power tool used for grinding. It is a type of machining using an abrasive wheel as the cutting tool. Each grain of abrasive on the wheel's surface cuts a small chip from the workpiece via shear deformation.

Diamond turning is turning using a cutting tool with a diamond tip. It is a process of mechanical machining of precision elements using lathes or derivative machine tools equipped with natural or synthetic diamond-tipped tool bits. The term single-point diamond turning (SPDT) is sometimes applied, although as with other lathe work, the "single-point" label is sometimes only nominal. The process of diamond turning is widely used to manufacture high-quality aspheric optical elements from crystals, metals, acrylic, and other materials. Plastic optics are frequently molded using diamond turned mold inserts. Optical elements produced by the means of diamond turning are used in optical assemblies in telescopes, video projectors, missile guidance systems, lasers, scientific research instruments, and numerous other systems and devices. Most SPDT today is done with computer numerical control (CNC) machine tools. Diamonds also serve in other machining processes, such as milling, grinding, and honing. Diamond turned surfaces have a high specular brightness and require no additional polishing or buffing, unlike other conventionally machined surfaces.

A chuck is a specialized type of clamp used to hold an object with radial symmetry, especially a cylinder. In a drill, a mill and a transmission, a chuck holds the rotating tool; in a lathe, it holds the rotating workpiece.

In various contexts of science, technology, and manufacturing, an indicator is any of various instruments used to accurately measure small distances and angles, and amplify them to make them more obvious. The name comes from the concept of indicating to the user that which their naked eye cannot discern; such as the presence, or exact quantity, of some small distance.

Turning is a machining process in which a cutting tool, typically a non-rotary tool bit, describes a helix toolpath by moving more or less linearly while the workpiece rotates.

In machining, a metal lathe or metalworking lathe is a large class of lathes designed for precisely machining relatively hard materials. They were originally designed to machine metals; however, with the advent of plastics and other materials, and with their inherent versatility, they are used in a wide range of applications, and a broad range of materials. In machining jargon, where the larger context is already understood, they are usually simply called lathes, or else referred to by more-specific subtype names. These rigid machine tools remove material from a rotating workpiece via the movements of various cutting tools, such as tool bits and drill bits.

In machining, boring is the process of enlarging a hole that has already been drilled by means of a single-point cutting tool, such as in boring a gun barrel or an engine cylinder. Boring is used to achieve greater accuracy of the diameter of a hole, and can be used to cut a tapered hole. Boring can be viewed as the internal-diameter counterpart to turning, which cuts external diameters.

A machine shop or engineering workshop is a room, building, or company where machining, a form of subtractive manufacturing, is done. In a machine shop, machinists use machine tools and cutting tools to make parts, usually of metal or plastic. A machine shop can be a small business or a portion of a factory, whether a toolroom or a production area for manufacturing. The building construction and the layout of the place and equipment vary, and are specific to the shop; for instance, the flooring in one shop may be concrete, or even compacted dirt, and another shop may have asphalt floors. A shop may be air-conditioned or not; but in other shops it may be necessary to maintain a controlled climate. Each shop has its own tools and machinery which differ from other shops in quantity, capability and focus of expertise.

Ultrasonic machining is a subtractive manufacturing process that removes material from the surface of a part through high frequency, low amplitude vibrations of a tool against the material surface in the presence of fine abrasive particles. The tool travels vertically or orthogonal to the surface of the part at amplitudes of 0.05 to 0.125 mm. The fine abrasive grains are mixed with water to form a slurry that is distributed across the part and the tip of the tool. Typical grain sizes of the abrasive material range from 100 to 1000, where smaller grains produce smoother surface finishes.

Grinding is a type of abrasive machining process which uses a grinding wheel as cutting tool.

A screw is an externally helical threaded fastener capable of being tightened or released by a twisting force (torque) to the head. The most common uses of screws are to hold objects together and there are many forms for a variety of materials. Screws might be inserted into holes in assembled parts or a screw may form its own thread.
In manufacturing, threading is the process of creating a screw thread. More screw threads are produced each year than any other machine element. There are many methods of generating threads, including subtractive methods ; deformative or transformative methods ; additive methods ; or combinations thereof.
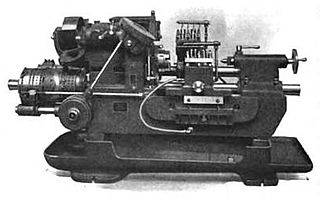
In metalworking and woodworking, an automatic lathe is a lathe with an automatically controlled cutting process. Automatic lathes were first developed in the 1870s and were mechanically controlled. From the advent of NC and CNC in the 1950s, the term automatic lathe has generally been used for only mechanically controlled lathes, although some manufacturers market Swiss-type CNC lathes as 'automatic'.
Mesoscale manufacturing is the process of creating components and products in a range of approximately from 0.1mm to 5mm with high accuracy and precision using a wide variety of engineering materials. Mesomanufacturing processes are filling the gap between macro- and micromanufacturing processes and overlaps both of them. Other manufacturing technologies are nanoscale, microscale and macroscale manufacturing.















