
Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye. There are three well-known branches of microscopy: optical, electron, and scanning probe microscopy, along with the emerging field of X-ray microscopy.

A microscope is a laboratory instrument used to examine objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Microscopy is the science of investigating small objects and structures using a microscope. Microscopic means being invisible to the eye unless aided by a microscope.

Holography is a technique that enables a wavefront to be recorded and later re-constructed. Holography is best known as a method of generating three-dimensional images, but it also has a wide range of other applications. In principle, it is possible to make a hologram for any type of wave.

The optical microscope, also referred to as a light microscope, is a type of microscope that commonly uses visible light and a system of lenses to generate magnified images of small objects. Optical microscopes are the oldest design of microscope and were possibly invented in their present compound form in the 17th century. Basic optical microscopes can be very simple, although many complex designs aim to improve resolution and sample contrast.
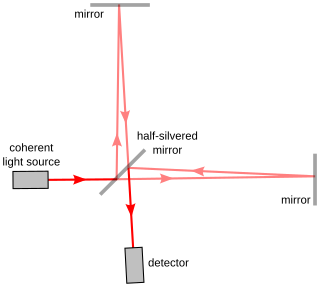
Interferometry is a technique which uses the interference of superimposed waves to extract information. Interferometry typically uses electromagnetic waves and is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy, fiber optics, engineering metrology, optical metrology, oceanography, seismology, spectroscopy, quantum mechanics, nuclear and particle physics, plasma physics, remote sensing, biomolecular interactions, surface profiling, microfluidics, mechanical stress/strain measurement, velocimetry, optometry, and making holograms.

The resolution of an optical imaging system – a microscope, telescope, or camera – can be limited by factors such as imperfections in the lenses or misalignment. However, there is a principal limit to the resolution of any optical system, due to the physics of diffraction. An optical system with resolution performance at the instrument's theoretical limit is said to be diffraction-limited.

A dye laser is a laser that uses an organic dye as the lasing medium, usually as a liquid solution. Compared to gases and most solid state lasing media, a dye can usually be used for a much wider range of wavelengths, often spanning 50 to 100 nanometers or more. The wide bandwidth makes them particularly suitable for tunable lasers and pulsed lasers. The dye rhodamine 6G, for example, can be tuned from 635 nm (orangish-red) to 560 nm (greenish-yellow), and produce pulses as short as 16 femtoseconds. Moreover, the dye can be replaced by another type in order to generate an even broader range of wavelengths with the same laser, from the near-infrared to the near-ultraviolet, although this usually requires replacing other optical components in the laser as well, such as dielectric mirrors or pump lasers.
Particle image velocimetry (PIV) is an optical method of flow visualization used in education and research. It is used to obtain instantaneous velocity measurements and related properties in fluids. The fluid is seeded with tracer particles which, for sufficiently small particles, are assumed to faithfully follow the flow dynamics. The fluid with entrained particles is illuminated so that particles are visible. The motion of the seeding particles is used to calculate speed and direction of the flow being studied.

Confocal microscopy, most frequently confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) or laser confocal scanning microscopy (LCSM), is an optical imaging technique for increasing optical resolution and contrast of a micrograph by means of using a spatial pinhole to block out-of-focus light in image formation. Capturing multiple two-dimensional images at different depths in a sample enables the reconstruction of three-dimensional structures within an object. This technique is used extensively in the scientific and industrial communities and typical applications are in life sciences, semiconductor inspection and materials science.

A tunable laser is a laser whose wavelength of operation can be altered in a controlled manner. While all laser gain media allow small shifts in output wavelength, only a few types of lasers allow continuous tuning over a significant wavelength range.
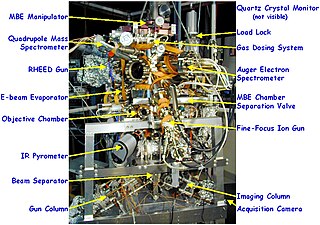
Low-energy electron microscopy, or LEEM, is an analytical surface science technique used to image atomically clean surfaces, atom-surface interactions, and thin (crystalline) films. In LEEM, high-energy electrons are emitted from an electron gun, focused using a set of condenser optics, and sent through a magnetic beam deflector. The “fast” electrons travel through an objective lens and begin decelerating to low energies near the sample surface because the sample is held at a potential near that of the gun. The low-energy electrons are now termed “surface-sensitive” and the near-surface sampling depth can be varied by tuning the energy of the incident electrons. The low-energy elastically backscattered electrons travel back through the objective lens, reaccelerate to the gun voltage, and pass through the beam separator again. However, now the electrons travel away from the condenser optics and into the projector lenses. Imaging of the back focal plane of the objective lens into the object plane of the projector lens produces a diffraction pattern at the imaging plane and recorded in a number of different ways. The intensity distribution of the diffraction pattern will depend on the periodicity at the sample surface and is a direct result of the wave nature of the electrons. One can produce individual images of the diffraction pattern spot intensities by turning off the intermediate lens and inserting a contrast aperture in the back focal plane of the objective lens, thus allowing for real-time observations of dynamic processes at surfaces. Such phenomena include : tomography, phase transitions, adsorption, reaction, segregation, thin film growth, etching, strain relief, sublimation, and magnetic microstructure. These investigations are only possible because of the accessibility of the sample; allowing for a wide variety of in situ studies over a wide temperature range. LEEM was invented by Ernst Bauer in 1962; however, not fully developed until 1985.
Photothermal spectroscopy is a group of high sensitivity spectroscopy techniques used to measure optical absorption and thermal characteristics of a sample. The basis of photothermal spectroscopy is the change in thermal state of the sample resulting from the absorption of radiation. Light absorbed and not lost by emission results in heating. The heat raises temperature thereby influencing the thermodynamic properties of the sample or of a suitable material adjacent to it. Measurement of the temperature, pressure, or density changes that occur due to optical absorption are ultimately the basis for the photothermal spectroscopic measurements.

Francisco Javier "Frank" Duarte is a laser physicist and author/editor of several books on tunable lasers.
Beam expanders are optical devices that take a collimated beam of light and expand its size.

The first description of multiple-prism arrays, and multiple-prism dispersion, was given by Newton in his book Opticks. Prism pair expanders were introduced by Brewster in 1813. A modern mathematical description of the single-prism dispersion was given by Born and Wolf in 1959. The generalized multiple-prism dispersion theory was introduced by Duarte and Piper in 1982.
The N-slit interferometer is an extension of the double-slit interferometer also known as Young's double-slit interferometer. One of the first known uses of N-slit arrays in optics was illustrated by Newton. In the first part of the twentieth century, Michelson described various cases of N-slit diffraction.

Multiple-prism grating laser oscillators, or MPG laser oscillators, use multiple-prism beam expansion to illuminate a diffraction grating mounted either in Littrow configuration or grazing-incidence configuration. Originally, these narrow-linewidth tunable dispersive oscillators were introduced as multiple-prism Littrow (MPL) grating oscillators, or hybrid multiple-prism near-grazing-incidence (HMPGI) grating cavities, in organic dye lasers. However, these designs were quickly adopted for other types of lasers such as gas lasers, diode lasers, and more recently fiber lasers.

Photoconductive atomic force microscopy (PC-AFM) is a variant of atomic force microscopy that measures photoconductivity in addition to surface forces.
Photon etc. is a Canadian manufacturer of infrared cameras, widely tunable optical filters, hyperspectral imaging and spectroscopic scientific instruments for academic and industrial applications. Its main technology is based on volume Bragg gratings, which are used as filters either for swept lasers or for global imaging.













