Related Research Articles

Palau, officially the Republic of Palau, is an island country in the Micronesia subregion of Oceania in the western Pacific. The republic consists of approximately 340 islands and connects the western chain of the Caroline Islands with parts of the Federated States of Micronesia. It has a total area of 466 square kilometers (180 sq mi), making it one of the smallest countries in the world. The most populous island is Koror, home to the country's most populous city of the same name. The capital Ngerulmud is located on the largest island of Babeldaob, in Melekeok State. Palau shares maritime boundaries with international waters to the north, the Federated States of Micronesia to the east, Indonesia to the south, and the Philippines to the northwest.

The politics of Palau take place in a presidential representative democratic republic, whereby the President of Palau is both head of state and head of government. Palau currently has no political parties and is a de facto non-partisan democracy although there is no law preventing the formation of political parties.

The Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands (TTPI) was a United Nations trust territory in Micronesia administered by the United States from 1947 to 1994. The Imperial Japanese South Seas Mandate had been seized by the US during the Pacific War, as Japan had occupied the territory since the League of Nations gave Japan mandate over the area after World War I. However, in the 1930s, Japan left the League of Nations, and then invaded additional lands. During World War II, military control of the islands was disputed, but by the end of the war the islands had come under control of the Allies. The Trust Territory of the Pacific was created to administer the islands as part of the United States, while still under the auspices of the United Nations. Most of the island groups in the territory became independent states, with some degree of ties kept with the United States: the Federated States of Micronesia, Marshall Islands and Palau are today independent states in a Compact of Free Association with the US, while the Northern Mariana Islands remain under US jurisdiction, as an unincorporated territory and commonwealth.

In the law of the United States, an insular area is a U.S.-associated jurisdiction that is not part of the several states or the District of Columbia. This includes fourteen U.S. territories administered under U.S. sovereignty, as well as three sovereign states each with a Compact of Free Association with the United States. The term also may be used to refer to the previous status of the Swan Islands, Hawaii, Puerto Rico, and the Philippines, as well as the Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands when it existed.

The Office of Insular Affairs (OIA) is a unit of the United States Department of the Interior that oversees federal administration of several United States insular areas. It is the successor to the Bureau of Insular Affairs of the War Department, which administered certain territories from 1902 to 1939, and the Office of Territorial Affairs in the Interior Department, which was responsible for certain territories from the 1930s to the 1990s. The word "insular" comes from the Latin word insula ("island").

The Compacts of Free Association (COFA) are international agreements establishing and governing the relationships of free association between the United States and the three Pacific Island sovereign states of the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM), the Republic of the Marshall Islands (RMI), and the Republic of Palau. As a result, these countries are sometimes known as the Freely Associated States (FAS's). All three agreements next expire in 2043.
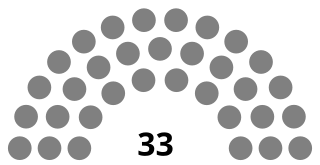
The Legislature of the Marshall Islands has 33 members, elected for a four-year term in nineteen single-seat and five multi-seat constituencies. The last election was November 18, 2019. Elections in the Marshall Islands are officially nonpartisan, but most members of the Nitijeļā are affiliated with one of the four active political parties in the Marshall Islands: Aelon Kein Ad (AKA), Kien Eo Am (KEA), United People's Party (UPP), and United Democratic Party (UDP).
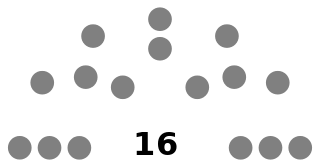
The House of Delegates of Palau is the lower house of the Palau National Congress, Palau's bicameral legislature. The Senate of Palau is the upper house. The House of Delegates has 16 members, each serving four-year terms in single-seat constituencies. Each state represents one constituency. No political parties exist. The last election was held on 3 November 2020.
Title 48 of the United States Code outlines the role of United States territories and insular areas in the United States Code.

The high commissioner of the Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands was an official who administered the Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands (TTPI), a United Nations trusteeship in the Pacific Ocean under the administration of the United States, between 1947 and 1994. The territory consisted of islands captured by America during World War II, prior to which they had been part of the Empire of Japan as the South Seas Mandate, within the Japanese colonial empire. After World War II, United Nations Security Council Resolution 21 placed the territory under the United States trusteeship as the Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands. The islands are now part of Palau, Northern Mariana Islands, Federated States of Micronesia, and Marshall Islands.

The Deputy Prime Minister is a former political position in Zimbabwe which has existed twice in the history of Zimbabwe.

The Ministry of Economy and Finance accounts for the administration of financial and economic policy and affair in the Kingdom of Cambodia. In accordance to the official website, the ministry was commissioned by the Royal Government of Cambodia to perform missions of guidances and administrations in economic and financial affairs. The current Minister responsible for the Ministry of Economic and Finance is Aun Porn Moniroth, as of 2013. The main ministerial office is located in Phnom Penh, while the provincial branches are located across the main capitals of each province.

Cannabis in Palau is illegal, but reports indicate the drug is widely produced and consumed on the island nation. Palau is a former Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands of the United States which gained independence in 1994, and has a population under 20,000.

Vice presidents of Guyana is a political position in Guyana. The Prime Minister of Guyana serves as the First Vice President and acts as the constitutional successor for the President of Guyana in case of a vacancy. Historically, other members of the cabinet have also been appointed as Vice Presidents, who can perform the functions of the President. Vice presidency was created in October 1980 when the executive presidency was created.
The Ministry of Justice in Palau is part of the Executive Branch and consists of the following bureaus:

The Congress of Micronesia was a bicameral legislature in Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands from 1964 to 1979.

Minister of Finance of Fiji is heading the ministry of Finance in Fiji.

Ministry of Finance of the Marshall Islands is a government ministry in the Marshall Islands responsible for providing a management system for public finances to manage revenue and fiscal functions of the Government of the Marshall Islands.
Franz Reksid is a Palauan civil servant and politician, former Minister of Administration of Palau, and former official in Northern Mariana Islands government.
Shiro Kyota is a Palauan politician and a former speaker of the House of Delegates of Palau from January 1989 to November 1992.
References
- 1 2 "Palau Government". 16 February 2012. Archived from the original on 2012-02-16.
- ↑ "DevelopmentAid". DevelopmentAid.
- ↑ State, United States Department of (1980). "Report to the United Nations on the Administration of the Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands, Transmitted by the United States of America".
- ↑ "Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands". Bureau of International Organization Affairs, Office of United Nations Political Affairs. 1982.
- ↑ United States Congress House Committee on Interior and Insular Affairs Subcommittee on Public Lands (1987). "Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands Budget Request for Fiscal Year 1987: Oversight Hearing Before the Subcommittee on Public Lands of the Committee on Interior and Insular Affairs, House of Representatives, Ninety-ninth Congress, Second Session ... Hearing Held in Washington, D.C., February 7, 1986". U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ "Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands". Bureau of International Organization Affairs, Office of United Nations Political Affairs.
- ↑ "Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands". Bureau of International Organization Affairs, Office of United Nations Political Affairs. 1988.
- ↑ United States Dept of State (1988). "Report to the United Nations on the Administration of the Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands".
- 1 2 "Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands". Bureau of International Organization Affairs, Office of United Nations Political Affairs. 1991.
- ↑ "Chiefs of State and Cabinet members of foreign governments". The Center : Document Expediting (DOCEX) Project, Exchange and Gift Division, Library of Congress distributor ; National Technical Information Service distributor. 1994. hdl:2027/nyp.33433070825330.
- ↑ "Chiefs of State and Cabinet members of foreign governments". The Center : Document Expediting (DOCEX) Project, Exchange and Gift Division, Library of Congress distributor ; National Technical Information Service distributor. 2000. hdl:2027/osu.32435083449215.
- ↑ "Chiefs of State and Cabinet members of foreign governments". The Center : Document Expediting (DOCEX) Project, Exchange and Gift Division, Library of Congress distributor ; National Technical Information Service distributor. 2001. hdl:2027/uc1.c081688708.
- 1 2 "Our Board". 25 December 2019. Archived from the original on 2019-12-25.
- ↑ "2002 / 2003 YEARBOOK".
- ↑ "Sadang, Elbuchel". International Year Book and Statesmen's Who's Who. Brill.
- ↑ Reklai, Leilani (9 February 2021). "Obichang and Udui take on major tasks as new ministers". Island Times.
- ↑ "EDITORIAL: Palau Ministerial Appointments – Oceania Television Network". www.oceaniatv.net.