| Type | Curry |
|---|---|
| Place of origin | Maldives |
| Main ingredients | Octopus tentacles, curry leaves, chili, garlic, cloves, onions, pepper, coconut oil |
Miruhulee boava is a Maldivian delicacy made of octopus tentacles braised in curry leaves, chili, garlic, cloves, onion, pepper, and coconut oil. [1]
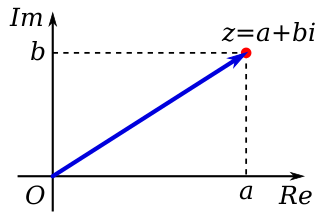
In mathematics, a complex number is an element of a number system that extends the real numbers with a specific element denoted i, called the imaginary unit and satisfying the equation ; every complex number can be expressed in the form , where a and b are real numbers. Because no real number satisfies the above equation, i was called an imaginary number by René Descartes. For the complex number ,a is called the real part, and b is called the imaginary part. The set of complex numbers is denoted by either of the symbols or C. Despite the historical nomenclature, "imaginary" complex numbers have a mathematical existence as firm as that of the real numbers, and they are fundamental tools in the scientific description of the natural world.
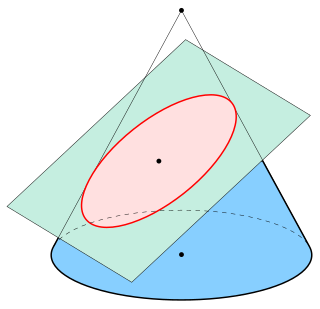
In mathematics, an ellipse is a plane curve surrounding two focal points, such that for all points on the curve, the sum of the two distances to the focal points is a constant. It generalizes a circle, which is the special type of ellipse in which the two focal points are the same. The elongation of an ellipse is measured by its eccentricity , a number ranging from to .

In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the form of energy that it possesses due to its motion.

In Newtonian mechanics, momentum is the product of the mass and velocity of an object. It is a vector quantity, possessing a magnitude and a direction. If m is an object's mass and v is its velocity, then the object's momentum p is:

In mathematics, a tensor is an algebraic object that describes a multilinear relationship between sets of algebraic objects related to a vector space. Tensors may map between different objects such as vectors, scalars, and even other tensors. There are many types of tensors, including scalars and vectors, dual vectors, multilinear maps between vector spaces, and even some operations such as the dot product. Tensors are defined independent of any basis, although they are often referred to by their components in a basis related to a particular coordinate system; those components form an array, which can be thought of as a high-dimensional matrix.
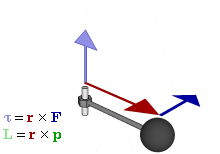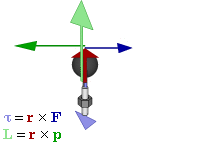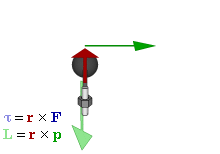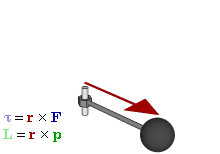
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational analogue of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force. It describes the rate of change of angular momentum that would be imparted to an isolated body.

An electric field is the physical field that surrounds electrically charged particles. Charged particles exert attractive forces on each other when their charges are opposite, and repulsion forces on each other when their charges are the same. Because these forces are exerted mutually, two charges must be present for the forces to take place. The electric field of a single charge describes their capacity to exert such forces on another charged object. These forces are described by Coulomb's law, which says that the greater the magnitude of the charges, the greater the force, and the greater the distance between them, the weaker the force. Thus, we may informally say that the greater the charge of an object, the stronger its electric field. Similarly, an electric field is stronger nearer charged objects and weaker further away. Electric fields originate from electric charges and time-varying electric currents. Electric fields and magnetic fields are both manifestations of the electromagnetic field, Electromagnetism is one of the four fundamental interactions of nature.

In electrical engineering, impedance is the opposition to alternating current presented by the combined effect of resistance and reactance in a circuit.
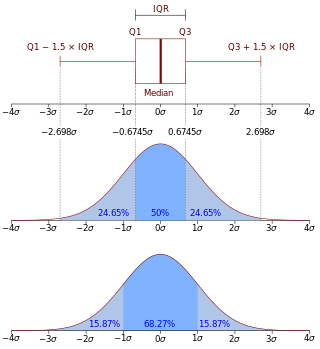
In probability theory, a probability density function (PDF), density function, or density of an absolutely continuous random variable, is a function whose value at any given sample in the sample space can be interpreted as providing a relative likelihood that the value of the random variable would be equal to that sample. Probability density is the probability per unit length, in other words, while the absolute likelihood for a continuous random variable to take on any particular value is 0, the value of the PDF at two different samples can be used to infer, in any particular draw of the random variable, how much more likely it is that the random variable would be close to one sample compared to the other sample.

The Boltzmann constant is the proportionality factor that relates the average relative thermal energy of particles in a gas with the thermodynamic temperature of the gas. It occurs in the definitions of the kelvin and the gas constant, and in Planck's law of black-body radiation and Boltzmann's entropy formula, and is used in calculating thermal noise in resistors. The Boltzmann constant has dimensions of energy divided by temperature, the same as entropy. It is named after the Austrian scientist Ludwig Boltzmann.
Newton's laws of motion are three laws that describe the relationship between the motion of an object and the forces acting on it. These laws, which provide the basis for Newtonian mechanics, can be paraphrased as follows:
The Schrödinger equation is a linear partial differential equation that governs the wave function of a quantum-mechanical system. Its discovery was a significant landmark in the development of quantum mechanics. It is named after Erwin Schrödinger, who postulated the equation in 1925 and published it in 1926, forming the basis for the work that resulted in his Nobel Prize in Physics in 1933.

The ideal gas law, also called the general gas equation, is the equation of state of a hypothetical ideal gas. It is a good approximation of the behavior of many gases under many conditions, although it has several limitations. It was first stated by Benoît Paul Émile Clapeyron in 1834 as a combination of the empirical Boyle's law, Charles's law, Avogadro's law, and Gay-Lussac's law. The ideal gas law is often written in an empirical form:
The Black–Scholes or Black–Scholes–Merton model is a mathematical model for the dynamics of a financial market containing derivative investment instruments, using various underlying assumptions. From the parabolic partial differential equation in the model, known as the Black–Scholes equation, one can deduce the Black–Scholes formula, which gives a theoretical estimate of the price of European-style options and shows that the option has a unique price given the risk of the security and its expected return. The equation and model are named after economists Fischer Black and Myron Scholes. Robert C. Merton, who first wrote an academic paper on the subject, is sometimes also credited.

In physics, work is the energy transferred to or from an object via the application of force along a displacement. In its simplest form, for a constant force aligned with the direction of motion, the work equals the product of the force strength and the distance traveled. A force is said to do positive work if when applied it has a component in the direction of the displacement of the point of application. A force does negative work if it has a component opposite to the direction of the displacement at the point of application of the force.

In biochemistry, Michaelis–Menten kinetics, named after Leonor Michaelis and Maud Menten, is the simplest case of enzyme kinetics, applied to enzyme-catalysed reactions of one substrate and one product. It takes the form of a differential equation describing the reaction rate to , the concentration of the substrate A. Its formula is given by the Michaelis–Menten equation:
Time dilation is the difference in elapsed time as measured by two clocks, either due to a relative velocity between them, or a difference in gravitational potential between their locations. When unspecified, "time dilation" usually refers to the effect due to velocity.
In linear algebra, it is often important to know which vectors have their directions unchanged by a given linear transformation. An eigenvector or characteristic vector is such a vector. Thus an eigenvector of a linear transformation is scaled by a constant factor when the linear transformation is applied to it: . The corresponding eigenvalue, characteristic value, or characteristic root is the multiplying factor .

In electrical engineering, a capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy by accumulating electric charges on two closely spaced surfaces that are insulated from each other. The capacitor was originally known as the condenser, a term still encountered in a few compound names, such as the condenser microphone. It is a passive electronic component with two terminals.

Velocity is the speed in combination with the direction of motion of an object. Velocity is a fundamental concept in kinematics, the branch of classical mechanics that describes the motion of bodies.