Related Research Articles

Madagascar, officially the Republic of Madagascar, and previously known as the Malagasy Republic, is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately 400 kilometres off the coast of East Africa across the Mozambique Channel. At 592,800 square kilometres (228,900 sq mi) Madagascar is the world's second-largest island country, after Indonesia. The nation comprises the island of Madagascar and numerous smaller peripheral islands. Following the prehistoric breakup of the supercontinent Gondwana, Madagascar split from the Indian subcontinent around 88 million years ago, allowing native plants and animals to evolve in relative isolation. Consequently, Madagascar is a biodiversity hotspot; over 90% of its wildlife is found nowhere else on Earth. The island's diverse ecosystems and unique wildlife are threatened by the encroachment of the rapidly growing human population and other environmental threats.

The Southern Africa-Indian Ocean Division (SID) of Seventh-day Adventists is a sub-entity of the General Conference of Seventh-day Adventists, which coordinates the Church's activities in the southern portion of Africa, which include the nations of Angola, Ascension Island, Botswana, Comoro Islands, Lesotho, Madagascar, Malawi, Mauritius, Mozambique, Namibia, Réunion, São Tomé and Príncipe, Seychelles, South Africa, Swaziland, Zambia, Zimbabwe; as well as St. Helena and Tristan da Cunha, territories of the United Kingdom, and the Kerguelen Islands, territory of France. Its headquarters is in Johannesburg, South Africa. The Division membership as of June 30, 2018 is 3,969,099.

Campos do Jordão is a municipality in the state of São Paulo in southeastern Brazil. It is part of the Metropolitan Region of Vale do Paraíba e Litoral Norte. The population is 52,405 in an area of 290.52 square kilometres (112.17 sq mi). The city is situated 1,628 metres (5,341 ft) above sea level and is the highest city in Brazil.

Réunion Creole, or Reunionese Creole, is a French-based creole language spoken on Réunion. It is derived mainly from French and includes terms from Malagasy, Hindi, Portuguese, Gujarati and Tamil. In recent years, there has been an effort to develop a spelling dictionary and grammar rules. Partly because of the lack of an official orthography but also because schools are taught in French, Réunion Creole is rarely written. Notably, two translations of the French comic Asterix have been published.

Malagasy cuisine encompasses the many diverse culinary traditions of the Indian Ocean island of Madagascar. Foods eaten in Madagascar reflect the influence of Southeast Asian, African, Indian, Chinese and European migrants that have settled on the island since it was first populated by seafarers from Borneo between 100 CE and 500 CE. Rice, the cornerstone of the Malagasy diet, was cultivated alongside tubers and other Southeast Asian staples by these earliest settlers. Their diet was supplemented by foraging and hunting wild game, which contributed to the extinction of the island's bird and mammal megafauna. These food sources were later complemented by beef in the form of zebu introduced into Madagascar by East African migrants arriving around 1,000 CE.

Baghāre baingan is a curry from the Hyderabadi cuisine made with eggplant (brinjal) Hyderabad. It is also used as a side dish with the Hyderabadi biryani.

The culture of Madagascar reflects the origins of the people Malagasy people in Southeast Asia and East Africa. The influence of Arabs, Indians, British, French and Chinese settlers is also evident. The most emblematic instrument of Madagascar, the valiha, is a bamboo tube zither carried to the island by early settlers from southern Borneo, and is very similar in form to those found in Indonesia and the Philippines today. Traditional houses in Madagascar are likewise similar to those of southern Borneo in terms of symbolism and construction, featuring a rectangular layout with a peaked roof and central support pillar. Reflecting a widespread veneration of the ancestors, tombs are culturally significant in many regions and tend to be built of more durable material, typically stone, and display more elaborate decoration than the houses of the living. The production and weaving of silk can be traced back to the island's earliest settlers, and Madagascar's national dress, the woven lamba, has evolved into a varied and refined art. The Southeast Asian cultural influence is also evident in Malagasy cuisine, in which rice is consumed at every meal, typically accompanied by one of a variety of flavorful vegetable or meat dishes. African influence is reflected in the sacred importance of zebu cattle and their embodiment of their owner's wealth, traditions originating on the African mainland. Cattle rustling, originally a rite of passage for young men in the plains areas of Madagascar where the largest herds of cattle are kept, has become a dangerous and sometimes deadly criminal enterprise as herdsmen in the southwest attempt to defend their cattle with traditional spears against increasingly armed professional rustlers.

Basbousa is a traditional Ottoman sweet cake that originated in Turkey, although it is also popular in other countries. It is made from a semolina batter and cooked in a pan, then sweetened with orange flower water, rose water or simple syrup, and typically cut into diamond shapes. It is found in most former areas of the Ottoman Empire, and is featured in Middle Eastern cuisines, Greek cuisine, Azerbaijani cuisine, Turkish cuisine, and many others.

Goan Catholic Cuisine is the cuisine of the Goan Catholic community and is largely influenced by the Saraswat, Konkani, Portuguese, South Indian, and British cuisines. Due to over 450 years of Portuguese rule, the cuisine of Goan Catholics is dominated by ingredients and techniques of Portuguese cuisine like deep-frying, oven-baking, pork, vinegar, egg-based desserts, alcohol, etc.

São Tomé and Príncipe, officially the Democratic Republic of São Tomé and Príncipe, is an island country in the Gulf of Guinea, off the western equatorial coast of Central Africa. It consists of two archipelagos around the two main islands of São Tomé and Príncipe, about 140 km (87 mi) apart and about 250 and 225 km off the northwestern coast of Gabon.

Faneva Imà Andriatsima is a Malagasy professional footballer who plays as a forward.

Black Bird is a Japanese shōjo manga series written and illustrated by Kanoko Sakurakoji. The story depicts the life of a high school girl who can see supernatural beings. It was serialized in Shogakukan's Betsucomi magazine from July 2006 to December 2012 and published in 18 bound volumes from January 2007 to April 2013. The series won the 54th Shogakukan Manga Award in the shōjo manga category.

Flia, also known as fli or flija, is a dish in Kosovan cuisine and Albanian cuisine. It consists of multiple crêpe-like layers brushed with cream and served with sour cream. The name translates to "sacrifice".
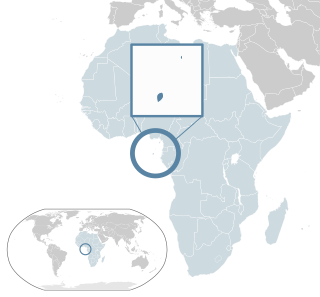
Santomean cuisine comprises the cuisine, dishes and foods of São Tomé and Príncipe, a Portuguese-speaking island nation in the Gulf of Guinea, off the western equatorial coast of Central Africa. The country consists of two archipelagos around the two main islands: São Tomé and Príncipe, located about 140 kilometres (87 mi) apart and about 250 and 225 kilometres, respectively, off the northwestern coast of Gabon.
Yuto Misao is a Japanese football player for Oita Trinita.

Kento Misao is a Japanese footballer who plays for Kashima Antlers.
Misao Kodate is a Japanese biathlete. He competed at the 1988 Winter Olympics, the 1992 Winter Olympics and the 1994 Winter Olympics.
Lasary is a type of Malagasy salad. It is believed that the dish originates from northern Madagascar. The dish is also named Antsary or Ansary in some places.

Ravitoto is a traditional Malagasy cuisine. Ravitoto means “crushed cassava leaves”. These are specifically sweet cassava leaves pounded with a mortar or meat grinder. It is cooked with garlic and very fatty pork. In other societies, coconut milk is used instead to cook cassava leaves, like mataba in the Comoros. You can add dried fish or small shrimp, called tsivaki.
References
- ↑ "Min Sao". MADAMAGAZINE. Retrieved 2019-09-17.
- ↑ "Madagascar Food: A Culinary Travel Guide". Uncornered Market. 2018-09-04. Retrieved 2019-09-17.