
Beaufort County is a county in the U.S. state of South Carolina. As of the 2020 census, its population was 187,117. Its county seat is Beaufort and its largest town is Hilton Head Island.

Beaufort is a city in and the county seat of Beaufort County, South Carolina, United States. Chartered in 1711, it is the second-oldest city in South Carolina, behind Charleston. A city rich in history, culture, southern hospitality, and a seaside charm, Beaufort is affectionally known as the "Queen of the Carolina Sea Islands". The city's population was 13,607 at the 2020 census. It is part of the Hilton Head Island–Bluffton metropolitan area.

Forty acres and a mule was part of Special Field Orders No. 15, a wartime order proclaimed by Union General William Tecumseh Sherman on January 16, 1865, during the American Civil War, to allot land to some freed families, in plots of land no larger than 40 acres (16 ha). Sherman later ordered the army to lend mules for the agrarian reform effort. The field orders followed a series of conversations between Secretary of War Edwin M. Stanton and Radical Republican abolitionists Charles Sumner and Thaddeus Stevens following disruptions to the institution of slavery provoked by the American Civil War. Many freed people believed, after being told by various political figures, that they had a right to own the land they had been forced to work as slaves and were eager to control their own property. Freed people widely expected to legally claim 40 acres of land. However, Abraham Lincoln's successor as president, Andrew Johnson, tried to reverse the intent of Sherman's wartime Order No. 15 and similar provisions included in the second Freedmen's Bureau bills.

St. Helena Island is a Sea Island in Beaufort County, South Carolina, United States. The island is connected to Beaufort by U.S. Highway 21. The island has a land area of about 64 sq mi (170 km2) and a population of 8,763 as of the 2010 census. It is included as part of the Hilton Head Island-Beaufort Micropolitan Area. The island is renowned for its rural Lowcountry character and being a major center of African-American Gullah culture and language. It is considered to be the geographic influence behind the children's television program Gullah Gullah Island.

Thomas Fenwick Drayton was a planter, politician, railroad president, slave owner and military officer from Charleston, South Carolina. He served in the United States Army and then as a brigadier general in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War. His brother, Percival Drayton, was a Naval Officer and fought on the Union side during the war.
Charles Pickard Ware (1840–1921), was an American educator and music transcriber. An abolitionist, he served as a civilian administrator in the Union Army, where he was a labor superintendent of freedmen on plantations at Port Royal, South Carolina, during the American Civil War. This included Seaside Plantation. It is here that he transcribed many slave songs with tunes and lyrics, later published in Slave Songs of the United States, which he edited with William Francis Allen and Lucy McKim Garrison. It was the first published collection of American folk music.

Robert Smalls was an American politician, publisher, businessman, and maritime pilot. Born into slavery in Beaufort, South Carolina, he freed himself, his crew, and their families during the American Civil War by commandeering a Confederate transport ship, CSS Planter, in Charleston harbor, on May 13, 1862, and sailing it from the Confederate-controlled waters of the harbor to the U.S. blockade that surrounded it. He then piloted the ship to the Union-controlled enclave in Beaufort–Port Royal–Hilton Head area, where it became a Union warship. His example and persuasion helped convince President Abraham Lincoln to accept African-American soldiers into the Union Army.
Contraband was a term commonly used in the US military during the American Civil War to describe a new status for certain people who escaped slavery or those who affiliated with Union forces. In August 1861, the Union Army and the US Congress determined that the US would no longer return people who escaped slavery who went to Union lines, but they would be classified as "contraband of war," or captured enemy property. They used many as laborers to support Union efforts and soon began to pay wages.

Rufus Saxton was a Union Army brigadier general during the American Civil War who received America's highest military decoration, the Medal of Honor, for his actions defending Harpers Ferry during Confederate General Jackson's Valley Campaign. After the war he served as the Freedmen's Bureau's first assistant commissioner.
Fort Howell is an earthworks fort built in 1864 during the American Civil War, located on Hilton Head Island, South Carolina. It was named in honor of Union Army Brigadier General Joshua B. Howell, and Its primary function was to protect Mitchelville, a Freedman's town located to its east.

The Port Royal Experiment was a program begun during the American Civil War in which former slaves successfully worked on the land abandoned by planters. In 1861 the Union captured the Sea Islands off the coast of South Carolina and their main harbor, Port Royal. The white residents fled, leaving behind 10,000 black slaves. Several private Northern charity organizations stepped in to help the former slaves become self-sufficient. The result was a model of what Reconstruction could have been. The African Americans demonstrated their ability to work the land efficiently and live independently of white control. They assigned themselves daily tasks for cotton growing and spent their extra time cultivating their own crops, fishing and hunting. By selling their surplus crops, the locals acquired small amounts of property.
The Grand Contraband Camp was located in Elizabeth City County, Virginia, on the Virginia Peninsula near Fort Monroe, during and immediately after the American Civil War. The area was a refuge for escaped slaves who the Union forces refused to return to their former Confederate masters, by defining them as "contraband of war". The Grand Contraband Camp was the first self-contained black community in the United States and occupied the area of the downtown section of the present-day independent city of Hampton, Virginia.
The Freedmen's Colony of Roanoke Island, also known as the Roanoke Island Freedmen's Colony, or "Freedman's Colony", was founded in 1863 during the Civil War after Union Major General John G. Foster, Commander of the 18th Army Corps, captured the Confederate fortifications on Roanoke Island off North Carolina in 1862. He classified the slaves living there as "contraband", following the precedent of General Benjamin Butler at Fort Monroe in 1861, and did not return them to Confederate slaveholders. In 1863, by the Emancipation Proclamation, all slaves in Union-occupied territories were freed.

Stoney-Baynard Plantation on Hilton Head Island, SC was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1994. The listing included one contributing site on 6 acres (2.4 ha).

The Fish Haul Archaeological Site, an "address restricted" site located in Beaufort County, South Carolina, is significant because of its archaeological remains from two different eras. The pre-historic findings, which date from 1800 to 1300 BC, offer evidence that small groups of people lived in the area. The historic component represents a freemen's village, Mitchelville, which was occupied during the transition between slavery and freedom by Sea Island blacks. The Fish Haul site represents the only known freedmen village established by occupying Union troops. The site was listed in the National Register of Historic Places on June 30, 1988.
Green's Shell Enclosure is a historic archeological site located at Hilton Head Island, Beaufort County, South Carolina. The site includes one of 20 or more prehistoric Indian shell middens in a ring shape located from the central coast of South Carolina to the central coast of Georgia. They are believed to date early in the second millennium BC, and they contain some of the earliest pottery known in North America.

Cherry Hill School is a historic school for African-American students located at Hilton Head Island, Beaufort County, South Carolina. It was the first separate school building for African-American students on the island.
The Battle of The Pineberry Battery was a series of minor engagements, fought April 29, 1862, in Charleston County, South Carolina, during the American Civil War. The engagements proceeded from an attack by the Union Navy on a battery on John Berkeley Grimball's plantation on Edisto Island. After successfully destroying the battery, the ship was attacked twice by Confederate artillery forces before returning to its station. The attack was a part of Union efforts to secure Edisto Island, which housed a large colony of escaped African Americans and served as a launching point of a campaign against Charleston.
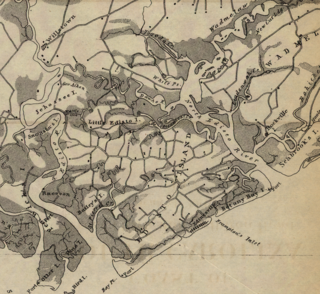
Edisto Island during the American Civil War was the location of a number of minor engagements and for a time of a large colony of escaped African-American slaves during the American Civil War (1861–1865). Edisto Island was largely abandoned by planters in November 1861 and in December 1861, escaped slaves began setting up their own refugee camps there. In January 1862, armed African Americans from the island and Confederate forces clashed and a Confederate raid in reprisal killed a small number of unarmed African Americans. In February, Union forces were stationed on the island to develop it as a staging area for future campaigns against Charleston, twenty-five miles away, as well as to protect the colony, which would eventually number thousands of African Americans. As Union forces took control of the island, a number of skirmishes occurred, but Confederates withdrew. In June, most of the Union troops left the island in a campaign, which culminated in the Battle of Secessionville. In July, the remaining troops withdrew, and the colony was removed to St. Helena Island. For the rest of the war, a small number of escaped slaves and plantation owners remained and farmed the island, but it was largely abandoned. Near the end of the war, the island was again used as a location of colonies of freed slaves.

The Laurel Hill Plantation, also known as Laurel Hill Farm was a historic Southern plantation located on Lady's Island, Beaufort County, South Carolina. The area is now called Coosaw Point, a upscale community with clubhouse, pool, tennis courts, and dock. The area is known for its woodlands, parks, wetlands, and the Coosaw River.
















