Transport in Lithuania relies mainly on road and rail networks.

A standard-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge of 1,435 mm. The standard gauge is also called Stephenson gauge, international gauge, UIC gauge, uniform gauge, normal gauge and European gauge in Europe, and SGR in East Africa. It is the most widely used track gauge around the world, with about 55% of the lines in the world using it. All high-speed rail lines use standard gauge except those in Russia, Finland, and Uzbekistan. The distance between the inside edges of the rails is defined to be 1,435 mm except in the United States and on some heritage British lines, where it is defined in U.S. customary/Imperial units as exactly "four feet eight and one half inches", which is equivalent to 1,435.1 mm.

A broad-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge broader than the 1,435 mm used by standard-gauge railways.

In rail transport, track gauge is the distance between the two rails of a railway track. All vehicles on a rail network must have wheelsets that are compatible with the track gauge. Since many different track gauges exist worldwide, gauge differences often present a barrier to wider operation on railway networks.
The Trans-Asian Railway(TAR) is a project to create an integrated freight railway network across Europe and Asia. The project is of the United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (UNESCAP).
In railway engineering, "gauge" is the transverse distance between the inner surfaces of the heads of two rails, which for the vast majority of railway lines is the number of rails in place. However, it is sometimes necessary for track to carry railway vehicles with wheels matched to two different gauges. Such track is described as dual gauge – achieved either by addition of a third rail, if it will fit, or by two additional rails. Dual-gauge tracks are more expensive to configure with signals and sidings, and to maintain, than two separate single-gauge tracks. It is therefore usual to build dual-gauge or other multi-gauge tracks only when necessitated by lack of space or when tracks of two different gauges meet in marshalling yards or passenger stations. Dual-gauge tracks are by far the most common configuration, but triple-gauge tracks have been built in some situations.

With railways, a break of gauge occurs where a line of one track gauge meets a line of a different gauge. Trains and rolling stock generally cannot run through without some form of conversion between gauges, leading to passengers having to change trains and freight requiring transloading or transshipping; this can add delays, costs, and inconvenience to travel on such a route.

The Finnish railway network consists of a total track length of 9,216 km (5,727 mi). The railways are built with a broad 1,524 mm track gauge, of which 3,249 km (2,019 mi) is electrified. Passenger trains are operated by the state-owned enterprise VR that runs services on 7,225 km (4,489 mi) of track. These services cover all major cities and many rural areas, though the coverage is less than the coverage provided by the bus services. Most passenger train services originate or terminate at Helsinki Central railway station, and a large proportion of the passenger rail network radiates out of Helsinki. VR also operates freight services. Maintenance and construction of the railway network itself is the responsibility of the Finnish Rail Administration, which is a part of the Finnish Transport Agency. The network consists of six areal centres, that manage the use and maintenance of the routes in co-operation. Cargo yards and large stations may have their own signalling systems.

Railways with a railway track gauge of 5 ft first appeared in the United Kingdom and the United States. This gauge became commonly known as Russian gauge because the government of the Russian Empire later chose it in 1843 — former areas of the Empire have inherited this standard. In 1970, Soviet Railways re-defined the gauge as 1,520 mm.

A variable gauge system allows railway vehicles in a train to travel across a break of gauge between two railway networks with different track gauges.
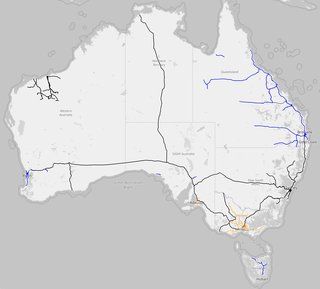
Rail gauges in Australia display significant variations, which has presented an extremely difficult problem for rail transport on the Australian continent for over 150 years. As of 2022, there are 11,914 kilometres (7,403 mi) of narrow-gauge railways, 18,007 kilometres (11,189 mi) of standard gauge railways and 2,685 kilometres (1,668 mi) of broad gauge railways. In the 19th century, each of the colonies of Australia adopted their own gauges. However, with Federation in 1901 and the removal of trade barriers, the short sightedness of three gauges became apparent. It would be 94 years before all mainland state capitals were joined by one standard gauge.

Wolseley is a small South Australian town near the Victorian border. It is five kilometres south of the Dukes Highway and 13 kilometres east of Bordertown. It was first proclaimed a town in 1884.

Rail transport in Lithuania consists of freight shipments and passenger services. The construction of the first railway line in Lithuania began in 1859. As of 2021, the total length of railways in Lithuania was 1,868.8 km (1,161.2 mi). Lietuvos Geležinkeliai, the national state-owned railway company, operates most of the passenger and freight services.

Bogie exchange is a system for operating railway wagons on two or more gauges to overcome difference in the track gauge. To perform a bogie exchange, a car is converted from one gauge to another by removing the bogies or trucks, and installing a new bogie with differently spaced wheels. It is generally limited to wagons and carriages, though the bogies on diesel locomotives can be exchanged if enough time is available.

Zabaykalsk is an urban locality and the administrative center of Zabaykalsky District of Zabaykalsky Krai, Russia, located on the Sino-Russian border just opposite the Chinese border town of Manzhouli. Population: 10,210 (2002 Census); 8,632 (1989 Census).

The Polish railways network consists of around 18,510 kilometres (11,500 mi) of track as of 2019, of which 11,998 km (7,455 mi) is electrified. National electrification system is 3 kV DC.
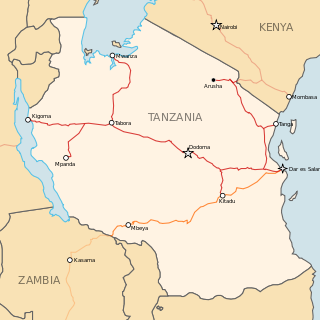
Railway stations in Tanzania include:
SUW 2000 is a Polish variable gauge system that allows trains to cross a break of gauge. It is interoperable with the German Rafil Type V system.

Rail transport in Belarus is owned by the national rail company BŽD / BČ. The railway network consists of 5,512 km, its gauge is 1,520 mm and 874 km are electrified.

Originally, various track gauges were used in the United States. Some railways, primarily in the northeast, used standard gauge of 4 ft 8+1⁄2 in ; others used gauges ranging from 2 ft to 6 ft. As a general rule, southern railroads were built to one or another broad gauge, mostly 5 ft, while northern railroads that were not standard-gauge tended to be narrow-gauge. The Pacific Railroad Acts of 1863 specified standard gauge.











