
An optical spectrometer is an instrument used to measure properties of light over a specific portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, typically used in spectroscopic analysis to identify materials. The variable measured is most often the irradiance of the light but could also, for instance, be the polarization state. The independent variable is usually the wavelength of the light or a closely derived physical quantity, such as the corresponding wavenumber or the photon energy, in units of measurement such as centimeters, reciprocal centimeters, or electron volts, respectively.

In optics, a diffraction grating is an optical grating with a periodic structure that diffracts light, or another type of electromagnetic radiation, into several beams traveling in different directions. The emerging coloration is a form of structural coloration. The directions or diffraction angles of these beams depend on the wave (light) incident angle to the diffraction grating, the spacing or periodic distance between adjacent diffracting elements on the grating, and the wavelength of the incident light. The grating acts as a dispersive element. Because of this, diffraction gratings are commonly used in monochromators and spectrometers, but other applications are also possible such as optical encoders for high-precision motion control and wavefront measurement.

Ultraviolet (UV) spectroscopy or ultraviolet–visible (UV–VIS) spectrophotometry refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in part of the ultraviolet and the full, adjacent visible regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Being relatively inexpensive and easily implemented, this methodology is widely used in diverse applied and fundamental applications. The only requirement is that the sample absorb in the UV-Vis region, i.e. be a chromophore. Absorption spectroscopy is complementary to fluorescence spectroscopy. Parameters of interest, besides the wavelength of measurement, are absorbance (A) or transmittance (%T) or reflectance (%R), and its change with time.
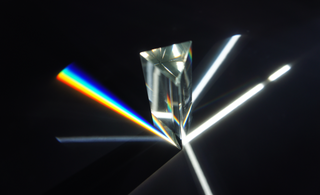
An optical prism is a transparent optical element with flat, polished surfaces that are designed to refract light. At least one surface must be angled — elements with two parallel surfaces are not prisms. The most familiar type of optical prism is the triangular prism, which has a triangular base and rectangular sides. Not all optical prisms are geometric prisms, and not all geometric prisms would count as an optical prism. Prisms can be made from any material that is transparent to the wavelengths for which they are designed. Typical materials include glass, acrylic and fluorite.
Optics is the branch of physics which involves the behavior and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behavior of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light. Because light is an electromagnetic wave, other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves exhibit similar properties.

Spectrophotometry is a branch of electromagnetic spectroscopy concerned with the quantitative measurement of the reflection or transmission properties of a material as a function of wavelength. Spectrophotometry uses photometers, known as spectrophotometers, that can measure the intensity of a light beam at different wavelengths. Although spectrophotometry is most commonly applied to ultraviolet, visible, and infrared radiation, modern spectrophotometers can interrogate wide swaths of the electromagnetic spectrum, including x-ray, ultraviolet, visible, infrared, and/or microwave wavelengths.
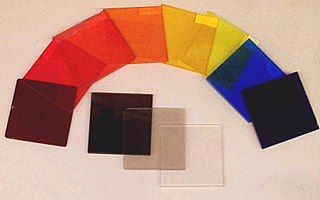
An optical filter is a device that selectively transmits light of different wavelengths, usually implemented as a glass plane or plastic device in the optical path, which are either dyed in the bulk or have interference coatings. The optical properties of filters are completely described by their frequency response, which specifies how the magnitude and phase of each frequency component of an incoming signal is modified by the filter.

A photometer is an instrument that measures the strength of electromagnetic radiation in the range from ultraviolet to infrared and including the visible spectrum. Most photometers convert light into an electric current using a photoresistor, photodiode, or photomultiplier.

The spectroheliograph is an instrument used in astronomy which captures a photographic image of the Sun at a single wavelength of light, a monochromatic image. The wavelength is usually chosen to coincide with a spectral wavelength of one of the chemical elements present in the Sun.
A spectroradiometer is a light measurement tool that is able to measure both the wavelength and amplitude of the light emitted from a light source. Spectrometers discriminate the wavelength based on the position the light hits at the detector array allowing the full spectrum to be obtained with a single acquisition. Most spectrometers have a base measurement of counts which is the un-calibrated reading and is thus impacted by the sensitivity of the detector to each wavelength. By applying a calibration, the spectrometer is then able to provide measurements of spectral irradiance, spectral radiance and/or spectral flux. This data is also then used with built in or PC software and numerous algorithms to provide readings or Irradiance (W/cm2), Illuminance, Radiance (W/sr), Luminance (cd), Flux, Chromaticity, Color Temperature, Peak and Dominant Wavelength. Some more complex spectrometer software packages also allow calculation of PAR μmol/m2/s, Metamerism, and candela calculations based on distance and include features like 2- and 20-degree observer, baseline overlay comparisons, transmission and reflectance.
Chirped pulse amplification (CPA) is a technique for amplifying an ultrashort laser pulse up to the petawatt level, with the laser pulse being stretched out temporally and spectrally, then amplified, and then compressed again. The stretching and compression uses devices that ensure that the different color components of the pulse travel different distances.

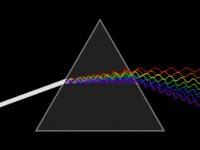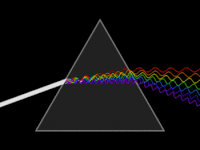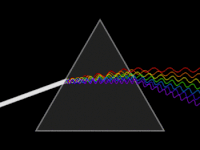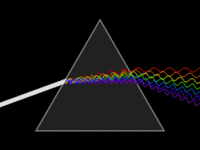
In optics, a dispersive prism is an optical prism that is used to disperse light, that is, to separate light into its spectral components. Different wavelengths (colors) of light will be deflected by the prism at different angles. This is a result of the prism material's index of refraction varying with wavelength (dispersion). Generally, longer wavelengths (red) undergo a smaller deviation than shorter wavelengths (blue). The dispersion of white light into colors by a prism led Sir Isaac Newton to conclude that white light consisted of a mixture of different colors.

An echelle grating is a type of diffraction grating characterised by a relatively low groove density, but a groove shape which is optimized for use at high incidence angles and therefore in high diffraction orders. Higher diffraction orders allow for increased dispersion (spacing) of spectral features at the detector, enabling increased differentiation of these features. Echelle gratings are, like other types of diffraction gratings, used in spectrometers and similar instruments. They are most useful in cross-dispersed high resolution spectrographs, such as HARPS, PARAS, and numerous other astronomical instruments.

Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) is a technique used to obtain an infrared spectrum of absorption or emission of a solid, liquid, or gas. An FTIR spectrometer simultaneously collects high-resolution spectral data over a wide spectral range. This confers a significant advantage over a dispersive spectrometer, which measures intensity over a narrow range of wavelengths at a time.
Stray light is light in an optical system which was not intended in the design. The light may be from the intended source, but follow paths other than intended, or it may be from a source other than that intended. This light will often set a working limit on the dynamic range of the system; it limits the signal-to-noise ratio or contrast ratio, by limiting how dark the system can be. Ocular straylight is stray light in the human eye.
Fiber-optic filter is an optical fiber instrument used for wavelength selection, which can select desired wavelengths to pass and reject the others. It is Widely used in DWDM systems dynamic wavelength selection, DWDM signal separation, optical performance monitoring, field tunable optical noise filtering and optical amplifier noise suppression, etc. Optical multiplexers (couplers) makes different wavelength coupling into an optical fiber and different wavelength carries different information. At the receiving end, if you want to separate desired wavelengths from optical fiber, it is necessary to use optical filter.

A spectrometer is a scientific instrument used to separate and measure spectral components of a physical phenomenon. Spectrometer is a broad term often used to describe instruments that measure a continuous variable of a phenomenon where the spectral components are somehow mixed. In visible light a spectrometer can separate white light and measure individual narrow bands of color, called a spectrum. A mass spectrometer measures the spectrum of the masses of the atoms or molecules present in a gas. The first spectrometers were used to split light into an array of separate colors. Spectrometers were developed in early studies of physics, astronomy, and chemistry. The capability of spectroscopy to determine chemical composition drove its advancement and continues to be one of its primary uses. Spectrometers are used in astronomy to analyze the chemical composition of stars and planets, and spectrometers gather data on the origin of the universe.
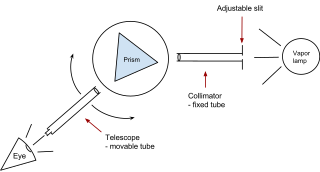
A prism spectrometer is an optical spectrometer which uses a dispersive prism as its dispersive element. The prism refracts light into its different colors (wavelengths). The dispersion occurs because the angle of refraction is dependent on the refractive index of the prism's material, which in turn is slightly dependent on the wavelength of light that is traveling through it.

The Cary Model 14 UV-VIS Spectrophotometer was a double beam recording spectrophotometer designed to operate over the wide spectral range of ultraviolet, visible and near infrared wavelengths (UV/Vis/NIR). This included wavelengths ranging from 185 nanometers to 870 nanometers.
An ultraviolet detector is a type of non-destructive chromatography detector which measures the amount of ultraviolet or visible light absorbed by components of the mixture being eluted off the chromatography column. They are often used as detectors for high-performance liquid chromatography.

![Neutron monochromator for the ECHIDNA powder diffractometer at OPAL in Australia. It is made by slabs of [113] oriented Germanium crystals which are inclined towards each other in order to focus down the Bragg reflected beam. NeutronMonochromatorBNL.jpg](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d9/NeutronMonochromatorBNL.jpg/200px-NeutronMonochromatorBNL.jpg)

















