Smalltalk is a purely object oriented programming language (OOP) that was originally created in the 1970s for educational use, specifically for constructionist learning, but later found use in business. It was created at Xerox PARC by Learning Research Group (LRG) scientists, including Alan Kay, Dan Ingalls, Adele Goldberg, Ted Kaehler, Diana Merry, and Scott Wallace.

Squeak is an object-oriented, class-based, and reflective programming language. It was derived from Smalltalk-80 by a group that included some of Smalltalk-80's original developers, initially at Apple Computer, then at Walt Disney Imagineering, where it was intended for use in internal Disney projects. The group would later go on to be supported by HP Labs, SAP, and most recently, Y Combinator.
The XML Metadata Interchange (XMI) is an Object Management Group (OMG) standard for exchanging metadata information via Extensible Markup Language (XML).

The Meta-Object Facility (MOF) is an Object Management Group (OMG) standard for model-driven engineering. Its purpose is to provide a type system for entities in the CORBA architecture and a set of interfaces through which those types can be created and manipulated. MOF may be used for domain-driven software design and object-oriented modelling.
The Object Constraint Language (OCL) is a declarative language describing rules applying to Unified Modeling Language (UML) models developed at IBM and is now part of the UML standard. Initially, OCL was merely a formal specification language extension for UML. OCL may now be used with any Meta-Object Facility (MOF) Object Management Group (OMG) meta-model, including UML. The Object Constraint Language is a precise text language that provides constraint and object query expressions on any MOF model or meta-model that cannot otherwise be expressed by diagrammatic notation. OCL is a key component of the new OMG standard recommendation for transforming models, the Queries/Views/Transformations (QVT) specification.
Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) consists of a set of extensions to the Windows Driver Model that provides an operating system interface through which instrumented components provide information and notification. WMI is Microsoft's implementation of the Web-Based Enterprise Management (WBEM) and Common Information Model (CIM) standards from the Distributed Management Task Force (DMTF).
Given that metadata is a set of descriptive, structural and administrative data about a group of computer data, Java Metadata Interface is a platform-neutral specification that defines the creation, storage, access, lookup and exchange of metadata in the Java programming language.
The common warehouse metamodel (CWM) defines a specification for modeling metadata for relational, non-relational, multi-dimensional, and most other objects found in a data warehousing environment. The specification is released and owned by the Object Management Group, which also claims a trademark in the use of "CWM".
GXL is designed to be a standard exchange format for graphs. GXL is an extensible markup language (XML) sublanguage and the syntax is given by an XML document type definition (DTD). This exchange format offers an adaptable and flexible means to support interoperability between graph-based tools.
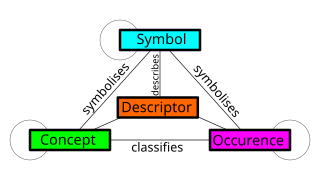
A metamodel is a model of a model, and metamodeling is the process of generating such metamodels. Thus metamodeling or meta-modeling is the analysis, construction, and development of the frames, rules, constraints, models, and theories applicable and useful for modeling a predefined class of problems. As its name implies, this concept applies the notions of meta- and modeling in software engineering and systems engineering. Metamodels are of many types and have diverse applications.

A class browser is a feature of an integrated development environment (IDE) that allows the programmer to browse, navigate, or visualize the structure of object-oriented programming code.
Graph Modeling Language (GML) is a hierarchical ASCII-based file format for describing graphs. It has been also named Graph Meta Language.
In computer programming, a trait is a concept used in programming languages which represents a set of methods that can be used to extend the functionality of a class.
Application discovery and understanding (ADU) is the process of automatically analyzing artifacts of a software application and determining metadata structures associated with the application in the form of lists of data elements and business rules. The relationships discovered between this application and a central metadata registry is then stored in the metadata registry itself.

Seaside, an acronym that stands for “Squeak Enterprise Aubergines Server with Integrated Development Environment,” is computer software, a web framework to develop web applications in the programming language Smalltalk. It is distributed as free and open-source software under an MIT License.
The DMS Software Reengineering Toolkit is a proprietary set of program transformation tools available for automating custom source program analysis, modification, translation or generation of software systems for arbitrary mixtures of source languages for large scale software systems. DMS was originally motivated by a theory for maintaining designs of software called Design Maintenance Systems. DMS and "Design Maintenance System" are registered trademarks of Semantic Designs.

Pharo is a cross-platform implementation of the classic Smalltalk-80 programming language and runtime system. It is based on the OpenSmalltalk virtual machine (VM) named Cog, which evaluates a dynamic, reflective, and object-oriented programming language with a syntax closely resembling Smalltalk-80. It is free and open-source software, released under a mix of MIT, and Apache 2 licenses.

Oscar Marius Nierstrasz is a professor at the Computer Science Institute (IAM) at the University of Berne, and a specialist in software engineering and programming languages. He is active in the field of programming languages and mechanisms to support the flexible composition of high-level, component-based abstractions, tools and environments to support the understanding, analysis and transformation of software systems to more flexible, component-based designs, secure software engineering, and requirement engineering to support stakeholders and developers to have moldable and clear requirements. He has led the Software Composition Group at the University of Berne since 1994 to date.

Amber Smalltalk, formerly named Jtalk, is an implementation of the programming language Smalltalk-80, that runs on the JavaScript runtime of a web browser. It is designed to enable client-side development using Smalltalk. The programming environment in Amber is named Helios.










