Related Research Articles

The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts of the world. This "Neolithic package" included the introduction of farming, domestication of animals, and change from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to one of settlement.
The history of Senegal is commonly divided into a number of periods, encompassing the prehistoric era, the precolonial period, colonialism, and the contemporary era.

The Stone Age was a broad prehistoric period during which stone was widely used to make stone tools with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted for roughly 3.4 million years, and ended between 4,000 BC and 2,000 BC, with the advent of metalworking. Though some simple metalworking of malleable metals, particularly the use of gold and copper for purposes of ornamentation, was known in the Stone Age, it is the melting and smelting of copper that marks the end of the Stone Age. In Western Asia, this occurred by about 3,000 BC, when bronze became widespread. The term Bronze Age is used to describe the period that followed the Stone Age, as well as to describe cultures that had developed techniques and technologies for working copper alloys into tools, supplanting stone in many uses.

Dakar, is the capital and largest city of Senegal. The city of Dakar proper has a population of 1,030,594, whereas the population of the Dakar metropolitan area is estimated at 3.94 million in 2021.

West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, Mauritania, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal, Sierra Leone, and Togo, as well as Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha. The population of West Africa is estimated at 419 million people as of 2021, and at 381,981,000 as of 2017, of which 189,672,000 were female and 192,309,000 male. The region is demographically and economically one of the fastest growing on the African continent.

The prehistory of North Africa spans the period of earliest human presence in the region to gradual onset of historicity in the Maghreb (Berber:Tamazgha) during classical antiquity. Early anatomically modern humans are known to have been present at Jebel Irhoud, in what is now Morocco, approximately 300,000 years ago. The Nile Valley region, via ancient Egypt, contributed to the Neolithic, Bronze Age and Iron Age periods of the Old World, along with the ancient Near East.
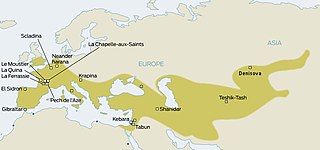
The Mousterian is an archaeological industry of stone tools, associated primarily with the Neanderthals in Europe, and to the earliest anatomically modern humans in North Africa and West Asia. The Mousterian largely defines the latter part of the Middle Paleolithic, the middle of the West Eurasian Old Stone Age. It lasted roughly from 160,000 to 40,000 BP. If its predecessor, known as Levallois or Levallois-Mousterian, is included, the range is extended to as early as c. 300,000–200,000 BP. The main following period is the Aurignacian of Homo sapiens.

The Aurignacian is an archaeological industry of the Upper Paleolithic associated with Early European modern humans (EEMH) lasting from 43,000 to 26,000 years ago. The Upper Paleolithic developed in Europe some time after the Levant, where the Emiran period and the Ahmarian period form the first periods of the Upper Paleolithic, corresponding to the first stages of the expansion of Homo sapiens out of Africa. They then migrated to Europe and created the first European culture of modern humans, the Aurignacian.

The Creswellian is a British Upper Palaeolithic culture named after the type site of Creswell Crags in Derbyshire by Dorothy Garrod in 1926. It is also known as the British Late Magdalenian. According to Andreas Maier: "In current research, the Creswellian and Hamburgian are considered to be independent but closely related entities which are rooted in the Magdalenian." The Creswellian is dated between 13,000 and 11,800 BP and was followed by the most recent ice age, the Younger Dryas, when Britain was at times unoccupied by humans.

Africa has the longest record of human habitation in the world. The first hominins emerged 6-7 million years ago, and among the earliest anatomically modern human skulls found so far were discovered at Omo Kibish, Jebel Irhoud, and Florisbad.

The Aterian is a Middle Stone Age stone tool industry centered in North Africa, from Mauritania to Egypt, but also possibly found in Oman and the Thar Desert. The earliest Aterian dates to c. 150,000 years ago, at the site of Ifri n'Ammar in Morocco. However, most of the early dates cluster around the beginning of the Last Interglacial, around 150,000 to 130,000 years ago, when the environment of North Africa began to ameliorate. The Aterian disappeared around 20,000 years ago.

The Capsian culture was a Mesolithic and Neolithic culture centered in the Maghreb that lasted from about 8,000 to 2,700 BC. It was named after the town of Gafsa in Tunisia, which was known as Capsa in Roman times.

Prehistoric Egypt and Predynastic Egypt span the period from the earliest human settlement to the beginning of the Early Dynastic Period around 3100 BC, starting with the first Pharaoh, Narmer for some Egyptologists, Hor-Aha for others, with the name Menes also possibly used for one of these kings.

The Middle Stone Age was a period of African prehistory between the Early Stone Age and the Late Stone Age. It is generally considered to have begun around 280,000 years ago and ended around 50–25,000 years ago. The beginnings of particular MSA stone tools have their origins as far back as 550–500,000 years ago and as such some researchers consider this to be the beginnings of the MSA. The MSA is often mistakenly understood to be synonymous with the Middle Paleolithic of Europe, especially due to their roughly contemporaneous time span; however, the Middle Paleolithic of Europe represents an entirely different hominin population, Homo neanderthalensis, than the MSA of Africa, which did not have Neanderthal populations. Additionally, current archaeological research in Africa has yielded much evidence to suggest that modern human behavior and cognition was beginning to develop much earlier in Africa during the MSA than it was in Europe during the Middle Paleolithic. The MSA is associated with both anatomically modern humans as well as archaic Homo sapiens, sometimes referred to as Homo helmei. Early physical evidence comes from the Gademotta Formation in Ethiopia, the Kapthurin Formation in Kenya and Kathu Pan in South Africa.
The prehistory of the Levant includes the various cultural changes that occurred, as revealed by archaeological evidence, prior to recorded traditions in the area of the Levant. Archaeological evidence suggests that Homo sapiens and other hominid species originated in Africa and that one of the routes taken to colonize Eurasia was through the Sinai Peninsula desert and the Levant, which means that this is one of the most important and most occupied locations in the history of the Earth. Not only have many cultures and traditions of humans lived here, but also many species of the genus Homo. In addition, this region is one of the centers for the development of agriculture.
IFAN is a cultural and scientific institute in the nations of the former French West Africa. Founded in Dakar, Senegal in 1938 as the Institut français d’Afrique noire, the name was changed only in 1966. It was headquartered in what is now the building of the IFAN Museum of African Arts. Since its founding, its charge was to study the language, history, and culture of the peoples ruled by French colonialism in Africa.

Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the first known use of stone tools by hominins c. 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared c. 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently.
Prehistoric technology is technology that predates recorded history. History is the study of the past using written records. Anything prior to the first written accounts of history is prehistoric, including earlier technologies. About 2.5 million years before writing was developed, technology began with the earliest hominids who used stone tools, which they may have used to start fires, hunt, and bury their dead.
Sebilian is a pre-historic archaeological culture in Egypt spanning the period c.13,000-10,000 B.C.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to prehistoric technology.
References
- ↑ O. Davies (1964)
- ↑ J. D. Clark (1967)
- ↑ G. W. Barendson et al (1965)
- ↑ R. Guillot and C. Descamps (1969)
- ↑ C. T. SHAW THE PRE-HISTORY OF WEST AFRICA in Unesco International Scientific Committee for the Drafting of a General History of Africa General History of Africa: Methodology and African prehistory 819 pages University of California Press, 1981 ISBN 0-435-94808-3 [Retrieved 2012-01-09]
- ↑ Corbeil 1943
- ↑ Oliver Davies West Africa before the Europeans: archaeology & prehistory - 364 pages Methuen's handbooks of archaeology references (Corbeil NA 17 (1943) Corbeil R. , Mauny R. , Charbonnier J. , 1948 , Richard 1955)Taylor & Francis, 1967 [Retrieved 2012-01-09]