| Glossop | |
|---|---|
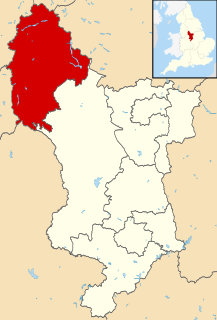
 Municipal Borough of Glossop shown within Derbyshire in 1970. | |
| Area | |
| • 1911 | 3,052 acres (12.35 km2) |
| • 1961 | 3,323 acres (13.45 km2) |
| Population | |
| • 1911 | 21,688 |
| • 1961 | 17,500 |
| History | |
| • Created | 1866 |
| • Abolished | 1974 |
| • Succeeded by | High Peak |
| Status | Municipal Borough |
| Government | Glossop Borough Council |
| • HQ | Glossop |
Glossop was a Municipal Borough in Derbyshire, England from 1866 to 1974. [1] It was created under the Municipal Corporations Act 1835.

Derbyshire is a county in the East Midlands of England. A substantial portion of the Peak District National Park lies within Derbyshire, containing the southern extremity of the Pennine range of hills which extend into the north of the county. The county contains part of the National Forest, and borders on Greater Manchester to the northwest, West Yorkshire to the north, South Yorkshire to the northeast, Nottinghamshire to the east, Leicestershire to the southeast, Staffordshire to the west and southwest and Cheshire also to the west. Kinder Scout, at 636 metres (2,087 ft), is the highest point in the county, whilst Trent Meadows, where the River Trent leaves Derbyshire, is its lowest point at 27 metres (89 ft). The River Derwent is the county's longest river at 66 miles (106 km), and runs roughly north to south through the county. In 2003 the Ordnance Survey placed Church Flatts Farm at Coton in the Elms as the furthest point from the sea in Great Britain.

England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to the west and Scotland to the north-northwest. The Irish Sea lies west of England and the Celtic Sea lies to the southwest. England is separated from continental Europe by the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south. The country covers five-eighths of the island of Great Britain, which lies in the North Atlantic, and includes over 100 smaller islands, such as the Isles of Scilly and the Isle of Wight.

The Municipal Corporations Act 1835, sometimes known as the Municipal Reform Act, was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that reformed local government in the incorporated boroughs of England and Wales. The legislation was part of the reform programme of the Whigs and followed the Reform Act 1832, which had abolished most of the rotten boroughs for parliamentary purposes.
It was enlarged in 1934 when part of the civil parish of Charlesworth was incorporated into the borough. [2]

Charlesworth is a village and civil parish near Glossop, Derbyshire, England. The population of the civil parish at the 2011 Census was 2,449. It is 2 miles (3.2 km) south-west of Glossop town centre and close to the borders of Greater Manchester with the nearby village of Broadbottom in Tameside. The parish church of St John the Baptist was built in 1848–49. The Congregational Chapel was rebuilt from an earlier chapel in 1797. Broadbottom Bridge, one end of which is in Cheshire, was built in 1683. Charlesworth holds an annual carnival on the second Saturday in July on its recreation ground on Marple Road, which includes fell races and other events.
The borough was abolished in 1974 under the Local Government Act 1972 and combined with the Municipal Borough of Buxton, the urban districts of New Mills and Whaley Bridge and the rural districts of Chapel en le Frith and Tintwistle to form the new High Peak district. [3]

The Local Government Act 1972 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that reformed local government in England and Wales on 1 April 1974.

Buxton was an Urban District from 1894 to 1917 and a Municipal Borough from 1917 to 1974 in Derbyshire, England.
New Mills was an Urban District in Derbyshire, England from 1894 to 1974. It was created under the Local Government Act 1894.