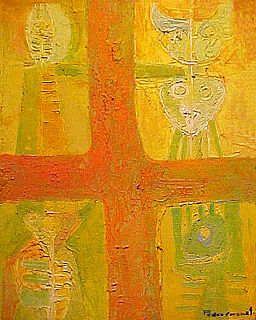Puebla de Zaragoza, formally Heroica Puebla de Zaragoza, during the colonial times its name was Puebla de los Ángeles, or known in English simply as Puebla, is the seat of Puebla Municipality. It is the capital and largest city of the state of Puebla, and the fourth largest city in Mexico, after Mexico City, Monterrey, and Guadalajara. A viceregal era planned city, it is located in the southern part of Central Mexico on the main route between Mexico City and Mexico's main Atlantic port, Veracruz—about 100 km (62 mi) east southeast of Mexico City and about 220 km (140 mi) west of Veracruz.

Tlaxcala, officially Tlaxcala de Xicohténcatl, is the capital city of the Mexican state of Tlaxcala and seat of the municipality of the same name. The city did not exist during the pre Hispanic period but was laid out by the Spanish as a center of evangelization and governance after the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire. It was designated as a diocese but eventually lost this status to Puebla as its population declined. The city still has many of its old colonial structures including the former Franciscan monastery, as well as newer civic structures such as the Xicohtencatl Theatre.

Atlixco is a city and a municipality in the Mexican state of Puebla. It is a regional industrial and commercial center but economically it is much better known for its production of ornamental plants and cut flowers. The city was founded early in the colonial period, originally under the jurisdiction of Huejotzingo, but eventually separated to become an independent municipality. The municipality has a number of notable cultural events, the most important of which is the El Huey Atlixcayotl, a modern adaptation of an old indigenous celebration. This event brings anywhere from 800 to 1,500 participants from all over the state of Puebla to create music, dance, and other cultural and artistic performances.

San Pablo de Mitla is a town and municipality in Mexico which is most famous for being the site of the Mitla archeological ruins. It is part of the Tlacolula District in the east of the Valles Centrales Region. The town is also known for its handcrafted textiles, especially embroidered pieces and mezcal. The town also contains a museum which was closed without explanation in 1995, since when its entire collection of Zapotec and Mixtec cultural items has disappeared. The name “San Pablo” is in honor of Saint Paul, and “Mitla” is a hispanization of the Nahuatl name “Mictlán.” This is the name the Aztecs gave the old pre-Hispanic city before the Spanish arrived and means “land of the dead.” It is located in the Central Valleys regions of Oaxaca, 46 km from the city of Oaxaca, in the District of Tlacolula.

Tonalá is a city and municipality within the Guadalajara Metropolitan Area in the state of Jalisco in Mexico. With a population of 374,258, it is the fourth largest city in the state, the other three being the other major population centres in the metro area: Guadalajara, Zapopan, and Tlaquepaque. It is best known as a major handcrafts center for Jalisco, especially pottery, as well as its very large Thursday and Sunday street market, dedicated to handcrafts.

The Museo de Arte Moderno is located in Chapultepec park, Mexico City, Mexico.

The Museo Nacional de Arte (MUNAL) is the Mexican national art museum, located in the historical center of Mexico City. The museum is housed in a neoclassical building at No. 8 Tacuba, Col. Centro, Mexico City. It includes a large collection representing the history of Mexican art from the mid-sixteenth century to the mid 20th century. It is recognizable by Manuel Tolsá's large equestrian statue of Charles IV of Spain, who was the monarch just before Mexico gained its independence. It was originally in the Zocalo but it was moved to several locations, not out of deference to the king but rather to conserve a piece of art, according to the plaque at the base. It arrived at its present location in 1979.

The Franz Mayer Museum, in Mexico City opened in 1986 to house, display and maintain Latin America’s largest collection of decorative arts. The collection was amassed by stockbroker and financial professional Franz Mayer, who collected fine artworks, books, furniture, ceramics, textiles and many other types of decorative items over fifty years of his life. A large portion comes from Europe and Asia but most comes from Mexico itself with items dating from the 15th to the 20th centuries. Many pieces in the collection are fine handcrafts, such as textiles and Talavera pottery, and they are important because they are items that often did not survive because most did not consider them worth preserving.

Talavera pottery is a Mexican and Spanish pottery tradition from Talavera de la Reina, in Spain. The Mexican pottery is a type of majolica (faience) or tin-glazed earthenware, with a white base glaze typical of the type. It comes from the town of San Pablo del Monte and the cities of Puebla, Atlixco, Cholula, and Tecali, because of the quality of the natural clay found there and the tradition of production which goes back to the 16th century. Much of this pottery was decorated only in blue, but colors such as yellow, black, green, orange and mauve have also been used. Majolica pottery was brought to Mexico by the Spanish in the first century of the colonial period. Production of this ceramic became highly developed in Puebla because of the availability of fine clays and the demand for tiles from the newly established churches and monasteries in the area. The industry had grown sufficiently that by the mid-17th century, standards and guilds had been established which further improved the quality, leading Puebla into what is called the "golden age" of Talavera pottery. Formally, the tradition that developed there is called Talavera Poblana to distinguish it from the similarly named Talavera pottery of Spain. It is a mixture of Italian, Spanish and indigenous ceramic techniques.
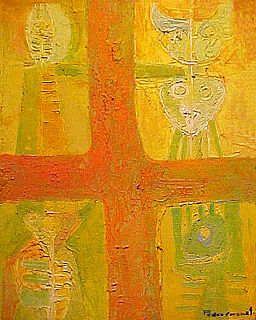
Pedro Coronel was a Mexican sculptor and painter, part of the Generación de la Ruptura, bringing innovation into Mexican art in the mid 20th century. Coronel’s training was with artists of the Mexican muralism tradition, with influence from artists like Diego Rivera. This influence remained with the use of pre Hispanic themes and colors in his work. However, his artistic trajectory took him towards more use of color and more abstract forms in his work, due to influences from artists such as Rufino Tamayo. His work was exhibited and gained recognition in Mexico, the United States and Europe. Shortly before his death, he donated his considerable personal art collection to the people of Mexico, which was used to open the Museo Pedro Coronel in the city of Zacatecas.

Alejandro Colunga Marín is a Mexican artist, painter and sculptor.

Many of Mexico's older architectural structures, including entire sections of Pre-Hispanic and colonial cities, have been designated World Heritage sites for their historical and artistic significance. The country has the largest number of sites declared World Heritage Sites by UNESCO in the Americas.

The Museum of Mexico City is located at Pino Suarez 30, a few blocks south of the Zocalo, on what was the Iztapalapa Causeway, near where Hernán Cortés and Moctezuma II met for the first time. This building used to be the palace of the Counts of Santiago de Calimaya, who were the descendants of one of the conquistadors with Cortés. The house was extensively remodeled during the colony to much the appearance that it has today and remained in the family until 1960, when the Mexico City government acquired it from them in order to found the Museum that is found there today. The museum contains a number of elements of the old palace as well as 26 rooms dedicated to the history and development of Mexico City from Aztec times to the present. It also contains a library and the studios of painter Joaquín Clausell, who lived here in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.

The Museo de la Estampa is a museum in Mexico City, dedicated to the history, preservation and promotion of Mexican graphic arts. The word “estampa” means “engraving” or “printing” refers to works which have the quality of being reproducible and include seals, woodcuts, lithography and others. The museum was created in 1986 and located in a 19th-century Neoclassical building located in the Plaza de Santa Veracruz in the historic center of the city. This building was remodeled both to house the museum and to conserve its original look.

The Palace of Cortés in Cuernavaca, Mexico, built between 1523–1528, is the oldest conserved colonial-era civil structure in the continental Americas. The architecture is a blend between Gothic and Mudéjar, typical of the early 16th century colonial architecture. The building began as a fortified residence for conqueror Hernán Cortés and his aristocratic second wife, Doña Juana Zúñiga. It was built in 1526, over a Tlahuica Aztec tribute collection center, which was destroyed by the Spanish during the Conquest. Cortés replaced it with a personal residence to assert authority over the newly conquered peoples. As Cortés's residence, it reached its height in the 1530s, but the family eventually abandoned it due to on-going legal troubles. In the 18th century, colonial authorities had the structure renovated and used it as a barracks and jail. During the Mexican War of Independence, it held prisoners such as José María Morelos y Pavón. After the war, it became the seat of government for the state of Morelos until the late 20th century, when the state government moved out and the structure was renovated and converted into the current Museo Regional Cuauhnahuac, or regional museum, with exhibits on the history of Morelos.

The Museo Soumaya is a private museum in Mexico City and a non-profit cultural institution with two museum buildings in Mexico City — Plaza Carso and Plaza Loreto. It has over 66,000 works from 30 centuries of art including sculptures from Pre-Hispanic Mesoamerica, 19th- and 20th-century Mexican art and an extensive repertoire of works by European old masters and masters of modern western art such as Auguste Rodin, Salvador Dalí, Bartolomé Esteban Murillo and Tintoretto. It is called one of the most complete collections of its kind.

The Regional Museum of Anthropology and History of Chiapas is the largest museum in Tuxtla Gutiérrez in Chiapas and one of the most important of its kind in Mexico. It primarily consists of two main halls with one dedicated to the state’s Mesoamerican archeology and the other to the history of the state starting from the Spanish conquest. The archeological display focus on the native Zoque and Mayan cities, and the historical displays extend in time until the early 20th century. In addition to its permanent collection, it also has a temporary exhibit hall and auditorium to host events such as book signings, summer classes, conferences and more.

Centro Cultural Mexiquense is a cultural center located on the western edge of the city of Toluca in central Mexico. The center is run by the State of Mexico government through an agency called the Instituto Mexiquense de Cultura (IMC), the largest and most important of this agency, receiving about 80,000 visitors a year. It contains the Museum of Anthropology and History, the Modern Art Museum and the Museum of Popular Cultures as well as a Central Public Library and the Historical Archives of the State of Mexico, as well as facilities for research.

Uriarte Talavera is a traditional Talavera enterprise in the city of Puebla, Mexico, which has been in existence since 1824. It was begun as a family workshop by Dimas Uriarte, but today it is run by a business group. However, the enterprise still makes Talavera pottery using 16th century methods. Much of its work still uses traditional colors and designs, and eligible for certificates of authenticity by the Mexican government, but it has also experimented with new designs and forms since the early 20th century. This has included collaborating with various plastic artists to create modern designs and even artistic pieces.

Betsabeé Romero is a Mexican visual artist. Her works include sculptures, installations, printmaking, perforated paper, photographs, and videos. She has exhibited widely, and has been featured in more than forty one-person exhibitions in the Americas, Africa, Asia and Europe.