
Helen Adams Keller was an American author, disability rights advocate, political activist and lecturer. Born in West Tuscumbia, Alabama, she lost her sight and her hearing after a bout of illness when she was 19 months old. She then communicated primarily using home signs until the age of seven, when she met her first teacher and life-long companion Anne Sullivan. Sullivan taught Keller language, including reading and writing. After an education at both specialist and mainstream schools, Keller attended Radcliffe College of Harvard University and became the first deafblind person in the United States to earn a Bachelor of Arts degree.

Emanuel Swedenborg was a Swedish pluralistic-Christian theologian, scientist, philosopher and mystic. He became best known for his book on the afterlife, Heaven and Hell (1758).

James John Garth Wilkinson, was an English homeopathic physician, social reformer, translator and editor of Swedenborg's works, and a writer on Swedenborgian topics.

Henry James Sr. was an American theologian, father of the philosopher William James, the novelist Henry James, and the diarist Alice James.

Correspondence is a relationship between two levels of existence. The term was coined by the 18th-century theologian Emanuel Swedenborg in his Arcana Cœlestia (1749–1756), Heaven and Hell (1758) and other works.

Celestial marriage is a doctrine that marriage can last forever in heaven. This is a unique teaching of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints or Mormonism, and branches of Mormon fundamentalism.

The General Church of the New Jerusalem is an international church based in Bryn Athyn, Pennsylvania, and based on the Old Testament, the New Testament, and the theological works of Emanuel Swedenborg. The General Church of the New Jerusalem distinguishes itself from other Swedenborgian churches by teaching that the Writings for the New Church are the Heavenly Doctrine revealed by the Lord in His Second Coming and have authority equal to the Old and New Testaments. It is larger, newer, and more conservative than the Swedenborgian Church of North America.
Henry Corbin was a French philosopher, theologian, and Iranologist, professor of Islamic studies at the École pratique des hautes études. He was influential in extending the modern study of traditional Islamic philosophy from early falsafa to later and "mystical" figures such as Suhrawardi, Ibn Arabi, and Mulla Sadra Shirazi.

Heaven and Hell is the common English title of a book written by Emanuel Swedenborg in Latin, published in 1758. The full title is Heaven and its Wonders and Hell From Things Heard and Seen, or, in Latin: De Caelo et Eius Mirabilibus et de inferno, ex Auditis et Visis. It gives a detailed description of the afterlife; how people live after the death of the physical body. The book owes its popular appeal to that subject matter.
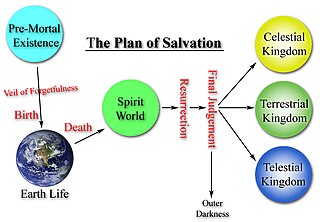
In the Mormon theology and cosmology there are three degrees of glory which are the ultimate, eternal dwelling place for nearly all who lived on earth after they are resurrected from the spirit world.

The New Church is any of several historically related Christian denominations that developed as a new religious group, influenced by the writings of scientist and mystic Emanuel Swedenborg (1688–1772).
"The Frost King" is a short story about King Jack Frost written by Helen Keller, then 11. Keller's teacher, Anne Sullivan, had mentioned that the autumn leaves were "painted ruby, emerald, gold, crimson, and brown," and Keller, by her own account, imagined fairies doing the work. Keller wrote a story about how a cask of jewels, being transported by fairy servants, had melted in the sun and covered the leaves.

Inferno is an autobiographical novel by August Strindberg. Written in French in 1896–97 at the height of Strindberg's troubles with both censors and women, the book is concerned with Strindberg's life both in and after he lived in Paris, and explores his various obsessions, including alchemy, occultism, and Swedenborgianism, and shows signs of paranoia and neuroticism.

The Arcana Cœlestia, quae in Scriptura Sacra seu Verbo Domini sunt, detecta, usually abbreviated as Arcana Cœlestia or under its Latin variant, Arcana Cælestia, is a 12-volume theological work published by Emanuel Swedenborg in the 1750s.
The spirit world, according to Spiritualism, is the world or realm inhabited by spirits, both good or evil of various spiritual manifestations. Whereas religion regards an inner life, the spirit world is regarded as an external environment for spirits. Although independent from the natural world, both the spirit world and the natural world are in constant interaction. Through mediumship, these worlds can consciously communicate with each other. The spirit world is sometimes described by mediums from the natural world in trance.
The nineteenth day of June is celebrated as a holiday by some branches of the New Church. The holiday commemorates events reported by Emanuel Swedenborg in the work True Christian Religion and it is considered by some to be the "birthday" of the New Church.

Louis Lambert is an 1832 novel by French novelist and playwright Honoré de Balzac (1799–1850), included in the Études philosophiques section of his novel sequence La Comédie humaine. Set mostly in a school at Vendôme, it examines the life and theories of a boy genius fascinated by the Swedish philosopher Emanuel Swedenborg (1688–1772).

George Bush was an American biblical scholar, pastor, abolitionist, and academic. A member of the Bush family, he is a distant relative of both President George H. W. Bush and President George W. Bush.
The Lord's New Church Which Is Nova Hierosolyma, usually referred to as the Lord's New Church, is an international, Christian church based on the Old Testament, the New Testament, and the theological writings of Emanuel Swedenborg, which its members view as the Third Testament.
John Clowes was an English cleric and Fellow of Trinity College, Cambridge. Despite his position in the Anglican church, for which he served as Rector of St John's Church, Manchester from 1769 until 1831, he was a noted disciple of Emanuel Swedenborg and did much to propagate his ideas in the Manchester area.












