
NGC 2264 is the designation number of the New General Catalogue that identifies two astronomical objects as a single object: the Cone Nebula, and the Christmas Tree Cluster. Two other objects are within this designation but not officially included, the Snowflake Cluster, and the Fox Fur Nebula.

The Helix Nebula is a planetary nebula (PN) located in the constellation Aquarius. Discovered by Karl Ludwig Harding, most likely before 1824, this object is one of the closest of all the bright planetary nebulae to Earth. The distance, measured by the Gaia mission, is 655±13 light-years. It is similar in appearance to the Cat's Eye Nebula and the Ring Nebula, whose size, age, and physical characteristics are similar to the Dumbbell Nebula, varying only in its relative proximity and the appearance from the equatorial viewing angle. The Helix Nebula has sometimes been referred to as the "Eye of God" in pop culture, as well as the "Eye of Sauron".

The Trifid Nebula is an H II region in the north-west of Sagittarius in a star-forming region in the Milky Way's Scutum-Centaurus Arm. It was discovered by Charles Messier on June 5, 1764. Its name means 'three-lobe'. The object is an unusual combination of an open cluster of stars, an emission nebula, a reflection nebula, and a dark nebula. Viewed through a small telescope, the Trifid Nebula is a bright and peculiar object, and is thus a perennial favorite of amateur astronomers.

The Eagle Nebula is a young open cluster of stars in the constellation Serpens, discovered by Jean-Philippe de Cheseaux in 1745–46. Both the "Eagle" and the "Star Queen" refer to visual impressions of the dark silhouette near the center of the nebula, an area made famous as the "Pillars of Creation" imaged by the Hubble Space Telescope. The nebula contains several active star-forming gas and dust regions, including the aforementioned Pillars of Creation. The Eagle Nebula lies in the Sagittarius Arm of the Milky Way.

The North America Nebula is an emission nebula in the constellation Cygnus, close to Deneb. It is named because its shape resembles North America.

The Carina Nebula or Eta Carinae Nebula is a large, complex area of bright and dark nebulosity in the constellation Carina, located in the Carina–Sagittarius Arm of the Milky Way galaxy. The nebula is approximately 8,500 light-years (2,600 pc) from Earth.

Messier 78 or M78, also known as NGC 2068, is a reflection nebula in the constellation Orion. It was discovered by Pierre Méchain in 1780 and included by Charles Messier in his catalog of comet-like objects that same year.

Open Cluster NGC 2175 is an open cluster in the Orion constellation, embedded in a diffusion nebula. It was discovered by Giovanni Batista Hodierna before 1654 and independently discovered by Karl Christian Bruhns in 1857. NGC 2175 is at a distance of about 6,350 light years away from Earth.

Sh2-279 is an HII region and bright nebulae that includes a reflection nebula located in the constellation Orion. It is the northernmost part of the asterism known as Orion's Sword, lying 0.6° north of the Orion Nebula. The reflection nebula embedded in Sh2-279 is popularly known as the Running Man Nebula.

The Veil Nebula is a cloud of heated and ionized gas and dust in the constellation Cygnus.

NGC 2080, also known as the Ghost Head Nebula, is a star-forming region and emission nebula to the south of the 30 Doradus (Tarantula) nebula, in the southern constellation Dorado. It belongs to the Large Magellanic Cloud, a satellite galaxy to the Milky Way, which is at a distance of 168,000 light years. NGC 2080 was discovered by John Frederick William Herschel in 1834. The Ghost Head Nebula has a diameter of 50 light-years and is named for the two distinct white patches it possesses, called the "eyes of the ghost". The western patch, called A1, has a bubble in the center which was created by the young, massive star it contains. The eastern patch, called A2, has several young stars in a newly formed cluster, but they are still obscured by their originating dust cloud. Because neither dust cloud has dissipated due to the stellar radiation, astronomers have deduced that both sets of stars formed within the past 10,000 years. These stars together have begun to create a bubble in the nebula with their outpourings of material, called stellar wind.

The Flame Nebula, designated as NGC 2024 and Sh2-277, is an emission nebula in the constellation Orion. It is about 900 to 1,500 light-years away.

NGC 2023 is an emission and reflection nebula in the equatorial constellation of Orion. It was discovered by the German-born astronomer William Herschel on 6 January 1785. This reflection nebula is one of the largest in the sky, with a size of 10 × 10 arcminutes. It is located at a distance of 1,300 ly (400 pc) from the Sun, and is positioned ~15′ to the northeast of the Horsehead Nebula.

NGC 7635, also known as the Bubble Nebula, Sharpless 162, or Caldwell 11, is an H II region emission nebula in the constellation Cassiopeia. It lies close to the direction of the open cluster Messier 52. The "bubble" is created by the stellar wind from a massive hot, 8.7 magnitude young central star, SAO 20575 (BD+60°2522). The nebula is near a giant molecular cloud which contains the expansion of the bubble nebula while itself being excited by the hot central star, causing it to glow. It was discovered in 1787 by William Herschel. The star BD+60°2522 is thought to have a mass of about 44 M☉.
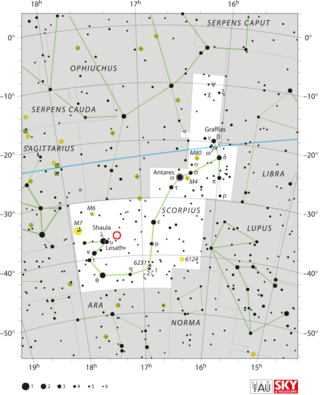
NGC 6334, colloquially known as the Cat's Paw Nebula, Bear Claw Nebula, or Gum 64, is an emission nebula and star-forming region located in the constellation Scorpius. NGC 6334 was discovered by astronomer John Herschel in 1837, who observed it from the Cape of Good Hope in South Africa. The nebula is located in the Carina–Sagittarius Arm of the Milky Way, at a distance of approximately 5.5 kilolight-years from the Sun.

NGC 1333 is a reflection nebula located in the northern constellation Perseus, positioned next to the southern constellation border with Taurus and Aries. It was first discovered by German astronomer Eduard Schönfeld in 1855. The nebula is visible as a hazy patch in a small telescope, while a larger aperture will show a pair of dark nebulae designated Barnard 1 and Barnard 2. It is associated with a dark cloud L1450. Estimates of the distance to this nebula range from 980–1,140 ly (300–350 pc).

IC 5146 is a reflection/emission nebula and Caldwell object in the constellation Cygnus. The NGC description refers to IC 5146 as a cluster of 9.5 mag stars involved in a bright and dark nebula. The cluster is also known as Collinder 470. It shines at magnitude +10.0/+9.3/+7.2. Its celestial coordinates are RA 21h 53.5m, dec +47° 16′. It is located near the naked-eye star Pi Cygni, the open cluster NGC 7209 in Lacerta, and the bright open cluster M39. The cluster is about 4,000 ly away, and the central star that lights it formed about 100,000 years ago; the nebula is about 12 arcmins across, which is equivalent to a span of 15 light years.

IC 405 is an emission and reflection nebula in the constellation Auriga north of the celestial equator, surrounding the bluish, irregular variable star AE Aurigae. It shines at magnitude +6.0. Its celestial coordinates are RA 05h 16.2m dec +34° 28′. It is located near the emission nebula IC 410, the open clusters M38 and M36, and the K-class star Iota Aurigae.

IC 2177 is a region of nebulosity that lies along the border between the constellations Monoceros and Canis Major. It is a roughly circular H II region centered on the Be star HD 53367. This nebula was discovered by Welsh amateur astronomer Isaac Roberts and was described by him as "pretty bright, extremely large, irregularly round, very diffuse."

RCW 79 is an emission nebula in the constellation Centaurus.



























