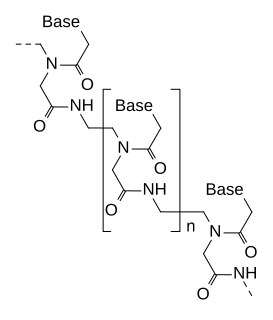
Peptide nucleic acid (PNA) is an artificially synthesized polymer similar to DNA or RNA.

A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is an RNA molecule that is not translated into a protein. The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene. Abundant and functionally important types of non-coding RNAs include transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), as well as small RNAs such as microRNAs, siRNAs, piRNAs, snoRNAs, snRNAs, exRNAs, scaRNAs and the long ncRNAs such as Xist and HOTAIR.

In cell biology, a paraspeckle is an irregularly shaped compartment of the cell, approximately 0.2-1 μm in size, found in the nucleus' interchromatin space. First documented in HeLa cells, where there are generally 10-30 per nucleus, Paraspeckles are now known to also exist in all human primary cells, transformed cell lines and tissue sections. Their name is derived from their distribution in the nucleus; the "para" is short for parallel and the "speckle" refers to the splicing speckles to which they are always in close proximity. Their function is still not fully understood, but they are thought to regulate gene expression by sequestrating proteins or mRNAs with inverted repeats in their 3′ UTRs.

Long non-coding RNAs are a type of RNA, generally defined as transcripts more than 200 nucleotides that are not translated into protein. This arbitrary limit distinguishes long ncRNAs from small non-coding RNAs, such as microRNAs (miRNAs), small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs), small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs), and other short RNAs. Long intervening/intergenic noncoding RNAs (lincRNAs) are sequences of lncRNA which do not overlap protein-coding genes.

HOTAIR is a human gene located between HOXC11 and HOXC12 on chromosome 12. It is the first example of an RNA expressed on one chromosome that has been found to influence transcription of HOXD cluster posterior genes located on chromosome 2. The sequence and function of HOTAIR is different in human and mouse. Sequence analysis of HOTAIR revealed that it exists in mammals, has poorly conserved sequences and considerably conserved structures, and has evolved faster than nearby HoxC genes. A subsequent study identified HOTAIR has 32 nucleotide long conserved noncoding element (CNE) that has a paralogous copy in HOXD cluster region, suggesting that the HOTAIR conserved sequences predates whole genome duplication events at the root of vertebrate. While the conserved sequence paralogous with HOXD cluster is 32 nucleotide long, the HOTAIR sequence conserved from human to fish is about 200 nucleotide long and is marked by active enhancer features.

MALAT 1 also known as NEAT2 is a large, infrequently spliced non-coding RNA, which is highly conserved amongst mammals and highly expressed in the nucleus. MALAT1 was identified in multiple types of physiological processes, such as alternative splicing, nuclear organization, epigenetic modulating of gene expression, and a number of evidences indicate that MALAT1 also closely relate to various pathological processes, ranging from diabetes complications to cancers. It regulates the expression of metastasis-associated genes. It also positively regulates cell motility via the transcriptional and/or post-transcriptional regulation of motility-related genes. MALAT1 may play a role in temperature-dependent sex determination in the Red-eared slider turtle.

MIAT, also known as RNCR2 or Gomafu, is a long non-coding RNA. Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in MIAT are associated with a risk of myocardial infarction. It is expressed in neurons, and located in the nucleus. It plays a role in the regulation of retinal cell fate specification. Crea and collaborators have shown that MIAT is highly up-regulated in aggressive prostate cancer samples, raising the possibility that this gene plays a role in cancer progression.
In bioinformatics, lncRNAdb is a biological database of Long non-coding RNAs The database focuses on those RNAs which have been experimentally characterised with a biological function. The database currently holds over 290 lncRNAs from around 60 species. Example lncRNAs in the database are HOTAIR and Xist.
In molecular biology, HOTTIP is a long non-coding RNA. The gene encoding HOTTIP is located at the 5′ tip of the HOXA locus, and coordinates the activation of several of the 5′ HOXA genes. The non-coding RNA is brought into close proximity with the HOXA genes by chromosomal looping. HOTTIP binds to the WDR5 protein, which forms a complex with the histone methyltransferase protein MLL. This targets the WDR5-MLL complex to the HOXA region and results in H3K4 methylation and transcriptional activation of the HOXA locus. More recently, HOTTIP has been shown to play a role in Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) progression. HOTTIP expression levels predict metastasis formation and poor disease outcome in HCC patients. HOTTIP has been shown to be transcriptionally regulated by a transcriptional coactivator PSIP1/p52

HOXA11-AS lncRNA is a long non-coding RNA from the antisense strand in the homeobox A. The HOX gene contains four clusters. The sense strand of the HOXA gene codes for proteins. Alternative names for HOXA11-AS lncRNA are: HOXA-AS5, HOXA11S, HOXA11-AS1, HOXA11AS, or NCRNA00076. This gene is 3,885 nucleotides long and resides at chromosome 7 (7p15.2) and is transcribed from an independent gene promoter. Being a lncRNA, it is longer than 200 nucleotides in length, in contrast to regular non-coding RNAs.
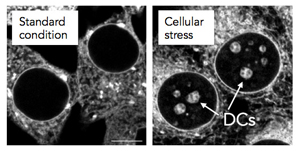
A nucleolar detention center (DC) is a region of the cell in which certain proteins are temporarily detained in periods of cellular stress. DCs are absent from cells under normal culture conditions, but form in response to specific environmental triggers. The detention of numerous proteins in DCs is believed to reduce metabolic activity and promote survival under unfavorable conditions. DCs form at the center of nucleoli and therefore disrupt the normal organization of these organelles. The structural remodeling that ensues leaves nucleoli unable to sustain their primary function, ribosomal biogenesis. Therefore, the formation of DCs is thought to convert nucleoli from “ribosome factories” to “prisons for proteins”.

Firre is a long non-coding RNA located on chromosome X. It is retained in the nucleus via interaction with the nuclear matrix factor hnRNPU. It mediates trans-chromosomal interactions and anchors the inactive X chromosome to the nucleolus. It plays a role in pluripotency and adipogenesis.
Evx1 is a mammalian gene located downstream of the HoxA cluster, which encodes for a homeobox transcription factor. Evx1 is a homolog of even-skipped (eve), which is a pair-rule gene that regulates body segmentation in Drosophila. The expression of Evx1 is developmentally regulated, displaying a biphasic expression pattern with peak expression in the primitive streak during gastrulation and in interneurons during neural development. Evx1 has been shown to regulate anterior-posterior patterning during gastrulation by acting as a downstream effector of the Wnt and BMP signalling pathways. It is also a critical regulator of interneuron identity.
Colon cancer associated transcript 1 is a long non-coding RNA that, in humans, is encoded by the CCAT1 gene.
Jeannie T. Lee is a Professor of Genetics at Harvard Medical School and the Massachusetts General Hospital, and a Howard Hughes Medical Institute Investigator. She is known for her work on X-chromosome inactivation and for discovering the functions of a new class of epigenetic regulators known as long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) for example Xist and Tsix.
BRAF-activated non-protein coding RNA is a noncoding RNA that in humans is encoded by the BANCR gene. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are involved in the intricate network of cancer and contribute significantly to tumorigenesis and progression. BRAF activated non-coding RNA (BANCR), a 693-bp four-exon transcript, was first identified in 2012 as an oncogenic long non-coding RNA in BRAFV600E melanomas cells and was found to be associated with melanoma cell migration. Apart from melanoma, growing evidence has implicated BANCR in the development and progression of a variety of other human malignancies, including retinoblastoma, lung cancer, and gastric cancer, since its discovery. The pattern of expression of BANCR varies according to the kind of cancer, acting as either a tumour suppressor or an accelerator. Functional BANCR may be a useful biomarker for cancer diagnosis and prognosis assessment. BANCR-targeted therapy may also prove to be a promising new treatment option for human cancers.

Cytoskeleton regulator RNA is a long non-coding RNA that in humans is encoded by the CYTOR gene.
Small nucleolar RNA host gene 1 is a non-protein coding RNA that in humans is encoded by the SNHG1 gene.

MIR22HG, also known as C17orf91, MGC14376, MIRN22, hsa-mir-22, and miR-22 is a human gene that encodes a noncoding RNA (ncRNA).This RNA molecule is not translated into a protein but nonetheless may have important functions.











