
A homeobox is a DNA sequence, around 180 base pairs long, that regulates large-scale anatomical features in the early stages of embryonic development. Mutations in a homeobox may change large-scale anatomical features of the full-grown organism.

The tumor suppressor gene FLCN encodes the protein folliculin, also known as Birt–Hogg–Dubé syndrome protein, which functions as an inhibitor of Lactate Dehydrogenase-A and a regulator of the Warburg effect. Folliculin (FLCN) is also associated with Birt–Hogg–Dubé syndrome, which is an autosomal dominant inherited cancer syndrome in which affected individuals are at risk for the development of benign cutaneous tumors (folliculomas), pulmonary cysts, and kidney tumors.
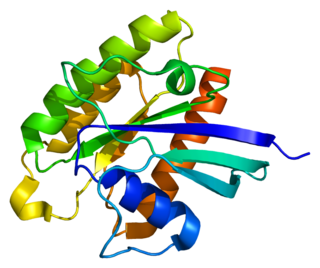
RHEB also known as Ras homolog enriched in brain (RHEB) is a GTP-binding protein that is ubiquitously expressed in humans and other mammals. The protein is largely involved in the mTOR pathway and the regulation of the cell cycle.
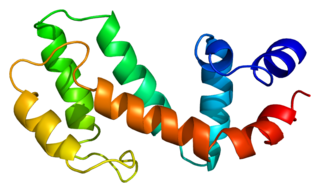
Regulator of G-protein signaling 19 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RGS19 gene.

Regulator of G-protein signaling 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RGS1 gene.

DnaJ homolog subfamily C member 5, also known as cysteine string protein or CSP is a protein, that in humans encoded by the DNAJC5 gene. It was first described in 1990.

Regulator of G-protein signaling 10 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RGS10 gene.

Homeobox protein Meis2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MEIS2 gene.

Nitrogen permease regulator 2-like protein (NPRL2) also known as tumor suppressor candidate 4 (TUSC4) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NPRL2 gene.

Dishevelled (Dsh) is a family of proteins involved in canonical and non-canonical Wnt signalling pathways. Dsh is a cytoplasmic phosphoprotein that acts directly downstream of frizzled receptors. It takes its name from its initial discovery in flies, where a mutation in the dishevelled gene was observed to cause improper orientation of body and wing hairs. There are vertebrate homologs in zebrafish, Xenopus (Xdsh), mice and humans. Dsh relays complex Wnt signals in tissues and cells, in normal and abnormal contexts. It is thought to interact with the SPATS1 protein when regulating the Wnt Signalling pathway.

GCN2 is a serine/threonine-protein kinase that senses amino acid deficiency through binding to uncharged transfer RNA (tRNA). It plays a key role in modulating amino acid metabolism as a response to nutrient deprivation.

DEPDC5 is a human protein of poorly understood function but has been associated with cancer in several studies. It is encoded by a gene of the same name, located on chromosome 22.

Uncharacterized protein C14orf80 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the chromosome 14 open reading frame 80, C14orf80, gene.

C12orf40, also known as Chromosome 12 Open Reading Frame 40, HEL-206, and Epididymis Luminal Protein 206 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the C12orf40 gene.
C6orf222 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the C6orf222 gene (6p21.31). C6orf222 is conserved in mammals, birds and reptiles with the most distant ortholog being the green sea turtle, Chelonia mydas. The C6orf222 protein contains one mammalian conserved domain: DUF3293. The protein is also predicted to contain a BH3 domain, which has predicted conservation in distant orthologs from the clade Aves.
C12orf66 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the C12orf66 gene. The C12orf66 protein is one of four proteins in the KICSTOR protein complex which negatively regulates mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) signaling.

SHLD1 or shieldin complex subunit 1 is a gene on chromosome 20. The C20orf196 gene encodes an mRNA that is 1,763 base pairs long, and a protein that is 205 amino acids long.

The Ragulator-Rag complex is a regulator of lysosomal signalling and trafficking in eukaryotic cells, which plays an important role in regulating cell metabolism and growth in response to nutrient availability in the cell. The Ragulator-Rag Complex is composed of five LAMTOR subunits, which work to regulate MAPK and mTOR complex 1. The LAMTOR subunits form a complex with Rag GTPase and v-ATPase, which sits on the cell’s lysosomes and detects the availability of amino acids. If the Ragulator complex receives signals for low amino acid count, it will start the process of catabolizing the cell. If there is an abundance of amino acids available to the cell, the Ragulator complex will signal that the cell can continue to grow. Ragulator proteins come in two different forms: Rag A/Rag B and Rag C/Rag D. These interact to form heterodimers with one another.

Ras-related protein Rab-2B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RAB2B gene.

C2orf72 is a gene in humans that encodes a protein currently named after its gene, C2orf72. It is also designated LOC257407 and can be found under GenBank accession code NM_001144994.2. The protein can be found under UniProt accession code A6NCS6.





















