Order is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between family and class. In biological classification, the order is a taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and recognized by the nomenclature codes. An immediately higher rank, superorder, is sometimes added directly above order, with suborder directly beneath order. An order can also be defined as a group of related families.

Isopoda is an order of crustaceans that includes woodlice and their relatives. Isopods live in the sea, in fresh water, or on land. All have rigid, segmented exoskeletons, two pairs of antennae, seven pairs of jointed limbs on the thorax, and five pairs of branching appendages on the abdomen that are used in respiration. Females brood their young in a pouch under their thorax.

Arteriviridae is a family of enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses in the order Nidovirales which infect vertebrates. Host organisms include equids, pigs, Possums, nonhuman primates, and rodents. The family includes, for example, equine arteritis virus in horses which causes mild-to-severe respiratory disease and reproductive failure, porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus type 1 and type 2 in pigs which causes a similar disease, simian hemorrhagic fever virus which causes a highly lethal fever, lactate dehydrogenase–elevating virus which affects mice, and wobbly possum disease virus.

Nidovirales is an order of enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses which infect vertebrates and invertebrates. Host organisms include mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, fish, arthropods, molluscs, and helminths. The order includes the families Coronaviridae, Arteriviridae, Roniviridae, and Mesoniviridae.

Torovirus is a genus of enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses in the order Nidovirales and family Tobaniviridae. They primarily infect vertebrates, especially cattle, pigs, and horses. Diseases associated with this genus include gastroenteritis, which commonly presents in mammals. Torovirus is the only genus in the monotypic subfamily Torovirinae. Torovirus is also a monotypic taxon, containing only one subgenus, Renitovirus.
Lactate dehydrogenase elevating virus (LDV) constitutes the species Gamamaarterivirus lacdeh which is part of the family Arteriviridae and order Nidovirales. The order Nidovirales also includes the family of coronaviruses. Arteriviruses infect macrophages in animals and cause a variety of diseases. LDV specifically causes lifelong persistent viremia in mice, but does not harm the host and only slightly harms the immune system. The main clinical sign is an increased level of the plasma enzyme lactate dehydrogenase (LDH). LDV has a remarkably narrow cell type specificity, meaning nothing homologous with LDV in mice has been found in another species.

The Herpesvirales is an order of dsDNA viruses with animal hosts, characterised by a common morphology consisting of an icosahedral capsid enclosed in a glycoprotein-containing lipid envelope. Common infections in humans caused by members of this order include cold sores, genital herpes, chickenpox, shingles, and glandular fever. Herpesvirales is the sole order in the class Herviviricetes, which is the sole class in the phylum Peploviricota.

Alloherpesviridae is a family of viruses in the order Herpesvirales. This family includes the species that infect fish and amphibians. Phylogenetic studies have confirmed the validity of this family and suggest that it may be divided into two clades: one consisting of viruses from cyprinid and anguillid hosts and the other of viruses from ictalurid, salmonid, acipenserid, and ranid hosts. There are currently 13 species in this family, divided among four genera. A disease associated with this family includes channel catfish disease.
Mesoniviridae is a family of enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses in the order Nidovirales which infect mosquitoes. The family is named after the size of the genomes relative to other nidoviruses, with meso- coming from the Greek word mesos, which means medium, and -ni being an abbreviation of nido.

Betacoronavirus is one of four genera of coronaviruses. Member viruses are enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses that infect mammals. The natural reservoir for betacoronaviruses are bats and rodents. Rodents are the reservoir for the subgenus Embecovirus, while bats are the reservoir for the other subgenera.
Ictalurivirus is a genus of viruses in the order Herpesvirales, in the family Alloherpesviridae. Fish serve as natural hosts. There are three species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: channel catfish disease.
Alphaabyssovirus is a genus of positive-strand RNA viruses in the order Nidovirales which infect sea hares. The genus is monotypic. It contains only the subgenus Aplyccavirus, which contains only one species, Aplysia abyssovirus 1. Alphaabyssovirus is also the only member of the subfamily Tiamatvirinae, which in turn is the only member of family Abyssoviridae, which likewise is the only member of the Abnidovirineae suborder. Aplysia abyssovirus 1 was first isolated from a sample from a California sea hare.
Alphamononivirus is a genus of enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses in the order Nidovirales which infect planarian flatworms. Member virus planarian secretory cell nidovirus (PSCNV) has the largest known nonsegmented RNA genome of 41.1kb of any RNA virus. The genus is monotypic. It contains the subgenus Dumedivirus, which contains only one species, Planidovirus 1. Alphamononivirus is also the only member of the subfamily Mononivirinae, which in turn is the only member of family Mononiviridae, which likewise is the only member of the Monidovirineae suborder.
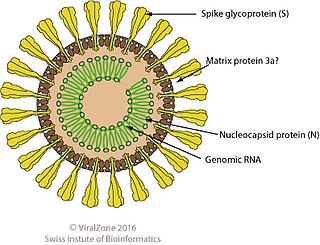
Mesnidovirineae is a suborder of enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses in the order Nidovirales which infect invertebrates. Host organisms include mosquitoes.

Tobaniviridae is a family of enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses in the order Nidovirales which infect vertebrates. Host organisms include mammals, fish, and snakes. The genome size of tobaniviruses ranges from 20 to 32 kilobases. The family is the only member of the suborder Tornidovirineae.
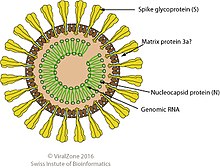
Ronidovirineae is a suborder of enveloped positive-strand RNA viruses in the order Nidovirales which infect arthropods. Host organisms include crustaceans such as shrimp.
Pisoniviricetes is a class of positive-strand RNA viruses which infect eukaryotes. A characteristic of the group is a conserved 3C-like protease from the PA clan of proteases for processing the translated polyprotein. The name of the group is a portmanteau of member orders "picornavirales, sobelivirales, nidovirales" and -viricetes which is the suffix for a virus class.

Piscanivirinae is a virus subfamily of the family Tobaniviridae within the order Nidovirales which comprises different fish viruses. The virions have a viral envelope and a positive-sense single-stranded RNA genome which is linear and unsegmented.

Arnidovirineae is a suborder of viruses in the order Nidovirales. There are 4 families and 16 genera in the Arnidovirineae suborder.