
German East Africa was a German colony in the African Great Lakes region, which included present-day Burundi, Rwanda, the Tanzania mainland, and the Kionga Triangle, a small region later incorporated into Mozambique. GEA's area was 994,996 km2 (384,170 sq mi), which was nearly three times the area of present-day Germany and almost double the area of metropolitan Germany at the time.

Moshi is a municipality and the capital of Kilimanjaro region in the north eastern Tanzania. As of 2017, the municipality has an estimated population of 201,150 and a population density of 3,409 persons per km2. In the last official census of 2022, the municipality had a population of 221,733. The municipality is situated on the lower slopes of Mount Kilimanjaro, a dormant volcano that is the highest mountain in Africa. The name Moshi has been reported to refer to the smoke that emanates from the nearby mountain. The municipality covers about 59 square kilometres (23 sq mi) and is the smallest municipality in Tanzania by area.
The Honourable Sir Charles Cecil Farquharson Dundas, KCMG, OBE was a British colonial administrator who served as Governor of the Bahamas from 1934 to 1937 and Governor of Uganda from 1940 to 1944. He was the fifth son of Charles Saunders Dundas, 6th Viscount Melville.

Marangu is a town located in Moshi District of Kilimanjaro Region. it is divided into Marangu East and Marangu west each with its own village, its one of the famous places in Tanzania recognized as one of the main gate for climbing Mount Kilimanjaro. it is also famous for being a place where Mangi mkuu of chagga Thomas Lenana Marreale was born in Lyamrakana Village on June 15, 1915 who ruled in 1952 up to 1961 when chieftains was abolished..

Chief Thomas Lenana Marealle II OBE (June 15, 1915 – February 14, 2007) was the Paramount Chief (Mangi Mkuu) of the Chagga people of Tanzania and a politician.

The Chagga are a Bantu ethnic group from Kilimanjaro Region of Tanzania. They are the third-largest ethnic group in Tanzania. They historically lived in sovereign Chagga states on the slopes of Mount Kilimanjaro in both Kilimanjaro Region and eastern Arusha Region.

Kilimanjaro Region is one of Tanzania's 31 administrative regions. The regional capital and largest city is the municipality of Moshi. With the 3rd highest HDI of 0.640 in the country, Kilimanjaro is one among the top five most developed regions of Tanzania. According to the 2012 national census, the region had a population of 1,640,087, which was lower than the pre-census projection of 1,702,207. For 2002–2012, the region's 1.8 percent average annual population growth rate was the 24th highest in the country. It was also the eighth most densely populated region with 124 people per square kilometer. The most well-known tribes in the Kilimanjaro region are the chagga, rombos, and pare.

Meli or Mangi Meli Kiusa bin Rindi Makindara, also known as, , was a king of the Chaga in Moshi, one of the sovereign Chagga states in the late 1890s. Mangi means king in Kichagga. He was hanged by the German colonial government together with 19 other Chagga, Meru, and Arusha leaders. Thomas Kitimbo Kirenga, Sindato Kiutesha Kiwelu, King Ngalami of Siha, Tanzania, King Lolbulu of Meru, King Rawaito of Arusha, King Marai of Arusha, and King Molelia of Kibosho were among the noblemen on 2 March 1900.
Augustino Lyatonga Mrema was a Tanzanian politician, who served as minister of home affairs from 1990 to 1995.
The Rwa or Meru sometimes Rwo are a Bantu ethnic and linguistic group based on the south and eastern slopes of Mount Meru in Meru District of the Arusha Region of Tanzania, the Rwa population is estimated to number 198,000.

The Arusha people are a Bantu ethnic and indigenous group based in the western slopes of mount Meru in Arusha District of Arusha Region in Tanzania. The Maasai regard the Arusha people as related as they were once a part of the immigrant Maasai whom arrived in Arusha in the late 18th century from Kenya. The Arusha people are not to be confused by Arusha residents who are a mix of people of different ethnic backgrounds that are born and reside within the borders of the Arusha Region.

Machame or Kingdom of Machame, was a historic sovereign Chagga state located in modern day Machame Kaskazini ward in Hai District of Kilimanjaro Region in Tanzania. Historically, the Machame kingdom was in 1889 referred by Hans Meyer as a great African giant, the kingdom was also the largest and most populous of all the Chagga sovereign states on Kilimanjaro, whose ruler as early as 1849 was reckoned as a giant African king with influence extending throughout all Chagga states except Rombo.
Sia Lives on Kilimanjaro is a children's book written by Astrid Lindgren and with photographs by Anna Riwkin-Brick. The original Swedish edition was published in 1958 by the Rabén & Sjögren publishing company in Stockholm. The English translation was published in 1959, in London by Methuen, and in New York by Macmillan. The book was published as part of the Children's Everywhere photo book series. It is a story of a young girl who wants to visit the king at the Chagga Feast, but her father tells her she is too young, and her brother tells her only boys are allowed. Story about self-determination.

Coffee production in Tanzania is a significant aspect of its economy as it is Tanzania's largest export crop. Tanzanian coffee production averages between 30,000 and 40,000 metric tons annually of which approximately 70% is Arabica and 30% is Robusta.
Marangu Defences or Chagga Caves are a man-made defence cave system that was erected in the late 18th century as defence of the Chaga from Maasai raids and expanded the system in the late 19th century as part of the Chagga resistance from the German occupation. The caves are located in various locations within Moshi District of Kilimanjaro Region in Tanzania.

Ngalami or Ngalami Mmari, also known as, , was one of many kings of the Chagga. He was the king of one of the Chagga states, namely; the Siha Kingdom in what is now modern Siha District of Tanzania's Kilimanjaro Region from the 1880s to 1900. Mangi means king in Kichagga. Ngalami ruled from the Siha seat of Komboko (Kibong'oto) in the 1880s to 1900 when he was executed in Moshi by the Germans alongside 19 other Chagga, Meru and Arusha leaders. The execution of 19 noblemen and leaders on Friday 2nd of March 1900, included noblemen Thomas Kitimbo Kirenga, Sindato Kiutesha Kiwelu, King Meli of Moshi, King Lolbulu of Meru, King Rawaito of Arusha, King Marai of Arusha, and King Molelia of Kibosho.
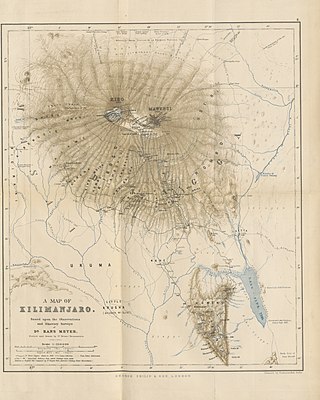
The Chagga States or Chagga Kingdoms also historically referred to as the Chaggaland were a pre-colonial series of a Bantu sovereign states of the Chagga people on Mount Kilimanjaro in modern-day northern Kilimanjaro Region of Tanzania. The Chagga kingdoms existed as far back as the 17th century according to oral tradition, a lot of recorded history of the Chagga states, was written with the arrival, and colonial occupation of Europeans in the mid to late 19th century. On the mountain, many minor dialects of one language are divided into three main groupings that are defined geographically from west to east: West Kilimanjaro, East Kilimanjaro, and Rombo. One word they all have in common is Mangi, meaning king in Kichagga. The British called them chiefs as they were deemed subjects to the British crown, thereby rendered unequal. After the conquest, substantial social disruption, domination, and reorganization by the German and British colonial administrations, the Chagga states were officially abolished in 1963 by the Nyerere administration during its third year as the newly independent nation of Tanganyika.

Kikafu River(Mto Kikafu in Swahili) is located in the northern Kilimanjaro Region, Tanzania. It begins in Machame Mashariki ward in Moshi District and drains into the Pangani River. The river plays an important part of Chagga history in the Chagga kingdom of Machame.

The Battle of Moshi was fought in what is now modern day city of Moshi in Kilimanjaro Region of Tanzania. The battle was between German Empire led by Von Burlow, and the Moshi kingdom led by Mangi Meli.
The Battle of Kibosho took place on February 12, 1891, in what is now Tanzania's Kilimanjaro Region, in Kibosho. The Kibosho kingdom was ruled by Mangi Sina while the conflict was between the German Empire, commanded by Major Hermann von Wissman.














