Related Research Articles

The Department of the Treasury (USDT) is the national treasury and finance department of the federal government of the United States, where it serves as an executive department. The department oversees the Bureau of Engraving and Printing and the U.S. Mint. These two agencies are responsible for printing all paper currency and minting coins, while the treasury executes currency circulation in the domestic fiscal system. It collects all federal taxes through the Internal Revenue Service; manages U.S. government debt instruments; licenses and supervises banks and thrift institutions; and advises the legislative and executive branches on matters of fiscal policy. The department is administered by the secretary of the treasury, who is a member of the Cabinet. The treasurer of the United States has limited statutory duties, but advises the Secretary on various matters such as coinage and currency production. Signatures of both officials appear on all Federal Reserve notes.

The National Trust is a heritage and nature conservation charity and membership organisation in England, Wales and Northern Ireland.

His Majesty's Treasury, occasionally referred to as the Exchequer, or more informally the Treasury, is a ministerial department of the Government of the United Kingdom. It is responsible for developing and executing the government's public finance policy and economic policy. The Treasury maintains the Online System for Central Accounting and Reporting, the replacement for the Combined Online Information System, which itemises departmental spending under thousands of category headings, and from which the Whole of Government Accounts annual financial statements are produced.
A civil list is a list of individuals to whom money is paid by the government, typically for service to the state or as honorary pensions. It is a term especially associated with the United Kingdom, and its former colonies and dominions. It was originally defined as expenses supporting the British monarchy.

Edward Hugh John Neale Dalton, Baron Dalton, was a British Labour Party economist and politician who served as Chancellor of the Exchequer from 1945 to 1947. He shaped Labour Party foreign policy in the 1930s, opposing pacifism; promoting rearmament against the German threat; and strongly opposed the appeasement policy of Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain in 1938. Dalton served in Winston Churchill's wartime coalition cabinet; after the Dunkirk evacuation he was Minister of Economic Warfare, and established Special Operations Executive. As Chancellor, he pushed his policy of cheap money too hard, and mishandled the sterling crisis of 1947. His political position was already in jeopardy in 1947 when he, seemingly inadvertently, revealed a sentence of the budget to a reporter minutes before delivering his budget speech. Prime Minister Clement Attlee accepted his resignation; Dalton later returned to the cabinet in relatively minor positions.
The Crown Estate is a collection of lands and holdings in the United Kingdom belonging to the British monarch as a corporation sole, making it "the sovereign's public estate", which is neither government property nor part of the monarch's private estate. The Crown Estate in England, Wales, and Northern Ireland is managed by the Crown Estate Commissioners, which trades as The Crown Estate. In Scotland, the Crown Estate is managed by Crown Estate Scotland, since the Scottish estate was devolved in 2017.

His Majesty's Revenue and Customs is a non-ministerial department of the UK Government responsible for the collection of taxes, the payment of some forms of state support, the administration of other regulatory regimes including the national minimum wage and the issuance of national insurance numbers. HMRC was formed by the merger of the Inland Revenue and HM Customs and Excise, which took effect on 18 April 2005. The department's logo is the Tudor Crown enclosed within a circle.

In the United Kingdom, taxation may involve payments to at least three different levels of government: central government, devolved governments and local government. Central government revenues come primarily from income tax, National Insurance contributions, value added tax, corporation tax and fuel duty. Local government revenues come primarily from grants from central government funds, business rates in England, Council Tax and increasingly from fees and charges such as those for on-street parking. In the fiscal year 2023–24, total government revenue was forecast to be £1,139.1 billion, or 40.9 per cent of GDP, with income taxes and National Insurance contributions standing at around £470 billion.
An International Finance Facility (IFF) is a bond issued against the security of donor government guarantees to maintain future aid flows for the purpose of international development.
The Barnett formula is a mechanism used by the Treasury in the United Kingdom to automatically adjust the amounts of public expenditure allocated to Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales to reflect changes in spending levels allocated to public services in England, Scotland and Wales, as appropriate. The formula applies to a large proportion, but not the whole, of the devolved governments' budgets − in 2013–14 it applied to about 85% of the Scottish Parliament's total budget.

The Commonwealth Education Trust was a registered charity established in 2007 as the successor trust to the Commonwealth Institute. The trust focuses on primary and secondary education and the training of teachers and invests on educational products and services to achieve both a beneficial and a financial reward to fund future charitable initiatives.

The National Heritage Memorial Fund (NHMF) was set up in 1980 to save the most outstanding parts of the British national heritage, in memory of those who have given their lives for the UK. It replaced the National Land Fund, which had fulfilled the same function since 1946. It received £20 million Government grant in aid between 2011–2015, allowing for an annual budget of between £4 million and £5 million. Between 1980 and 2020, the NHMF spent £368 million. Nearly a third was spent on buildings and monuments, and nearly £194 million was spent on paintings, furniture and other objects. A diverse list of over 1,200 heritage items have been safeguarded by the National Heritage Memorial Fund, including:
A Consolidated Fund Act is an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom passed to allow, like an Appropriation Act, the Treasury to issue funds out of the Consolidated Fund.
The Public Works Loan Board (PWLB) was a statutory body of the UK Government that provided loans to public bodies from the National Loans Fund. In 2020, the PWLB was abolished as a statutory organisation, and its functions were allocated to HM Treasury, where they are discharged through the UK Debt Management Office. The members of the PWLB were known as the Public Works Loan Commissioners.

James Meyer Sassoon, Baron Sassoon, is a British businessman and politician. After a career in the financial sector he served in various roles in HM Treasury, the UK's finance ministry, from 2002 to 2008, at which point he began advising David Cameron on financial issues. From May 2010 to January 2013, Sassoon was the first Commercial Secretary to the Treasury and was appointed to the House of Lords as a Conservative. In January 2013, he became an executive director of Jardine Matheson Holdings and of Matheson & Co. He is also a director of Hongkong Land, Dairy Farm and Mandarin Oriental and chairman of the China-Britain Business Council.

Acceptance in lieu (AiL) is a provision in British tax law under which inheritance tax debts can be written off in exchange for the acquisition of objects of national importance. It was originally established by Chancellor of the Exchequer David Lloyd George as a means for the wealthy to pay the increased estate taxes imposed by his People's Budget of 1909 but had its roots in similar schemes dating to the late 19th century. It has developed from the early years, when it was used mainly as a means for the aristocracy to dispose of country estates to the National Trust, to the modern day, when it is more associated with the transfer of works of art, antiquities and archive material to museums. The scheme is administered by Arts Council England, a non-departmental public body of the Department for Culture, Media and Sport. The scheme has brought many houses, works of art and other collections into publicly accessible institutions when they would otherwise have gone to auction. In April 2013 the Cultural Gifts Scheme was started which allows taxpayers to make a donation of art in return for a credit on income tax, capital gains tax or corporation tax. The Cultural Gifts Scheme is also administered by Arts Council England and is reported jointly with the Acceptance in Lieu scheme.
The Funding Act of 1790, the full title of which is An Act making provision for the [payment of the] Debt of the United States, was passed on August 4, 1790, by the United States Congress as part of the Compromise of 1790, to address the issue of funding of the domestic debt incurred by the state governments, first as Thirteen Colonies, then as states in rebellion, in independence, in Confederation, and finally as members of a single federal Union. By the Act, the newly-inaugurated federal government under the U.S. Constitution assumed and thereby retired the debts of each of the individual colonies in rebellion and the bonded debts of the States in Confederation, which each state had individually and independently issued on its own "full faith and credit" when each of them was, in effect, an independent nation.

The Budget of His Majesty's Government is an annual budget set by HM Treasury for the following financial year, with the revenues to be gathered by HM Revenue and Customs and the expenditures of the public sector, in compliance with government policy. The budget statement is one of two statements made by the Chancellor of the Exchequer in the House of Commons, with the Spring Statement being made the following year.
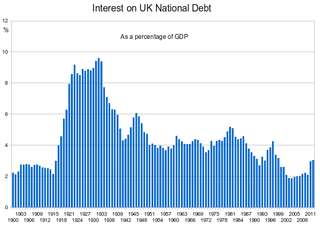
The history of the British national debt can be traced back to the reign of William III, who engaged a syndicate of City traders and merchants to offer for sale an issue of government debt, which evolved into the Bank of England. In 1815, at the end of the Napoleonic Wars, British government debt reached a peak of £1 billion.

Sir Thomas Leslie Rowan was a British civil servant and industrialist.
References
- ↑ "Finance Act 1946". 1 August 1946. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- 1 2 Rickwood, P.W. (1987). "The National Land fund, 1946–80: the failure of a policy initiative". Leisure Studies. 6: 15–23. doi:10.1080/02614368700390021.
- 1 2 "Saved for the Nation: 40 years of the NHMF". Historic Houses. 11 June 2021.