
Honduras was inhabited by many indigenous peoples when the Spanish arrived in the 16th century. The western-central part of Honduras was inhabited by the Lencas, the central north coast by the Tol, the area east and west of Trujillo by the Pech, the Maya and Sumo. These autonomous groups maintained commercial relationships with each other and with other populations as distant as Panama and Mexico. Honduras has ruins of several cities dating from the Mesoamerican pre-classic period that show the pre-Columbian past of the country.

Politics of Honduras takes place in a framework of a multi-party system presidential representative democratic republic. The President of Honduras is both head of state and head of government. Executive power is exercised by the government. Legislative power is vested in the National Congress of Honduras. The party system is dominated by the conservative National Party of Honduras, the Liberal Party of Honduras, and Liberty and Refoundation.

The Liberal Party of Honduras is a centrist liberal political party in Honduras that was founded in 1891. It is the oldest extant political party in the country; further, it is one of the two main parties that have, until recently, dominated Honduran politics. The party is a member of the Liberal International. The PLH is identified with the colours red and white, as the flag Francisco Morazán used in most of his military campaigns during time of the Central American Federal Republic.
Liberalism in Honduras is a form of Latin American liberalism. It was influenced by French revolutionaries from 1789 to 1799, when the door was open for ideas of positivism. During this time the populace were exposed to liberal ideas such as: liberty, equality, and popular sovereignty, causing enthusiasm for them to be increased.

Porfirio Lobo Sosa also known by his nickname, Pepe Lobo, is a former Honduran politician and agricultural landowner who served as President of Honduras from 2010 to 2014. A member of the conservative National Party and a former deputy in the National Congress of Honduras from 1990, he was president of the National Congress of Honduras from 2002 to 2006. He came second to Manuel Zelaya with 46% of the vote in the 2005 general election. After the military ousted Zelaya in a coup d'état, Lobo was elected president in the 2009 presidential election and took office on 27 January 2010.

The National Congress is the legislative branch of the government of Honduras.

General Manuel Bonilla Chirinos was a military officer with the rank of Major General and President of Honduras from 13 April 1903 to 25 February 1907, and again from 1 February 1912 to 21 March 1913. He had previously served as Vice President of Honduras from 1895 to 1899.

Luis Bográn Barahona was a president of Honduras, who served two consecutive terms from 30 November 1883 to 30 November 1891. He was born in the northern Honduran department of Santa Bárbara on 3 June 1849 to Saturnino Bográn Bonilla and Gertrudis Barahona Leiva. He was a member of a prominent and wealthy political family. The last name "Bográn" derives from the French surname "Beaugrand". Luis Bográn was the brother of future president Francisco Bográn and first cousin of future president Miguel Paz Barahona.

Honduras is a republic in Central America, at times referred to as Spanish Honduras to differentiate it from British Honduras, which became the modern-day state of Belize.

Juan Orlando Hernández Alvarado, also known as JOH, is a Honduran lawyer, politician and convicted drug trafficker who served as President of Honduras from 2014 to 2022 for two consecutive terms.

Liberty and Refoundation is a left-wing political party in Honduras. Libre was founded in 2011 by the National Popular Resistance Front (FNRP), a leftist coalition of organizations opposed to the 2009 coup.
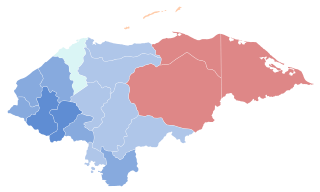
General elections were held in Honduras on 24 November 2013. Voters went to the polls to elect a new President, the 128 members of the National Congress, 298 Mayors and vice-mayors and their respective councilors and 20 representatives to the Central American Parliament.
List of events in the year 2012 in Honduras.

Salvador Alejandro César Nasralla Salum is a Honduran sports journalist, television presenter, businessman, and politician who has served as the First Vice President of Honduras since 27 January 2022.

Marlon Tábora Muñoz is a Honduran politician and diplomat, a PhD in economic sciences, and a member of the National Party of Honduras. Previously Tábora has been Honduras Ambassador to the United States and also worked as Executive Director for Central América and Belize at the Inter-American Development Bank and Counselor Minister of Economic and Energy Affairs of the President Juan Orlando Hernández

The Presidential Palace of Honduras is the official residence of the president of the Republic of Honduras. Currently the president resides in the Palacio José Cecilio del Valle.

General elections were held in Honduras on 26 November 2017. Voters went to the polls to elect the President of Honduras to serve a four-year term, as well as 128 members of the unicameral National Congress, 20 members for the Central American Parliament and mayors for the municipalities of Honduras.

Hilda Rosario Hernández Alvarado was an agronomy engineer and Honduran politician. She held posts in the nationalist governments of Ricardo Maduro, Porfirio Lobo Sosa, and of her brother, Juan Orlando Hernández, who served as Honduran president between 2014 and 2022. From January 2017 until her questionable death, she was a political advisor to her brother in his campaign for re-election in the Honduran general election of 2017.

Olga Margarita Alvarado Rodríguez is a Honduran politician who served as Vice President of Honduras under Juan Orlando Hernández from 2018 to 2022. She is from the National Party.



















