
The Henschel Hs 293 was a World War II German radio-guided glide bomb. It is the first operational anti-shipping missile, first used unsuccessfully on 25 August 1943 and then with increasing success over the next year, ultimately damaging or sinking at least 25 ships. Allied efforts to jam the radio control link were increasingly successful despite German efforts to counter them. The weapon remained in use through 1944 when it was also used as an air-to-ground weapon to attack bridges to prevent the Allied breakout after D-Day, but proved almost useless in this role.

HMS Dragon, also known in Polish service as ORP Dragon, was a D- or Danae-class cruiser built for the Royal Navy. She was launched in Glasgow, in December 1917, and scuttled in July 1944 off the Normandy beaches as part of the Arromanches Breakwater.

Kaiten were crewed torpedoes and suicide craft, used by the Imperial Japanese Navy in the final stages of World War II.

The Flower-class corvette was a British class of 294 corvettes used during World War II by the Allied navies particularly as anti-submarine convoy escorts in the Battle of the Atlantic. Royal Navy ships of this class were named after flowers.

Human torpedoes or manned torpedoes are a type of diver propulsion vehicle on which the diver rides, generally in a seated position behind a fairing. They were used as secret naval weapons in World War II. The basic concept is still in use.

HMS Quorn was a Hunt-class destroyer of the Royal Navy, built in 1940 and sunk off the Normandy coast on 3 August 1944. The class were named after British fox and stag hunts, in this case, the Quorn Hunt, predominantly based in Leicestershire.

HMS Ashanti was a Tribal-class destroyer of the Royal Navy. Following the style of her sister ships she was named for an ethnic group, in this case the Ashanti people of the Gold Coast in West Africa. She served in the Second World War and was broken up in 1949. She was the first of two Royal Navy ships to bear the name Ashanti.
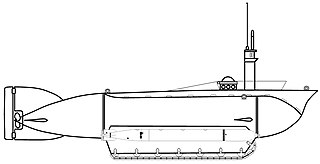
Seeteufel was a two-man amphibious midget submarine, developed by Nazi Germany during World War II. Only one prototype was built in 1944, although its testing was relatively successful and negotiations began for another series of three to test the necessary changes before beginning series production in 1945. These plans were cancelled at the beginning of that year when the decision was made to concentrate production on designs already being built.
Seehund, also known as Type XXVII, was a midget submarine built by Nazi Germany during World War II. Designed in 1944 and operated by two-man crews, it was used by the Kriegsmarine during the closing months of the war, sinking nine merchant vessels and damaging an additional three, while losing 35 boats, mostly attributed to bad weather. The French Navy used four captured boats after the war until 1953.

Molch was an unsuccessful series of one-man midget submarines created during World War II. Built in 1944, it was the first mini-submarine of Nazi Germany's Kriegsmarine, but was not successful in combat operations and suffered heavy losses.

German submarine U-515 was a Type IXC U-boat of Nazi Germany's Kriegsmarine built for service during World War II. She was commissioned on 21 February 1942 and sunk on 9 April 1944. U-515 completed seven operational patrols and sank 23 ships, badly damaged two ships which later sank, and damaged two additional ships.

HMS Storm was an S-class submarine of the Royal Navy, and part of the third group built of that class. She was built by Cammell Laird and launched on 18 May 1943. So far, she is the only RN ship to bear the name Storm.
HMS Pylades was a Catherine-class minesweeper of the Royal Navy.

Hecht, also known as Type XXVIIA, was a two-man all-electric German midget submarine created during World War II.

Marder was a German midget submarine developed from the Neger. The craft was 8.3 metres long and unlike the Neger included a flooding tank in the nose allowing it to dive. Another improvement was the dome through which the pilot viewed the outside world that also served as the craft's entrance and exit was made openable from the inside. Maximum diving depth was about 25 metres (82 ft).

The explosive motorboat MT also known as barchino, was a series of small explosive motor boats developed by the Italian Royal Navy, which was based on its predecessors, the prototype boat MA and the MAT, an airborne prototype. Explosive motorboats were designed to make a silent approach to a moored warship, set a collision course and run into full gear until the last 200 or 100 yards to the target, when the pilot would eject after blocking the rudder. At impact, the hull would be broken amidships by a small explosive charge, sinking the boat and the warhead, which was fitted with a water-pressure fuse set to go off at a depth of one metre.

HMS Trollope (K575) was a British Captain class frigate of the Royal Navy in commission during World War II. Originally constructed as a United States Navy Buckley class destroyer escort, she served in the Royal Navy from January to July 1944, when she was lost.
HMS Tyler (K576) was a British Captain-class frigate of the Royal Navy in commission during World War II. Originally constructed as a United States Navy Buckley-class destroyer escort, she served in the Royal Navy from 1944 to 1945.

A torpedo cruiser is a type of warship that is armed primarily with torpedoes. The major navies began building torpedo cruisers shortly after the invention of the locomotive Whitehead torpedo in the 1860s. The development of the torpedo gave rise to the Jeune École doctrine, which held that small warships armed with torpedoes could effectively and cheaply defeat much larger battleships. Torpedo cruisers fell out of favor in most of the great power navies in the 1890s, though many other navies continued to acquire them into the early 1900s.

HMS Cattistock (L35) was a Type I Hunt-class destroyer of the Royal Navy. She was a member of the first subgroup of the Hunt class and served throughout World War II before being scrapped in 1957.

![Walter Gerhold [de] in the cockpit of a Neger Starszy marynarz Walter Gerhold w jednoosobowej lodzi torpedowej (2-2585).jpg](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/2/2b/Starszy_marynarz_Walter_Gerhold_w_jednoosobowej_%C5%82odzi_torpedowej_%282-2585%29.jpg/220px-Starszy_marynarz_Walter_Gerhold_w_jednoosobowej_%C5%82odzi_torpedowej_%282-2585%29.jpg)

















