
Nehemiah 1 is the first chapter of the Book of Nehemiah in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible, or the 11th chapter of the book of Ezra-Nehemiah in the Hebrew Bible, which treats the book of Ezra and the book of Nehemiah as one book. Jewish tradition states that Ezra is the author of Ezra-Nehemiah as well as the Book of Chronicles, but modern scholars generally accept that a compiler from the 5th century BCE is the final author of these books. This chapter describes Nehemiah's position in the Persian court and his piety.

Ezra 1 is the first chapter of the Book of Ezra in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible, or the book of Ezra–Nehemiah in the Hebrew Bible, which treats the book of Ezra and book of Nehemiah as one book. Jewish tradition states that Ezra is the author of Ezra-Nehemiah as well as the Book of Chronicles, but modern scholars generally believe that a compiler from the 5th century BCE is the final author of these books.

Ezra 2 is the second chapter of the Book of Ezra in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible, or the book of Ezra-Nehemiah in the Hebrew Bible, which treats the book of Ezra and book of Nehemiah as one book. Jewish tradition states that Ezra is the author of Ezra-Nehemiah as well as the Book of Chronicles, but modern scholars generally accept that a compiler from the 5th century BCE is the final author of these books. The section comprising chapter 1 to 6 describes the history before the arrival of Ezra in the land of Judah in 468 BCE. This chapter contains a list, known as the "Golah List", of the people who returned from Babylon to Judah following Cyrus's edict "by genealogy, family and place of habitation".

Ezra 4 is the fourth chapter of the Book of Ezra in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible, or the book of Ezra-Nehemiah in the Hebrew Bible, which treats the book of Ezra and book of Nehemiah as one book. Jewish tradition states that Ezra is the author of Ezra-Nehemiah as well as the Book of Chronicles, but modern scholars generally accept that a compiler from the 5th century BCE is the final author of these books. The section comprising chapter 1 to 6 describes the history before the arrival of Ezra in the land of Judah in 468 BCE. This chapter records the opposition of the non-Jews to the re-building of the temple and their correspondence with the kings of Persia which brought a stop to the project until the reign of Darius the Great.

Ezra 5 is the fifth chapter of the Book of Ezra in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible, or the book of Ezra-Nehemiah in the Hebrew Bible, which treats the book of Ezra and book of Nehemiah as one book. Jewish tradition states that Ezra is the author of Ezra-Nehemiah as well as the Book of Chronicles, but modern scholars generally accept that a compiler from the 5th century BCE is the final author of these books. The section comprising chapter 1 to 6 describes the history before the arrival of Ezra to the land of Judah in 468 BCE. This chapter records the contribution of the prophets Haggai and Zechariah to the temple building project and the investigation by Persian officials.

Ezra 6 is the sixth chapter of the Book of Ezra in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible, or the book of Ezra-Nehemiah in the Hebrew Bible, which treats the book of Ezra and book of Nehemiah as one book. Jewish tradition states that Ezra is the author of Ezra-Nehemiah as well as the Book of Chronicles, but modern scholars generally accept that a compiler from the 5th century BCE is the final author of these books. The section comprising chapter 1 to 6 describes the history before the arrival of Ezra in the land of Judah in 468 BCE. This chapter records the response of the Persian court to the report from Tattenai in the previous chapter: a search is made for the original decree by Cyrus the Great and this is confirmed with a new decree from Darius the Great allowing the temple to be built. This chapter closes this first part of the book in a "glorious conclusion with the completion of the new temple and the celebration of Passover" by the people, as their worship life is restored according to the Law of Moses.

Ezra 7 is the seventh chapter of the Book of Ezra in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible, or the book of Ezra-Nehemiah in the Hebrew Bible, which treats the book of Ezra and book of Nehemiah as one book. Jewish tradition states that Ezra is the author of Ezra-Nehemiah as well as the Book of Chronicles, but modern scholars generally accept that a compiler from the 5th century BCE is the final author of these books. The section comprising chapters 7 to 10 mainly describes the activities of Ezra the scribe and the priest. This chapter focuses on the commission of Ezra by Artaxerxes I of Persia, and the start of his journey from Babylon to Jerusalem.

Ezra 8 is the eighth chapter of the Book of Ezra in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible, or the book of Ezra-Nehemiah in the Hebrew Bible, which treats the book of Ezra and book of Nehemiah as one book. Jewish tradition states that Ezra is the author of Ezra-Nehemiah as well as the Book of Chronicles, but modern scholars generally accept that a compiler from the 5th century BCE is the final author of these books. The section comprising chapters 7 to 10 mainly describes of activities of Ezra the scribe and the priest. This chapter follows Ezra's journey to Jerusalem and includes a genealogy of those returning with him.

Ezra 9 is the ninth chapter of the Book of Ezra in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible, or the book of Ezra-Nehemiah in the Hebrew Bible, which treats the book of Ezra and book of Nehemiah as one book. Jewish tradition states that Ezra is the author of Ezra-Nehemiah as well as the Book of Chronicles, but modern scholars generally accept that a compiler from the 5th century BCE is the final author of these books. The section comprising chapters 7 to 10 mainly describes the activities of Ezra the scribe and the priest. This chapter and the next deal with the problem of intermarriage, starting with the introduction of the crisis, then Ezra's public mourning and prayer of shame. J. Gordon McConville suggests that this chapter is central to the Book of Ezra because it draws a sharp contrast between what the people of God ought to be and what they actually are.

Ezra 10 is the tenth and final chapter of the Book of Ezra in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible, or the tenth chapter of the book of Ezra-Nehemiah in the Hebrew Bible, which treats the book of Ezra and book of Nehemiah as one book. Jewish tradition states that Ezra is the author of Ezra-Nehemiah as well as the Book of Chronicles, but modern scholars generally accept that a compiler from the 5th century BCE is the final author of these books. The section comprising chapters 7 to 10 mainly describes the activities of Ezra the scribe and the priest. This chapter and the previous one deal with the problem of intermarriage, especially the solution of it, ending with a list of those who sent away their "foreign" wives and children; a somber note which finds relief in the Book of Nehemiah, as the continuation of the Book of Ezra.

Nehemiah 2 is the second chapter of the Book of Nehemiah in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible, or the 12th chapter of the book of Ezra-Nehemiah in the Hebrew Bible, which treats the book of Ezra and the book of Nehemiah as one book. Jewish tradition states that Ezra is the author of Ezra-Nehemiah as well as the Book of Chronicles, but modern scholars generally accept that a compiler from the 5th century BCE is the final author of these books. From the time he hears about Jerusalem during the month of Kislev (November/December), Nehemiah waited until the month of Nisan (March/April) to petition Artaxerxes I of Persia to be allowed to go and help the rebuilding of Jerusalem. His petition is granted by the king, and although with less authority than Ezra over the officials of "Beyond-the-River", Nehemiah was given an official position with an escort of officers and cavalry.
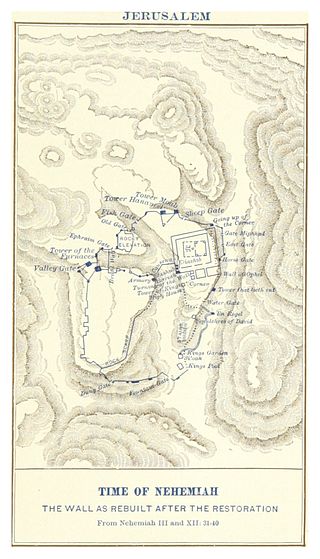
Nehemiah 3 is the third chapter of the Book of Nehemiah in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible, or the 13th chapter of the book of Ezra-Nehemiah in the Hebrew Bible, which treats the book of Ezra and the book of Nehemiah as one book. Jewish tradition states that Ezra is the author of Ezra-Nehemiah as well as the Book of Chronicles, but modern scholars generally accept that a compiler from the 5th century BCE is the final author of these books. This chapter records in detail the rebuilding of the walls and gates of Jerusalem, starting from the north to west sections, continued to south and east sections until reaching the Sheep Gate again, the initial starting point.
Nehemiah 5 is the fifth chapter of the Book of Nehemiah in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible, or the 15th chapter of the book of Ezra-Nehemiah in the Hebrew Bible, which treats the book of Ezra and the book of Nehemiah as one book. Jewish tradition states that Ezra is the author of Ezra-Nehemiah as well as the Book of Chronicles, but modern scholars generally accept that a compiler from the 5th century BCE is the final author of these books. This chapter records the reform of Nehemiah in the case of economic oppression among the Jews, and shows how he led by example.

Nehemiah 6 is the sixth chapter of the Book of Nehemiah in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible, or the 16th chapter of the book of Ezra-Nehemiah in the Hebrew Bible, which treats the book of Ezra and the book of Nehemiah as one book. Jewish tradition states that Ezra is the author of Ezra-Nehemiah as well as the Book of Chronicles, but modern scholars generally accept that a compiler from the 5th century BCE is the final author of these books. This chapter records the continuing opposition to Nehemiah from sources both external and internal.

Nehemiah 7 is the seventh chapter of the Book of Nehemiah in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible, or the 17th chapter of the book of Ezra-Nehemiah in the Hebrew Bible, which treats the book of Ezra and the book of Nehemiah as one book. Jewish tradition states that Ezra is the author of Ezra-Nehemiah as well as the Book of Chronicles, but modern scholars generally accept that a compiler from the 5th century BCE is the final author of these books. This chapter records the joint appointments of Hanani and Hananiah over Jerusalem and the second appearance of the Golah ("exiles") list, that is, the list of the first returning group of Jews from Babylon, which was documented earlier in Ezra 2 with few variations.

Nehemiah 8 is the eighth chapter of the Book of Nehemiah in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible, or the 18th chapter of the book of Ezra–Nehemiah in the Hebrew Bible, which treats the book of Ezra and the book of Nehemiah as one book. Jewish tradition states that Ezra is the author of Ezra-Nehemiah as well as the Book of Chronicles, but modern scholars generally accept that a compiler from the 5th century BCE is the final author of these books. This chapter and the next focus mainly on Ezra, with this chapter recording Ezra's reading and instructing God's law to the people, then together they celebrated the Feast of Tabernacles with great joy. Nehemiah the governor is mentioned briefly in verse 9 but Smith-Christopher argues that "the presence of Ezra and the virtual absence of Nehemiah support the argument that chapter 8 is among the displaced chapters from the Ezra material", and suggests that "the original place for [this chapter] would logically have been between Ezra 8 and 9".

Nehemiah 9 is the ninth chapter of the Book of Nehemiah in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible, or the 19th chapter of the book of Ezra-Nehemiah in the Hebrew Bible, which treats the book of Ezra and the book of Nehemiah as one book. Jewish tradition states that Ezra is the author of Ezra-Nehemiah as well as the Book of Chronicles, but modern scholars generally accept that a compiler from the 5th century BCE is the final author of these books. This chapter and the previous one focus mainly on Ezra; with this chapter recording Ezra's prayer of repentance for the sake of the people.

Nehemiah 10 is the tenth chapter of the Book of Nehemiah in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible, or the 20th chapter of the book of Ezra-Nehemiah in the Hebrew Bible, which treats the book of Ezra and the book of Nehemiah as one book. Jewish tradition states that Ezra is the author of Ezra-Nehemiah as well as the Book of Chronicles, but modern scholars generally accept that a compiler from the 5th century BCE is the final author of these books. The chapter contains the list of signatories to the people's pledge and the later part deals with intermarriage with the non-Jews among the “people of the land” punctuated with the pledge to separate from “foreigners”.

Nehemiah 11 is the eleventh chapter of the Book of Nehemiah in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible, or the 21st chapter of the book of Ezra-Nehemiah in the Hebrew Bible, which treats the book of Ezra and the book of Nehemiah as one book. Jewish tradition states that Ezra is the author of Ezra-Nehemiah as well as the Book of Chronicles, but modern scholars generally accept that a compiler from the 5th century BCE is the final author of these books. The chapter describes the repopulation of Jerusalem. Judahites (4-6), Benjamites (7-9), priests (10-14), Levites (15-18), gatekeepers (19) and "the rest of Israel" (20-21). Roles in relation to leadership, maintenance and prayer in the Temple are allocated. The people cast lots and 1 of 10 are to volunteer to live in the city whilst the remainder repopulate the surrounding areas.

Nehemiah 13 is the thirteenth chapter of the Book of Nehemiah in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible, or the 23rd chapter of the book of Ezra-Nehemiah in the Hebrew Bible, which treats the book of Ezra and the book of Nehemiah as one book. Jewish tradition states that Ezra is the author of Ezra-Nehemiah as well as the Book of Chronicles, but modern scholars generally accept that a compiler from the 5th century BCE is the final author of these books. This chapter addresses a series of problems handled by Nehemiah himself, which had arisen during his temporary absence from the land, with some similar issues to those related in Ezra 9–10 and Nehemiah 10.





















