
Wardriving is the act of searching for Wi-Fi wireless networks as well as cell towers, usually from a moving vehicle, using a laptop or smartphone. Software for wardriving is freely available on the internet.
IEEE 802.1X is an IEEE Standard for port-based network access control (PNAC). It is part of the IEEE 802.1 group of networking protocols. It provides an authentication mechanism to devices wishing to attach to a LAN or WLAN.

In computing, netstat is a command-line network utility that displays network connections for Transmission Control Protocol, routing tables, and a number of network interface and network protocol statistics. It is available on Unix, Plan 9, Inferno, and Unix-like operating systems including macOS, Linux, Solaris and BSD. It is also available on IBM OS/2 and on Microsoft Windows NT-based operating systems including Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8 and Windows 10.

ifconfig is a system administration utility in Unix-like operating systems for network interface configuration.

iStumbler is a utility for finding wireless networks and devices with AirPort or Bluetooth-enabled Macintosh computers.

Kismet is a network detector, packet sniffer, and intrusion detection system for 802.11 wireless LANs. Kismet will work with any wireless card which supports raw monitoring mode, and can sniff 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g, and 802.11n traffic. The program runs under Linux, FreeBSD, NetBSD, OpenBSD, and macOS. The client can also run on Microsoft Windows, although, aside from external drones, there's only one supported wireless hardware available as packet source.

KisMAC is a wireless network discovery tool for Mac OS X. It has a wide range of features, similar to those of Kismet. The program is geared toward network security professionals, and is not as novice-friendly as similar applications. Distributed under the GNU General Public License, KisMAC is free software.
In the field of computer network administration, pcap is an application programming interface (API) for capturing network traffic. While the name is an abbreviation of packet capture, that is not the API's proper name. Unix-like systems implement pcap in the libpcap library; for Windows, there is a port of libpcap named WinPcap that is no longer supported or developed, and a port named Npcap for Windows 7 and later that is still supported.

Wireless security is the prevention of unauthorized access or damage to computers or data using wireless networks, which include Wi-Fi networks. The term may also refer to the protection of the wireless network itself from adversaries seeking to damage the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of the network. The most common type is Wi-Fi security, which includes Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) and Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA). WEP is an old IEEE 802.11 standard from 1997. It is a notoriously weak security standard: the password it uses can often be cracked in a few minutes with a basic laptop computer and widely available software tools. WEP was superseded in 2003 by WPA, a quick alternative at the time to improve security over WEP. The current standard is WPA2; some hardware cannot support WPA2 without firmware upgrade or replacement. WPA2 uses an encryption device that encrypts the network with a 256-bit key; the longer key length improves security over WEP. Enterprises often enforce security using a certificate-based system to authenticate the connecting device, following the standard 802.11X.
Monitor mode, or RFMON mode, allows a computer with a wireless network interface controller (WNIC) to monitor all traffic received on a wireless channel. Unlike promiscuous mode, which is also used for packet sniffing, monitor mode allows packets to be captured without having to associate with an access point or ad hoc network first. Monitor mode only applies to wireless networks, while promiscuous mode can be used on both wired and wireless networks. Monitor mode is one of the eight modes that 802.11 wireless adapter can operate in: Master, Managed, Ad hoc, Repeater, Mesh, Wi-Fi Direct, TDLS and Monitor mode.
The Metasploit Project is a computer security project that provides information about security vulnerabilities and aids in penetration testing and IDS signature development. It is owned by Boston, Massachusetts-based security company, Rapid7.
Cisco NAC Appliance, formerly Cisco Clean Access (CCA), was a network admission control (NAC) system developed by Cisco Systems designed to produce a secure and clean computer network environment. Originally developed by Perfigo and marketed under the name of Perfigo SmartEnforcer, this network admission control device analyzes systems attempting to access the network and prevents vulnerable computers from joining the network. The system usually installs an application known as the Clean Access Agent on computers that will be connected to the network. This application, in conjunction with both a Clean Access server and a Clean Access Manager, has become common in many universities and corporate environments today. It is capable of managing wired or wireless networks in an in-band or out-of-band configuration mode, and Virtual Private networks (VPN) in an in-band only configuration mode.
A wireless site survey, sometimes called an RF site survey or wireless survey, is the process of planning and designing a wireless network, to provide a wireless solution that will deliver the required wireless coverage, data rates, network capacity, roaming capability and quality of service (QoS). The survey usually involves a site visit to test for RF interference, and to identify optimum installation locations for access points. This requires analysis of building floor plans, inspection of the facility, and use of site survey tools. Interviews with IT management and the end users of the wireless network are also important to determine the design parameters for the wireless network.

Aircrack-ng is a network software suite consisting of a detector, packet sniffer, WEP and WPA/WPA2-PSK cracker and analysis tool for 802.11 wireless LANs. It works with any wireless network interface controller whose driver supports raw monitoring mode and can sniff 802.11a, 802.11b and 802.11g traffic. Packages are released for Linux and Windows.
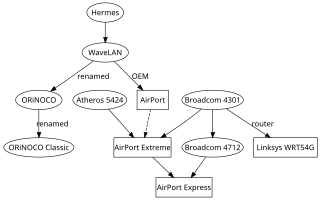
WaveLAN was a brand name for a family of wireless networking technology sold by NCR, AT&T, Lucent Technologies, and Agere Systems as well as being sold by other companies under OEM agreements. The WaveLAN name debuted on the market in 1990 and was in use until 2000, when Agere Systems renamed their products to ORiNOCO. WaveLAN laid the important foundation for the formation of IEEE 802.11 working group and the resultant creation of Wi-Fi.
Operating system Wi-Fi support is defined as the facilities an operating system may include for Wi-Fi networking. It usually consists of two pieces of software: device drivers, and applications for configuration and management.
Network detectors or network discovery software are computer programs that facilitate detection of wireless LANs using the 802.11b, 802.11a and 802.11g WLAN standards. Discovering networks may be done through active as well as passive scanning.
WiFi-Where was a tool that facilitated Wardriving and detection of wireless LANs using the 802.11b, 802.11a and 802.11g WLAN standards. Versions existed for the operating systems iOS and Palm OS. Originally created in June 2004 for the Palm OS by Jonathan Hays of Hazelware Software, the IP for WiFi-Where was licensed to 3Jacks Software in 2009. An iPhone version of the application was released in January 2010, but was pulled from the App Store by Apple in March 2010. The app was frequently listed as a common tool to facilitate Wardriving As of 2010, it is still available in the Jailbroken Cydia store.
NetSpot is a software tool for wireless network assessment, scanning, and surveys, analyzing Wi-Fi coverage and performance. It runs on Mac OS X 10.6+ and Windows 7, 8, 10, and 11. Netspot supports 802.11n, 802.11a, 802.11b, and 802.11g wireless networks and uses the standard Wi-Fi network adapter and its Airport interface to map radio signal strength and other wireless network parameters, and build reports on that. NetSpot was released in August 2011.

WiFi Explorer is a wireless network scanner tool for macOS that can help users identify channel conflicts, overlapping and network configuration issues that may be affecting the connectivity and performance of Wi-Fi networks.










