Related Research Articles
Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) is the standard for the communication and management of medical imaging information and related data. DICOM is most commonly used for storing and transmitting medical images enabling the integration of medical imaging devices such as scanners, servers, workstations, printers, network hardware, and picture archiving and communication systems (PACS) from multiple manufacturers. It has been widely adopted by hospitals and is making inroads into smaller applications such as dentists' and doctors' offices.
An open file format is a file format for storing digital data, defined by a openly published specification usually maintained by a standards organization, and which can be used and implemented by anyone. Open file format is licensed with open license. For example, an open format can be implemented by both proprietary and free and open-source software, using the typical software licenses used by each. In contrast to open file formats, closed file formats are considered trade secrets. However, the actual image used by an open file format may still be copyrighted or trademarked.
NIF or Nif may refer to:
A digital video recorder (DVR) is an electronic device that records video in a digital format to a disk drive, USB flash drive, SD memory card, SSD or other local or networked mass storage device. The term includes set-top boxes with direct to disk recording, portable media players and TV gateways with recording capability, and digital camcorders. Personal computers are often connected to video capture devices and used as DVRs; in such cases the application software used to record video is an integral part of the DVR. Many DVRs are classified as consumer electronic devices; such devices may alternatively be referred to as personal video recorders (PVRs), particularly in Canada. Similar small devices with built-in displays and SSD support may be used for professional film or video production, as these recorders often do not have the limitations that built-in recorders in cameras have, offering wider codec support, the removal of recording time limitations and higher bitrates.

Health informatics is the field of science and engineering that aims at developing methods and technologies for the acquisition, processing, and study of patient data, which can come from different sources and modalities, such as electronic health records, diagnostic test results, medical scans. The health domain provides an extremely wide variety of problems that can be tackled using computational techniques.
Analyze is a software package developed by the Biomedical Imaging Resource (BIR) at Mayo Clinic for multi-dimensional display, processing, and measurement of multi-modality biomedical images. It is a commercial program and is used for medical tomographic scans from magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography and positron emission tomography.
A digital image is an image composed of picture elements, also known as pixels, each with finite, discrete quantities of numeric representation for its intensity or gray level that is an output from its two-dimensional functions fed as input by its spatial coordinates denoted with x, y on the x-axis and y-axis, respectively. Depending on whether the image resolution is fixed, it may be of vector or raster type. By itself, the term "digital image" usually refers to raster images or bitmapped images.
Image markup is markup language that attaches annotations to image files. It is a critical technology for many researchers and practitioners, especially in the field of medicine.
Neuroinformatics is the field that combines informatics and neuroscience. Neuroinformatics is related with neuroscience data and information processing by artificial neural networks. There are three main directions where neuroinformatics has to be applied:
Cambridge Brain Analysis (CamBA), is a software repository developed at the Brain Mapping Unit, Department of Psychiatry, University of Cambridge, UK and contains software pipelines for functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) analysis. It is designed for batch processing and its main graphical user interface offers a spreadsheet-like look-and-feel.
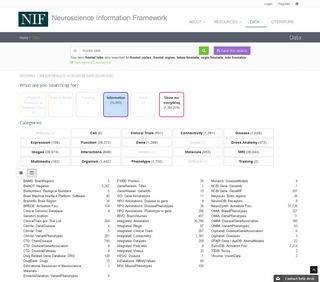
The Neuroscience Information Framework is a repository of global neuroscience web resources, including experimental, clinical, and translational neuroscience databases, knowledge bases, atlases, and genetic/genomic resources and provides many authoritative links throughout the neuroscience portal of Wikipedia.
National Innovation Foundation (NIF) – India is an autonomous body of the Department of Science and Technology (DST), Government of India. It was set up in February 2000 at Ahmedabad, Gujarat and is India's national initiative to strengthen the grassroots technological innovations and outstanding traditional knowledge. Its mission is to help India become a creative and knowledge-based society by expanding policy and institutional space for grassroots technological innovators.

Mango is a non-commercial software for viewing, editing and analyzing volumetric medical images. Mango is written in Java, and distributed freely in precompiled versions for Linux, Mac OS and Microsoft Windows. It supports NIfTI, ANALYZE, NEMA and DICOM formats and is able to load and save 2D, 3D and 4D images.

The LONI Pipeline is a free distributed system for designing, executing, monitoring and sharing scientific workflows on grid computing architectures. Pipeline allows users to connect and run any number of different software tools, and conveniently visualize and download the results.

Museum informatics is an interdisciplinary field of study that refers to the theory and application of informatics by museums. It represents a convergence of culture, digital technology, and information science. In the context of the digital age facilitating growing commonalities across museums, libraries and archives, its place in academe has grown substantially and also has connections with digital humanities.
The National Database for Autism Research (NDAR) is a secure research data repository promoting scientific data sharing and collaboration among autism spectrum disorder (ASD) investigators. The project was launched in 2006 as a joint effort between five institutes and centers at the National Institutes of Health (NIH): the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD), the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS), the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS), and the Center for Information Technology (CIT). The goal of NDAR is to provide a shared common platform for data collection, retrieval, and archiving to accelerate the advancement of research on autism spectrum disorders. The largest repository of its kind, NDAR makes available data at all levels of biological and behavioral organization for all data types. As of November 2013, data from over 90,000 research participants are available to qualified investigators through the NDAR portal. Summary information about the available data is accessible through the NDAR public website.

The Neuroimaging Tools and Resources Collaboratory is a neuroimaging informatics knowledge environment for MR, PET/SPECT, CT, EEG/MEG, optical imaging, clinical neuroinformatics, imaging genomics, and computational neuroscience tools and resources.

Ron Kikinis is an American physician and scientist best known for his research in the fields of imaging informatics, image guided surgery, and medical image computing. He is a professor of radiology at Harvard Medical School. Kikinis is the founding director of the Surgical Planning Laboratory in the Department of Radiology at Brigham and Women's Hospital, in Boston, Massachusetts. He is the Vice-Chair for Biomedical Informatics Research in the Department of Radiology.
References
- ↑ dfwg. "NIfTI: — Neuroimaging Informatics Technology Initiative". nifti.nimh.nih.gov. Retrieved 2019-08-03.