Related Research Articles

Captain William Hobson was a British Royal Navy officer who served as the first Governor of New Zealand. He was a co-author of the Treaty of Waitangi.

The Flagstaff War, also known as Heke's War, Hōne Heke's Rebellion and the Northern War, was fought between 11 March 1845 and 11 January 1846 in and around the Bay of Islands, New Zealand. The conflict is best remembered for the actions of Hōne Heke who challenged the authority of the British by cutting down the flagstaff on Flagstaff Hill at Kororāreka. The flagstaff had been a gift from Hōne Heke to James Busby, the first British Resident. The Northern War involved many major actions, including the Battle of Kororāreka on 11 March 1845, the Battle of Puketutu on 8 May 1845, the Battle of Ōhaeawai on 23 June 1845 and the siege of Ruapekapeka Pā from 27 December 1845 to 11 January 1846.

Tāmati Wāka Nene was a Māori rangatira (chief) of the Ngāpuhi iwi (tribe) who fought as an ally of the British in the Flagstaff War of 1845–46.
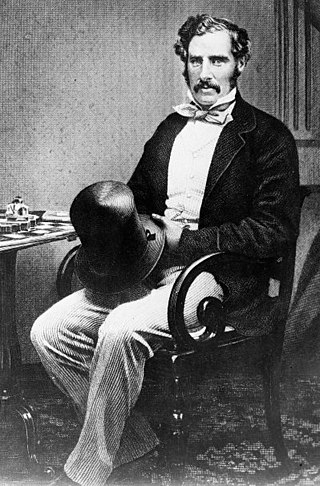
Sir George Grey, KCB was a British soldier, explorer, colonial administrator and writer. He served in a succession of governing positions: Governor of South Australia, twice Governor of New Zealand, Governor of Cape Colony, and the 11th premier of New Zealand. He played a key role in the colonisation of New Zealand, and both the purchase and annexation of Māori land.

The New Zealand Company, chartered in the United Kingdom, was a company that existed in the first half of the 19th century on a business model that was focused on the systematic colonisation of New Zealand. The company was formed to carry out the principles devised by Edward Gibbon Wakefield, who envisaged the creation of a new-model English society in the Southern Hemisphere. Under Wakefield's model, the colony would attract capitalists, who would then have a ready supply of labour: migrant labourers who could not initially afford to be property owners but would have the expectation of one-day buying land with their savings.

Hōne Wiremu Heke Pōkai, born Heke Pōkai and later often referred to as Hōne Heke, was a highly influential Māori rangatira (chief) of the Ngāpuhi iwi (tribe) and a war leader in northern New Zealand; he was affiliated with the Ngati Rahiri, Ngai Tawake, Ngati Tautahi, Te Matarahurahu and Te Uri-o-Hua hapū (subtribes) of Ngāpuhi. Hōne Heke fought with Hongi Hika, an earlier war leader of the Ngāpuhi, in the Musket Wars. Hōne Heke is considered the principal instigator of the Flagstaff War in 1845–46.

ASB Bank Limited, commonly stylised as ASB, is a bank owned by Commonwealth Bank of Australia, operating in New Zealand. It provides a range of financial services including retail, business and rural banking, funds management, as well as insurance through its Sovereign Limited subsidiary, and investment and securities services through its ASB Group Investments and ASB Securities divisions. ASB also operated BankDirect, a branchless banking service that provides service via phone, Internet, EFTPOS and ATMs only.

Bank of New Zealand (BNZ) is one of New Zealand's big four banks and has been operating in the country since the first office was opened in Auckland in October 1861 followed shortly after by the first branch in Dunedin in December 1861. The bank operates a variety of financial services covering retail, business and institutional banking and employs over 5,000 people in New Zealand. In 1992 the bank was purchased by the National Australia Bank and has since then operated as a subsidiary, but it retains local governance with a New Zealand board of directors.

The pound was the currency of New Zealand from 1840 until 1967, when it was replaced by the New Zealand dollar. Like the pound sterling, it was subdivided into 20 shillings each of 12 pence.

Henry Williams was the leader of the Church Missionary Society (CMS) mission in New Zealand in the first half of the 19th century.

Te Waimate Mission was the fourth mission station established in New Zealand and the first settlement inland from the Bay of Islands. The members of the Church Missionary Society (CMS) appointed to establish Te (the) Waimate Mission at Waimate North were the Rev. William Yate and lay members Richard Davis, George Clarke and James Hamlin.

Auckland Anniversary Day is a public holiday observed in the northern half of the North Island of New Zealand, being the area's provincial anniversary day. It is observed throughout the historic Auckland Province, even though the provinces of New Zealand were abolished in 1876. The modern area of observation consists of all of the Northland, Auckland, Waikato, Bay of Plenty and Gisborne regions, as well as some parts of the Manawatū-Whanganui and Hawke's Bay regions north of the 39th parallel. The holiday falls on the Monday closest to 29 January, the anniversary of the arrival of William Hobson, later the first Governor of New Zealand, in the country in 1840.

Westpac Banking Corporation, known simply as Westpac, is an Australian multinational banking and financial services company headquartered at Westpac Place in Sydney, New South Wales.

William Williams was consecrated as the first Anglican Bishop of Waiapu, New Zealand, on 3 April 1859 by the General Synod at Wellington. His son, Leonard Williams became the third Bishop of Waiapu and his grandson, Herbert Williams, the sixth. His brother, the Rev. Henry Williams, led the Church Missionary Society (CMS) mission in New Zealand. William Williams led the CMS missionaries in translating the Bible into Māori and published an early dictionary and grammar of the Māori language.
Wellington has been the capital of New Zealand since 1865. New Zealand's first capital city was Old Russell (Okiato) in 1840–41. Auckland was the second capital from 1841 until 1865, when Parliament was permanently moved to Wellington after an argument that persisted for a decade. As the members of parliament could not agree on the location of a more central capital, Wellington was decided on by three Australian commissioners.

The Battle of Kororāreka, or the Burning of Kororāreka, on 11 March 1845, was an engagement of the Flagstaff War in New Zealand. Following the establishment of British control of the islands, war broke out with a small group of the native population which resulted in the fall of the town of Kororāreka, present day Russell, to Māori warriors.

Edward Marsh Williams was a missionary, interpreter, and judge who played a significant role in the British colonisation of New Zealand. He was born in Hampstead, Middlesex, the eldest son of Archdeacon Henry Williams and Marianne Williams.
The New Zealand Church Missionary Society (NZCMS) is a mission society working within the Anglican Communion and Protestant, Evangelical Anglicanism. The parent organisation was founded in England in 1799. The Church Missionary Society (CMS) sent missionaries to settle in New Zealand. The Rev. Samuel Marsden, the Society's Agent and the Senior Chaplain to the New South Wales government, officiated at its first service on Christmas Day in 1814, at Oihi Bay in the Bay of Islands, New Zealand.

The New Zealand Company was a 19th-century English company that played a key role in the colonisation of New Zealand. The company was formed to carry out the principles of systematic colonisation devised by Edward Gibbon Wakefield, who envisaged the creation of a new-model English society in the southern hemisphere. Under Wakefield's model, the colony would attract capitalists who would then have a ready supply of labour—migrant labourers who could not initially afford to be property owners, but who would have the expectation of one day buying land with their savings.

Bank of Auckland was an Auckland, New Zealand note-issuing bank which took up deposits, made loans and was entitled to deal in precious metals but was not permitted to purchase real estate except to carry on its proper business. Its business focus was on Auckland Province.
References
- ↑ "Story - Stock market - New Zealand Banking Company". New Zealand Gazette and Wellington Spectator. 2 May 1840.
- ↑ Carleton, Hugh (1874). "Vol. II". The Life of Henry Williams. Early New Zealand Books (ENZB), University of Auckland Library. p. 48.
- ↑ "NEW ZEALAND Banking Company - Bank of New Zealand Archives". The community archive. Retrieved 5 May 2013.
- ↑ "Bank of New Zealand the twenty-first anniversary". New Zealand Herald. 14 October 1882. p. 5.
- ↑ "Auckland Savings Bank opens for business". Ministry for Culture and Heritage. 20 January 2021.
- ↑ "Auckland's 175th anniversary: Fall on steps can't stop rise of city". NZ Herald. 13 June 2015. Retrieved 25 April 2023.