The constructive vote of no confidence is a variation on the motion of no confidence that allows a parliament to withdraw confidence from a head of government only if there is a positive majority for a prospective successor. The principle is intended to ensure governments' stability by making sure that a replacement has enough parliamentary support to govern.

From 1989 through 1991, Poland engaged in a democratic transition which put an end to the Polish People's Republic and led to the foundation of a democratic government, known as the Third Polish Republic, following the First and Second Polish Republic. After ten years of democratic consolidation, Poland joined NATO in 1999 and the European Union on 1 May 2004.
A snap election is an election that is called earlier than the one that has been scheduled.

General elections were held in India in four phases between 20 April and 10 May 2004. Over 670 million people were eligible to vote, electing 543 members of the 14th Lok Sabha. Seven states also held assembly elections to elect state governments. They were the first elections fully carried out with electronic voting machines.
Dissolution of a legislative assembly is the simultaneous termination of service of all of its members, in anticipation that a successive legislative assembly will reconvene later with possibly different members. In a democracy, the new assembly is chosen by a general election. Dissolution is distinct on the one hand from abolition of the assembly, and on the other hand from its adjournment or prorogation, or the ending of a legislative session, any of which begins a period of inactivity after which it is anticipated that the same members will reassemble. For example, the "second session of the fifth parliament" could be followed by the "third session of the fifth parliament" after a prorogation, but would be followed by the "first session of the sixth parliament" after a dissolution.

The National Assembly of Pakistan is the lower house of the bicameral Parliament of Pakistan, with the upper house being the Senate. As of 2023, the National Assembly has a maximum membership of 336, of which 266 are directly elected by an adult universal suffrage and a first-past-the-post system to represent their respective constituencies, while 70 are elected on reserved seats for women and religious minorities from all over the country. Members hold their seats for five years or until the house is dissolved by the President on the advice of the Prime Minister. The house convenes at the Parliament House, Red Zone, Islamabad.

The Parliament of Egypt is the bicameral legislature of the Arab Republic of Egypt. It is composed of an upper house and a lower house.
The politics of Kosovo takes place in a framework of a multi-party parliamentary representative democratic republic, whereby the President (Presidenti) is the head of state and the Prime Minister (Kryeministri) the head of government. Parliamentary elections are held every four years, the most recent in 2021.

The Politics of Serbia are defined by a unitary parliamentary framework that is defined by the Constitution of Serbia in which the president, currently Aleksandar Vučić, is the head of state while the prime minister, currently Ana Brnabić, is the head of government. Executive power is exercised by the Serbian government and the President of Serbia. Legislative power is vested in the unicameral National Assembly which is composed of 250 proportionally elected deputies. The judiciary is independent and is headed by the Supreme Court of Cassation, which is also the highest court in Serbia.

Parliamentary elections were held in Serbia on 21 January 2007 to elect members of the National Assembly. The first session of the new National Assembly of the Republic of Serbia was held on 14 February 2007. The elections enabled the coalition of DS; DSS & G17+ to continue.

Parliamentary elections were held in Serbia on 11 May 2008 to elect members of the National Assembly. The election was held barely a year after the previous parliamentary election. There were 6,749,886 eligible electors who were able to vote in 8,682 voting places, as well as 157 special voting stations for refugees from Kosovo.

Parliamentary elections were held in Kosovo on 12 December 2010, following a vote of no-confidence in the government that brought forward the election. Those were the first elections after the country declared independence.

Parliamentary elections were held in Kosovo on 6 October 2019. The main opposition parties received the most votes, led by Vetëvendosje and the Democratic League of Kosovo (LDK). Vetëvendosje leader Albin Kurti became Prime Minister, forming a governing coalition with the LDK on an anti-corruption platform. He is the second Prime Minister not to have been a fighter of the Kosovo Liberation Army during the 1990s.

Parliamentary elections to both the Senate and the Sejm were held in Poland on 9 October 2011. The previous election, in 2007, resulted in a Civic Platform–Polish People's Party government. All seats of both Houses were up for re-election.

The 2015 Portuguese legislative election was held on 4 October. All 230 seats of the Assembly of the Republic were in contention.
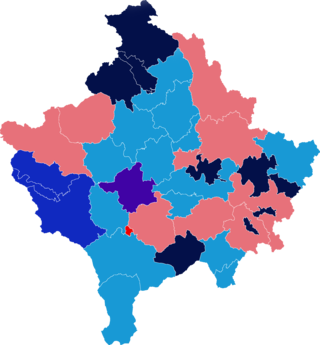
Parliamentary elections were held in Kosovo on 8 June 2014, after incumbent Prime Minister Hashim Thaçi announced his intention to hold elections.

The 2019 Portuguese legislative election was held on 6 October 2019. All 230 seats to the Assembly of the Republic were contested.

Parliamentary elections were held in Croatia on 11 September 2016, with all 151 seats in the Croatian Parliament up for election. The elections were preceded by a successful motion of no confidence against Prime Minister Tihomir Orešković and his cabinet on 16 June 2016, with 125 MPs voting in favour of the proposal. A subsequent attempt by the Patriotic Coalition to form a new parliamentary majority, with Minister of Finance Zdravko Marić as Prime Minister, failed and the Parliament voted to dissolve itself on 20 June 2016. The dissolution took effect on 15 July 2016, which made it possible for President Kolinda Grabar-Kitarović to officially call for elections on 11 September 2016. These were the ninth parliamentary elections since the 1990 multi-party elections.

Parliamentary elections were held in Kosovo on 14 February 2021. The results were a landslide victory for Vetëvendosje led by Albin Kurti and its coalition partner, Vjosa Osmani, former speaker of the parliament of Kosovo. The alliance won more than 50% of the total votes, the highest share since the first elections held in 2001, while their nearest rivals, the Democratic Party, finished in second place, trailing by more than 33%.

The Next Portuguese legislative election will take place on or before 8 October 2028 to elect members of the Assembly of the Republic to the 17h Legislature of Portugal. All 230 seats to the Assembly of the Republic will be at stake.














