Related Research Articles
Minoxidil is a medication used for the treatment of high blood pressure and pattern hair loss. It is an antihypertensive and a vasodilator. It is available as a generic medication by prescription in oral tablet form and over the counter as a topical liquid or foam.

Dantrolene sodium, sold under the brand name Dantrium among others, is a postsynaptic muscle relaxant that lessens excitation-contraction coupling in muscle cells. It achieves this by inhibiting Ca2+ ions release from sarcoplasmic reticulum stores by antagonizing ryanodine receptors. It is the primary drug used for the treatment and prevention of malignant hyperthermia, a rare, life-threatening disorder triggered by general anesthesia or drugs. It is also used in the management of neuroleptic malignant syndrome, muscle spasticity (e.g. after strokes, in paraplegia, cerebral palsy, or patients with multiple sclerosis), and poisoning by 2,4-dinitrophenol or by the related compounds dinoseb and dinoterb.

2,4-Dinitrophenol (2,4-DNP or simply DNP) is an organic compound with the formula HOC6H3(NO2)2. It has been used in explosives manufacturing and as a pesticide and herbicide.
Anti-obesity medication or weight loss medications are pharmacological agents that reduce or control excess body fat. These medications alter one of the fundamental processes of the human body, weight regulation, by: reducing appetite and consequently energy intake, increasing energy expenditure, redirecting nutrients from adipose to lean tissue, or interfering with the absorption of calories.
Thermogenic means tending to produce heat, and the term is commonly applied to drugs which increase heat through metabolic stimulation, or to microorganisms which create heat within organic waste. Approximately all enzymatic reaction in the human body is thermogenic, which gives rise to the basal metabolic rate.

A nucleophilic aromatic substitution (SNAr) is a substitution reaction in organic chemistry in which the nucleophile displaces a good leaving group, such as a halide, on an aromatic ring. Aromatic rings are usually nucleophilic, but some aromatic compounds do undergo nucleophilic substitution. Just as normally nucleophilic alkenes can be made to undergo conjugate substitution if they carry electron-withdrawing substituents, so normally nucleophilic aromatic rings also become electrophilic if they have the right substituents.

Daniel Duchaine was an American bodybuilder. Nicknamed the steroid guru, Duchaine gained worldwide notoriety due to his outspoken opinions on the use of performance-enhancing drugs, and made numerous television appearances discussing the subject on shows such as 20/20, Geraldo, and 60 Minutes. Steroid Nation author and ESPN writer Shaun Assael calls Duchaine "a founding father of the steroid movement." Duchaine was a low-carbohydrate diet advocate and promoted his own diet, the "Bodyopus diet".

Tesofensine (NS2330) is a serotonin–noradrenaline–dopamine reuptake inhibitor from the phenyltropane family of drugs, which is being developed for the treatment of obesity. Tesofensine was originally developed by a Danish biotechnology company, NeuroSearch, who transferred the rights to Saniona in 2014.

1-Fluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene is a chemical that reacts with the N-terminal amino acid of polypeptides. This can be helpful for sequencing proteins.

Dinoseb is a common industry name for 6-sec-butyl-2,4-dinitrophenol, a herbicide in the dinitrophenol family. It is a crystalline orange solid which does not readily dissolve in water. Dinoseb is banned as an herbicide in the European Union (EU) and the United States because of its toxicity.
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, also known as GLP-1 analogs, GLP-1DAs or incretin mimetics, are a class of drugs that reduce blood sugar and energy intake by activating the GLP-1 receptor. They mimic the actions of the endogenous incretin hormone GLP-1 that is released by the gut after eating.
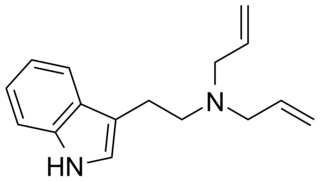
N,N-Diallyltryptamine (DALT) is a tryptamine derivative which has been identified as a new psychoactive substance. It has been used as an intermediate in the preparation of radiolabeled diethyltryptamine.
An uncoupler or uncoupling agent is a molecule that disrupts oxidative phosphorylation in prokaryotes and mitochondria or photophosphorylation in chloroplasts and cyanobacteria by dissociating the reactions of ATP synthesis from the electron transport chain. The result is that the cell or mitochondrion expends energy to generate a proton-motive force, but the proton-motive force is dissipated before the ATP synthase can recapture this energy and use it to make ATP. Because the intracellular supply of protons is replenished, uncouplers actually stimulate cellular metabolism. Uncouplers are capable of transporting protons through mitochondrial and lipid membranes.
A caloric deficit is any shortage in the number of calories consumed relative to the number of calories needed for maintenance of current body weight.
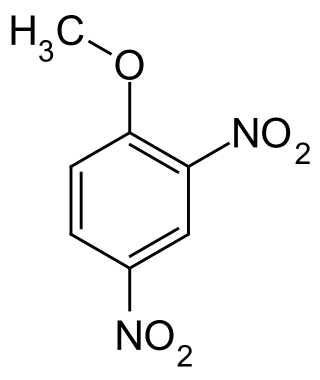
2,4-Dinitroanisole (DNAN) is a low sensitivity organic compound. It has an anisole (methoxybenzene) core, with two nitro groups (–NO2) attached.

Poisoning is the harmful effect which occurs when toxic substances are introduced into the body. The term "poisoning" is a derivative of poison, a term describing any chemical substance that may harm or kill a living organism upon ingestion. Poisoning can be brought on by swallowing, inhaling, injecting or absorbing toxins through the skin. Toxicology is the practice and study of symptoms, mechanisms, diagnoses, and treatments correlated to poisoning.
Maurice L. Tainter was a pharmacologist and professor at Stanford University. He helped pioneer the use of 2,4-dinitrophenol for weight loss, but the drug was later banned due to its safety profile. In 1943, he left Stanford for a job at Winthrop Company. In 1960, he began working for Sterling Drug.
Energy expenditure, often estimated as the total daily energy expenditure (TDEE), is the amount of energy burned by the human body.

TTFB (4,5,6,7-Tetrachloro-2-trifluoromethylbenzimidazole) is a halogenated benzimidazole derivative that acts as an uncoupling agent.

HU6 is a prodrug of the mitochondrial uncoupler 2,4-dinitrophenol (DNP) that is intended to "minimize the rapid absorption and high peak blood concentrations of DNP to provide a wider therapeutic index and improve safety." Developed by Rivus Pharmaceuticals, the drug is tested to reduce weight and liver fat in humans with risk factors for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis. In a phase 2a trial, the higher dosage levels reduced liver fat on average by more than 30 percent and also reduced body weight significantly. A phase 2b trial was launched in late 2023.
References
- ↑ Grundlingh, Johann; Dargan, Paul I.; El-Zanfaly, Marwa; Wood, David M. (1 September 2011). "2,4-Dinitrophenol (DNP): A Weight Loss Agent with Significant Acute Toxicity and Risk of Death". Journal of Medical Toxicology. 7 (3): 205–212. doi: 10.1007/s13181-011-0162-6 . ISSN 1937-6995. PMC 3550200 . PMID 21739343.
- ↑ "Dinitrophenol: Toxic Weight Loss: Food and Drug Administration". Journal of Pharmacy Technology. 3 (3): 109–112. May 1987. doi:10.1177/875512258700300306. ISSN 8755-1225.