Related Research Articles
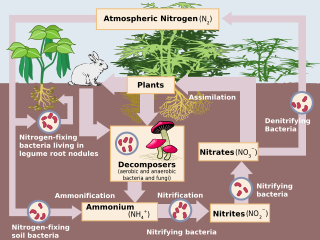
Nitrification is the biological oxidation of ammonia to nitrite followed by the oxidation of the nitrite to nitrate occurring through separate organisms or direct ammonia oxidation to nitrate in comammox bacteria. The transformation of ammonia to nitrite is usually the rate limiting step of nitrification. Nitrification is an important step in the nitrogen cycle in soil. Nitrification is an aerobic process performed by small groups of autotrophic bacteria and archaea.
The Thermomicrobia is a group of thermophilic green non-sulfur bacteria. Based on species Thermomicrobium roseum and Sphaerobacter thermophilus, this bacteria class has the following description:
Nitrosomonas europaea is a Gram-negative obligate chemolithoautotroph that can derive all its energy and reductant for growth from the oxidation of ammonia to nitrite and lives in several places such as soil, sewage, freshwater, the walls of buildings and on the surface of monuments especially in polluted areas where the air contains high levels of nitrogen compounds.

Nitrosomonas is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria, belonging to the Betaproteobacteria. It is one of the five genera of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and, as an obligate chemolithoautotroph, uses ammonia as an energy source and as a carbon source in presence of oxygen. Nitrosomonas are important in the global biogeochemical nitrogen cycle, since they increase the bioavailability of nitrogen to plants and in the denitrification, which is important for the release of nitrous oxide, a powerful greenhouse gas. This microbe is photophobic, and usually generate a biofilm matrix, or form clumps with other microbes, to avoid light. Nitrosomonas can be divided into six lineages: the first one includes the species Nitrosomonas europea, Nitrosomonas eutropha, Nitrosomonas halophila, and Nitrosomonas mobilis. The second lineage presents the species Nitrosomonas communis, N. sp. I and N. sp. II, meanwhile the third lineage includes only Nitrosomonas nitrosa. The fourth lineage includes the species Nitrosomonas ureae and Nitrosomonas oligotropha and the fifth and sixth lineages include the species Nitrosomonas marina, N. sp. III, Nitrosomonas estuarii and Nitrosomonas cryotolerans.
Nitrobacter is a genus comprising rod-shaped, gram-negative, and chemoautotrophic bacteria. The name Nitrobacter derives from the Latin neuter gender noun nitrum, nitri, alkalis; the Ancient Greek noun βακτηρία, βακτηρίᾱς, rod. They are non-motile and reproduce via budding or binary fission. Nitrobacter cells are obligate aerobes and have a doubling time of about 13 hours.

Methane monooxygenase (MMO) is an enzyme capable of oxidizing the C-H bond in methane as well as other alkanes. Methane monooxygenase belongs to the class of oxidoreductase enzymes.
Nitrifying bacteria are chemolithotrophic organisms that include species of the genera e.g. Nitrosomonas, Nitrosococcus, Nitrobacter, Nitrospina, Nitrospira and Nitrococcus. These bacteria get their energy by the oxidation of inorganic nitrogen compounds. Types include ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) and nitrite-oxidizing bacteria (NOB). Many species of nitrifying bacteria have complex internal membrane systems that are the location for key enzymes in nitrification: ammonia monooxygenase, hydroxylamine oxidoreductase, and nitrite oxidoreductase.
Paracoccus denitrificans, is a coccoid bacterium known for its nitrate reducing properties, its ability to replicate under conditions of hypergravity and for being a relative of the eukaryotic mitochondrion.

The Class Gammaproteobacteria belongs to the Proteobacteria phylum and contains about 250 genera, which makes it the most genera-rich taxa of the Prokaryotes. Several medically, ecologically, and scientifically important groups of bacteria belong to this class. It is composed by all Gram-negative microbes and is the most phylogenetically and physiologically diverse class of Proteobacteria.

Cupriavidus necator is a Gram-negative soil bacterium of the class Betaproteobacteria.
Hydroxylamine oxidoreductase (HAO) is an enzyme found in the prokaryote Nitrosomonas europaea. It plays a critically important role in the biogeochemical nitrogen cycle as part of the metabolism of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria.
Ammonia monooxygenase (EC 1.14.99.39, AMO) is an enzyme, which catalyses the following chemical reaction
Nitrospira moscoviensis was the second bacterium classified under the most diverse nitrite-oxidizing bacteria phylum, Nitrospirae. It is a gram-negative, non-motile, facultative lithoauthotropic bacterium that was discovered in Moscow, Russia in 1995. The genus name, Nitrospira, originates from the prefix “nitro” derived from nitrite, the microbe’s electron donor and “spira” meaning coil or spiral derived from the microbe’s shape. The species name, moscoviensis, is derived from Moscow, where the species was first discovered. N. moscoviensis could potentially be used in the production of bio-degradable polymers.
Nitrosomonas halophila is an ammonia-oxidizing, aerobe, Gram-negative bacterium from the genus of Nitrosomonas. Nitrosomonas halophila uses the enzyme Ammonia monooxygenase.
Nitrosomonas marina is an ammonia-oxidizing, aerobe, gram-negative bacterium from the genus of Nitrosomonas.
Nitrosomonas nitrosa is an ammonia-oxidizing, aerobe, gram-negative bacterium from the genus of Nitrosomonas.
Nitrosomonas oligotropha is an ammonia-oxidizing, aerobe, gram-negative bacterium from the genus of Nitrosomonas which occurs in chloraminated drinking water systems.
Nitrosomonas ureae is an ammonia-oxidizing, aerobe, gram-negative bacterium from the genus of Nitrosomonas.
Nitrosomonas halophila is an ammonia-oxidizing bacterium from the genus of Nitrosomonas.
Nitrosococcus is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria.
References
- ↑ Parte, A.C. "Nitrosomonas". LPSN . Retrieved 18 June 2016.
- ↑ "Nitrosomonas eutropha Taxon Passport - StrainInfo". www.straininfo.net. Retrieved 18 June 2016.
- ↑ Stein, LY; Arp, DJ; Berube, PM; Chain, PS; Hauser, L; Jetten, MS; Klotz, MG; Larimer, FW; Norton, JM; Op den Camp, HJ; Shin, M; Wei, X (December 2007). "Whole-genome analysis of the ammonia-oxidizing bacterium, Nitrosomonas eutropha C91: implications for niche adaptation". Environmental Microbiology. 9 (12): 2993–3007. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2007.01409.x. PMID 17991028.
- ↑ George M. Garrity: Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology. 2. Auflage. Springer, New York 2005, Vol. 2: The Proteobacteria Part C: The Alpha-, Beta-, Delta-, and Epsilonproteabacteria, ISBN 0-387-24145-0
- ↑ eol
- ↑ Scott, Julia (22 May 2014). "My No-Soap, No-Shampoo, Bacteria-Rich Hygiene Experiment". The New York Times. Retrieved 18 June 2016.
- ↑ "B 244". AdisInsight. Retrieved 12 June 2018.
- ↑ "Clinical data for April 23, 2018". BioWorld. Retrieved 2018-04-24.