
The Talent is a multiple unit railcar manufactured by Bombardier that was developed by Waggonfabrik Talbot in Aachen shortly before the company was acquired by Bombardier in 1995. The name Talent is an acronym in German for TALbot LEichter Nahverkehrs-Triebwagen.
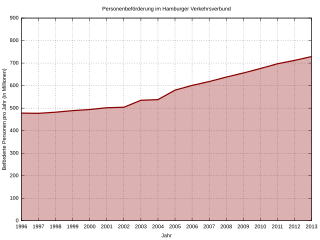
The Hamburger Verkehrsverbund (HVV) is a transport association coordinating public transport in and around Hamburg, Germany. Its main objectives are to provide a unified fare system, requiring only a single ticket for journeys with transfers between different operating companies, and to facilitate and speed up travel by harmonising the individual companies' schedules. At its inception in 1965, the HVV was the first organisation of its kind worldwide.

NSB Di 6, later designated ME 26 and DE 2700, is a class of twelve diesel-electric locomotives built by Siemens for the Norwegian State Railways (NSB). The prime mover provides a power output of 2,650 kilowatts (3,550 hp), a starting traction effort of 400 kilonewtons (90,000 lbf) and a maximum speed of 160 kilometres per hour (99 mph). They have a Co′Co′ wheel arrangement. The bidirectional locomotives were designed for use with both passenger and freight trains.
Transdev Germany is the largest private operator of passenger buses and trains in Germany. It is a subsidiary of Transdev.

The Nuremberg S-Bahn is an S-Bahn network covering the region of Nuremberg, Fürth and Erlangen which started operations in 1987 and is now integrated into the Greater Nuremberg Transport Association. The full length of the five current lines is about 277.6 kilometres.

The Voith Maxima locomotives are a family of diesel-hydraulic locomotives built by Voith Turbo Lokomotivtechnik GmbH & Co. KG., a subsidiary of Voith.

The DBAG Class 605, commonly known as the ICE TD is a high-speed diesel multiple unit (DMU) train, formerly in service with Deutsche Bahn and DSB.

The Eurorunner family of locomotives are a series of medium- to high-power diesel-electric locomotives built by Siemens for the European market. Introduced from 2002 onwards, they share design characteristics with the successful Eurosprinter range of electric locomotives, also built by Siemens.

DreiLänderBahn is the name under which HLB Hessenbahn, a subsidiary of the Hessian state railway company, Hessische Landesbahn, operates a group of regional rail services in the German states of Hesse, North Rhine-Westphalia and Rhineland-Palatinate.

The Main–Weser Railway is a railway line in central Germany that runs from Frankfurt am Main via Gießen to Kassel. it is named after the railway company that built the line and also operated it until 1880. It was opened between 1849 and 1852 and was one of the first railways in Germany.

The DBAG Class 474/874 is a three-car electric multiple unit train for the Hamburg S-Bahn. The class 474 were built to replace the nearly-60-year-old class 471 trains. Some units have a pantograph (474.3) to service the 2007 opened line to Stade on an overhead catenary track.
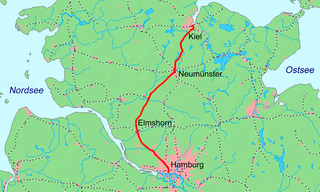
The Hamburg-Altona–Kiel railway is one of the most important main line railways of the states of Schleswig-Holstein and Hamburg in Northern Germany. The line runs through the region of Holstein and connects the cities of Hamburg, Elmshorn, Neumünster and Kiel. The 105 km (65 mi) long standard gauge double track electrified railway line is now owned by DB Netz.

The Husum–Kiel railway is a main line railway in the German state of Schleswig-Holstein. While the central section of the line, which is shared with the Neumünster–Flensburg line, has two tracks and is electrified, its western and eastern sections are single track and are not electrified. It connects the cities of Husum and Kiel via Rendsburg and serves as an important east-west rail axis between the North Sea and the Baltic Sea.

The Husum-Bad Sankt Peter-Ording railway is a 44 km-long, single-track non-electrified branch line in the German state of Schleswig-Holstein. The line connects the North Frisian town of Husum with all the important parts of the Eiderstedt peninsula, including Tönning, Garding and Sankt Peter-Ording. The line opened in 1854 and was one of the oldest railways in Germany.

Husum station is in Husum in the German state of Schleswig-Holstein. It was built in 1910 and is currently operated by Deutsche Bahn, which classifies it as a category 3 station. A less prestigious predecessor was located at the northern end of the station, another station is to the north of the current main station.

The Wilhelmshaven–Oldenburg railway is a predominantly double-track, electrified main line in the northwest in the German state of Lower Saxony. It runs to the south from the port city of Wilhelmshaven to Oldenburg.

The Vindobona is an international named passenger train which began service in 1957 between Berlin and Vienna via Dresden and Prague. In later years the route was extended to run from Hamburg via Berlin, Dresden, Prague, Brno and Vienna to Villach. It was named after the ancient settlement of Vindobona on the site of the modern city of Vienna. Labelled as a EuroCity train connection from 1993, services discontinued in 2014.

Heide (Holst) station is a junction station in the town of Heide in the district of Dithmarschen in the German state of Schleswig-Holstein. The Hamburg–Elmshorn–Heide–Westerland, the Neumünster–Heide and the Heide–Büsum lines cross here.

Itzehoe station is a railway station in the town of Itzehoe in the German state of Schleswig-Holstein. It is located on the Marsh Railway, which is electrified from Elmshorn up to this point. It is classified by Deutsche Bahn as a category 3 station.





















