Related Research Articles

The Nordic Council is the official body for formal inter-parliamentary Nordic cooperation among the Nordic countries. Formed in 1952, it has 87 representatives from Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden as well as from the autonomous areas of the Faroe Islands, Greenland, and Åland. The representatives are members of parliament in their respective countries or areas and are elected by those parliaments. The Council holds ordinary sessions each year in October/November and usually one extra session per year with a specific theme. The council's official languages are Danish, Finnish, Icelandic, Norwegian, and Swedish, though it uses only the mutually intelligible Scandinavian languages—Danish, Norwegian, and Swedish—as its working languages. These three comprise the first language of around 80% of the region's population and are learned as a second or foreign language by the remaining 20%.

The northern region of Europe has several definitions. A restrictive definition may describe Northern Europe as being roughly north of the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, which is about 54°N, or may be based on other geographical factors such as climate and ecology.

Established in 1918, Tallinn University of Technology is the only technical university in Estonia. TalTech, in the capital city of Tallinn, is a university for engineering, business, public administration and maritime affairs. TalTech has colleges in Tartu and Kohtla-Järve. Despite the similar names, Tallinn University and Tallinn University of Technology are separate institutions.

Mark Chasan is an American entrepreneur and lawyer known for founding eMusic, the first digital media streaming and distribution service, and Webcentral, one of the first cloud hosting companies. Chasan currently is the CEO of Transformative, an eco-social consulting firm, and AWE Global, a sustainable development company. Chasan has pioneered new financial models and process for liquidity and value creation utilizing a private-to-public strategy.
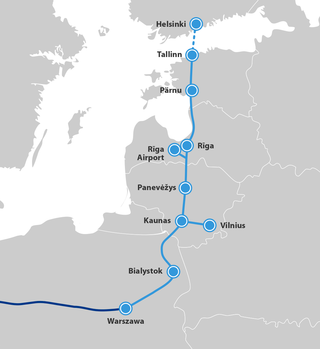
Rail Baltica is a greenfield rail transport infrastructure project with a goal to integrate the Baltic states in the European rail network. Its purpose is to provide passenger and freight service between participating countries and improve rail connections between Central and Northern Europe, specifically the area in the Southeast of the Baltic sea. Furthermore, it is intended to be a catalyst for building the economic corridor in Northeastern Europe. The project envisages a continuous rail link from Tallinn (Estonia) to Warsaw (Poland). It consists of links via Riga (Latvia), Kaunas and Vilnius (Lithuania) whose total length in the Baltic States is 870 kilometres (540 mi), with 213 kilometres (132 mi) in Estonia, 265 kilometres (165 mi) in Latvia, and 392 kilometres (244 mi) in Lithuania. Rail Baltica is one of the priority projects of the European Union. It is part of the North Sea–Baltic Corridor of the Trans-European Transport Networks (TEN-T).
All European countries show eGovernment initiatives, mainly related to the improvement of governance at the national level. Significant eGovernment activities also take place at the European Commission level as well. There is an extensive list of eGovernment Fact Sheets maintained by the European Commission.
Ken Rutkowski is founder, president and host of KenRadio Broadcasting which is syndicated on CBS Radio, He is also the founder of the media, entertainment and technology alliance known as METal. Rutkowski is the Local Partner of Founder Institute Chapter Los Angeles.

Nordic-Baltic Eight (NB8) is a regional co-operation format that includes Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Iceland, Latvia, Lithuania, Norway, and Sweden. Under NB8, regular meetings are held of the Baltic and Nordic countries' Prime Ministers, Speakers of Parliaments, Foreign Ministers, branch ministers, Secretaries of State and political directors of Foreign Ministries, as well as expert consultations where regional issues and current international topics are reviewed.
Civic technology, or civic tech, enhances the relationship between the people and government with software for communications, decision-making, service delivery, and political process. It includes information and communications technology supporting government with software built by community-led teams of volunteers, nonprofits, consultants, and private companies as well as embedded tech teams working within government.
e-Estonia refers to the digital society of Estonia, which facilitates its citizens' and residents' interactions with the state through the use of ICT solutions. Estonian e-services created under this initiative include e-Tax Board, e-Business, e-Banking, e-Ticket, e-School, University via the internet, the e-Governance Academy, i-Voting, as well as the release of several mobile applications. According to the goals set in Estonia's Digital Agenda 2030, the country aims to assure that high-speed internet is available across the country, the digital government services are the best in the world, and the country's cyberspace is reliable and safe by 2030.

Bolt is an Estonian mobility company that offers ride-hailing, micromobility rental, food and grocery delivery, and car-sharing services. The company is headquartered in Tallinn and operates in over 500 cities in more than 45 countries in Europe, Africa, Western Asia and Latin America. The company has more than 100 million customers globally and more than 3 million partners use Bolt's platforms to offer rides and deliveries to customers.

Tallinn Music Week (TMW) is an international new music showcase, city culture festival and networking event for music and creative industry professionals, held every spring in Tallinn, Estonia since 2009. Operated by Tallinn-based company Shiftworks OÜ, it showcases emerging artists from all over Europe and beyond, provides a networking platform for music and creative industry professionals, and introduces the city of Tallinn. The festival is attended by around 20,000 people and 1,000 music industry executives yearly. TMW has been acknowledged as an important industry event and attractive tourism destination by The Guardian,New York Times, Forbes, and Experty.by.
The once-only principle is an e-government concept that aims to ensure that citizens, institutions, and companies only have to provide certain standard information to the authorities and administrations once. By incorporating data protection regulations and the explicit consent of the users, the public administration is allowed to re-use and exchange the data with each other. The once-only principle is part of the European Union's (EU) plans to further develop the Digital Single Market by reducing the administrative burden on citizens and businesses.
X-Road is a centrally managed distributed Data Exchange Layer (DXL) between information systems. Organizations can exchange information over the Internet using X-Road to ensure confidentiality, integrity and interoperability between data exchange parties.
Sidewalk Toronto is a cancelled urban development project proposed by Sidewalk Labs at Quayside, a waterfront area in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. This project was first initiated by Waterfront Toronto in 2017 by issuing the request for proposal (RFP) on development of the Quayside area. Sidewalk Labs, which is a subsidiary of Google, won the bid in 2017. The Master Innovation Development Plan (MIDP) was created in 2019 through conversations with over 21,000 Torontonians and aimed to be an innovative reinvention of Toronto's neglected eastern downtown waterfront.
Code for Canada is a nonprofit organization (NPO) that was co-founded in 2017 by the government of the province of Ontario, Canada with a mandate to work with the technology and government sectors and innovators from the community, to improve digital technologies that underlie government services.
The regulation of artificial intelligence is the development of public sector policies and laws for promoting and regulating artificial intelligence (AI); it is therefore related to the broader regulation of algorithms. The regulatory and policy landscape for AI is an emerging issue in jurisdictions globally, including in the European Union and in supra-national bodies like the IEEE, OECD and others. Since 2016, a wave of AI ethics guidelines have been published in order to maintain social control over the technology. Regulation is considered necessary to both encourage AI and manage associated risks. In addition to regulation, AI-deploying organizations need to play a central role in creating and deploying trustworthy AI in line with the principles of trustworthy AI, and take accountability to mitigate the risks. Regulation of AI through mechanisms such as review boards can also be seen as social means to approach the AI control problem.
Cansu Canca is a moral and political philosopher, with a Ph.D. specializing in applied ethics, and founder and director of AI Ethics Lab. Formerly, she was a bioethicist at the University of Hong Kong, and an ethics researcher at Harvard Law School, Harvard School of Public Health, Harvard Medical School, National University of Singapore, Osaka University, and the World Health Organization.
e-Governance Academy is a non-profit foundation that assists public sector institutions worldwide in digital transformation. The organization was founded in 2002, by a joint initiative of the Government of Estonia, Open Society Institute (OSI), and the United Nations Development Program (UNDP).

Tiago Carneiro Peixoto is a Brazilian political scientist and Senior Governance Specialist at the World Bank, who promotes participatory democracy and digital government around the globe. Recognized as an expert in e-democracy and participatory democracy, he was nominated as one of the most innovative people in democracy, as well as one of the 100 most influential people in digital government.
References
- 1 2 ERR (2017-06-16). "Estonia, Finland establish nonprofit for developing X-Road". ERR. Retrieved 2023-03-19.
- ↑ NIIS 2017 Yearbook (PDF)
- ↑ ERR, BNS | (2019-02-28). "Iceland latest nation to adopt Estonia's X-Road platform". ERR. Retrieved 2023-03-19.
- ↑ Klatt, Karola (2020-09-10). "Estonia top of the (digital) class" . Retrieved 2023-03-19.
- ↑ "Nordic Institute for Interoperability Solutions". Nordic Institute for Interoperability Solutions (NIIS). Retrieved 2018-03-17.
- 1 2 Kristiansen Nordhaug, Liv Marte; Ngodup, Keyzom (26 Oct 2022). "Building resilience with digital public infrastructure". Observer Research Foundation . Retrieved 19 Mar 2023.
- ↑ Fourtané, Susan (2020-02-24). "e-Estonia: The World's Most Advanced Digital Society". interestingengineering.com. Retrieved 2023-03-19.
- ↑ Project, The Double Open (2022-07-14). "Nordic Institute For Interoperability Solutions (NIIS) Using Double Open". www.doubleopen.org. Retrieved 2023-03-19.
- 1 2 Orav, Maris (2022-11-16). "Greenergy Data Centers and NIIS are Laying the Foundations for a Sustainable Digital Future". e-Estonia. Retrieved 2023-03-19.
- ↑ Panel®, Expert. "Council Post: 15 Tips For Sharing Tech Plans With Non-Tech Team Members". Forbes. Retrieved 2023-03-19.
- ↑ Panel®, Expert. "Council Post: 12 Smart Steps For Building A Comprehensive And Effective IT Budget". Forbes. Retrieved 2023-03-19.