
Strychnine is a highly toxic, colorless, bitter, crystalline alkaloid used as a pesticide, particularly for killing small vertebrates such as birds and rodents. Strychnine, when inhaled, swallowed, or absorbed through the eyes or mouth, causes poisoning which results in muscular convulsions and eventually death through asphyxia. While it is no longer used medicinally, it was used historically in small doses to strengthen muscle contractions, such as a heart and bowel stimulant and performance-enhancing drug. The most common source is from the seeds of the Strychnos nux-vomica tree.

Strychnos nux-vomica, the strychnine tree, also known as nux vomica, poison fruit, semen strychnos, and quaker buttons, is a deciduous tree native to India and to southeast Asia. It is a medium-sized tree in the family Loganiaceae that grows in open habitats. Its leaves are ovate and 5–9 centimetres (2–3.5 in) in size. It is known for being the natural source of the extremely poisonous compound strychnine.

The Loganiaceae are a family of flowering plants classified in order Gentianales. The family includes up to 13 genera, distributed around the world's tropics. There are not any great morphological characteristics to distinguish these taxa from others in the order Gentianales.
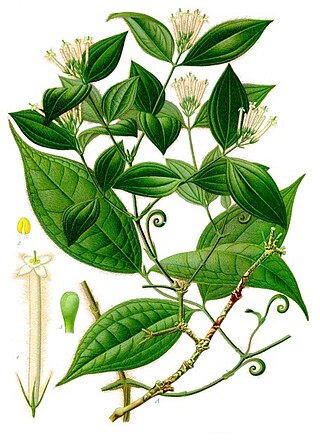
Strychnos is a genus of flowering plants, belonging to the family Loganiaceae. The genus includes about 100 accepted species of trees and lianas, and more than 200 that are as yet unresolved. The genus is widely distributed around the world's tropics and is noted for the presence of poisonous indole alkaloids in the roots, stems and leaves of various species. Among these alkaloids are the well-known and virulent poisons strychnine and curare.
Ocular hypertension is the presence of elevated fluid pressure inside the eye, usually with no optic nerve damage or visual field loss.

Strychnos spinosa, the Natal orange, is a tree indigenous to tropical and subtropical Africa. It produces sweet-sour, yellow fruits, containing numerous hard brown seeds. Greenish-white flowers grow in dense heads at the ends of branches. The fruits tend to appear only after good rains. It is related to the deadly Strychnos nux-vomica, which contains strychnine. The smooth, hard fruit are large and green, ripen to yellow colour. Inside the fruit are tightly packed seeds, which may be toxic, surrounded by a fleshy, brown, edible covering. Animals such as baboon, monkeys, bushpig, nyala and eland eat the fruit. The leaves are a popular food source for browsers such as duiker, kudu, impala, steenbok, nyala and elephant.

Strychnos pungens is a tree which belongs to the Loganiaceae. Usually about 5m tall, occurring in mixed woodland or in rocky places. Branches are short and rigid. Leaves are smooth, stiff, opposite, elliptic and with a sharp, spine-like tip. Occurring in South Africa on the Witwatersrand, Magaliesberg and further north to northern Namibia, northern Botswana and Zimbabwe.

Guanazodine is a hypotensive sympatholytic drug.

AL-34662 is an indazole derivative drug that is being developed for the treatment of glaucoma. It acts as a selective 5-HT2A receptor agonist, the same target as that of psychedelic drugs like psilocin, but unlike these drugs, AL-34662 was designed specifically as a peripherally selective drug, which does not cross the blood–brain barrier. This means that AL-34662 can exploit a useful side effect of the hallucinogenic 5-HT2A agonists, namely reduction in intra-ocular pressure and hence relief from the symptoms of glaucoma, but without causing the hallucinogenic effects that make centrally active 5-HT2A agonists unsuitable for clinical use. In animal studies, AL-34662 has been shown to be potent and effective in the treatment of symptoms of glaucoma, with minimal side effects.

Monatepil is a calcium channel blocker and α1-adrenergic receptor antagonist used as an antihypertensive.
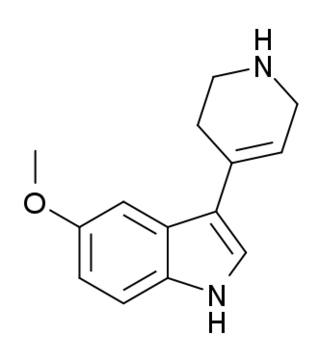
RU-24,969 is a drug and research chemical widely used in scientific studies. It is a selective agonist at the 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B receptors, with preference for the latter. As with other 5-HT1B agonists such as CP-94,253, RU-24,969 has been found to increase the reinforcing properties of cocaine, suggesting a role for 5-HT1B receptors in cocaine addiction.

AL-37350A (4,5-DHP-AMT) is a tryptamine derivative which acts as a potent and selective agonist for the serotonin receptor 5-HT2A, with a Ki of 2.0 nM, and moderate selectivity over the related 5-HT2B and 5-HT2C receptors. It has been shown to have ocular hypotensive activity in animal models, suggesting it may be useful for the treatment of glaucoma.

Strychnos potatorum also known as clearing-nut tree is a deciduous tree which has height up to 40 feet. The seeds of the tree are commonly used in traditional medicine as well as for purifying water in India and Myanmar.

Akuammicine is a monoterpene indole alkaloid of the Vinca sub-group. It is found in the Apocynaceae family of plants including Picralima nitida, Vinca minor and the Aspidosperma.

Chrysoeriol is a flavone, chemically the 3'-methoxy derivative of luteolin.

Pelanserin (TR2515) is an antagonist of the 5-HT2 and α1-adrenergic receptors.

CP-132,484 is a tryptamine derivative which acts as a potent and selective agonist for the 5-HT2 family of serotonin receptors. It has reasonable selectivity for 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C subtypes over 5-HT2B, but is only slightly selective for 5-HT2A over 5-HT2C. This compound and several related analogues have been shown to have ocular hypotensive activity in animal models, suggesting they may be useful for the treatment of glaucoma.

Stemmadenine is a terpene indole alkaloid. Stemmadenine is believed to be formed from preakuammicine by a carbon-carbon bond cleavage. Cleavage of a second carbon-carbon bond is thought to form dehydrosecodine. The enzymes forming stemmadenine and using it as a substrate remain unknown to date. It is thought to be intermediate compound in many different biosynthetic pathways such as in Aspidosperma species. Many alkaloids are proposed to be produced through intermediate stemmadenine. Some of them are:

Strychnos toxifera, called bush rope and devil doer, is a species of flowering plant in the genus Strychnos, native to Costa Rica, Panama, Colombia, Ecuador, Venezuela, the Guianas, Brazil, Peru and Bolivia. It is the principal source of calabash or gourd curare.

















