North | |
|---|---|
| Coordinates: Coordinates: 12°10′11″N15°38′01″W / 12.1696°N 15.6335°W | |
| Country | |
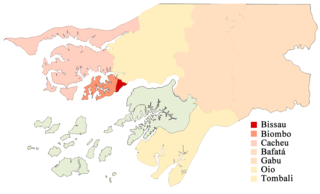
North is a province in Guinea-Bissau. It consists Biombo, Cacheu and Oio regions. [1] [2]
North | |
|---|---|
| Coordinates: Coordinates: 12°10′11″N15°38′01″W / 12.1696°N 15.6335°W | |
| Country | |
North is a province in Guinea-Bissau. It consists Biombo, Cacheu and Oio regions. [1] [2]

Guinea-Bissau, officially the Republic of Guinea-Bissau, is a country in West Africa that covers 36,125 square kilometres (13,948 sq mi) with an estimated population of 1,726,000. It borders Senegal to the north and Guinea to the south-east.

The economy of Guinea-Bissau comprises a mixture of state-owned and private companies. Guinea-Bissau is among the world's least developed nations and one of the 10 poorest countries in the world, and depends mainly on agriculture and fishing. Cashew crops have increased remarkably in recent years, and the country ranked ninth in cashew production for the year of 2019.

Bissau is the capital city of Guinea-Bissau. In 2015, Bissau had a population of 492,004. Bissau is located on the Geba River estuary, off the Atlantic Ocean, and is Guinea-Bissau's largest city, major port, and its administrative and military centre.

The Republic of Guinea-Bissau follows a nonaligned foreign policy and seeks friendly and cooperative relations with a wide variety of states and organizations. France, Portugal, Angola, Brazil, Egypt, Nigeria, Libya, Cuba, the Palestine Liberation Organization, Ghana, and Russia have diplomatic offices in Bissau.

Kumba Ialá Embaló, also spelled Yalá, was a Bissau-Guinean politician who was president from 17 February 2000 until he was deposed in a bloodless military coup on 14 September 2003. He belonged to the Balanta ethnic group and was President of the Social Renewal Party (PRS). In 2008 he converted to Islam and took the name Mohamed Ialá Embaló. He was the founder of the Party for Social Renewal. In 2014, Ialá died from a cardiopulmonary arrest.

Bolama is an administrative region in Guinea-Bissau, consisting primarily of the Bijagós Archipelago of the country's southern coast, together with a small coastal strip centred on the coastal town of São João. It has an area of 2,624 km2. Its capital is Bolama, on the island of the same name. It is a coastal region covered with Mangrove swamps, rain forest and tangled forest and receives an annual rainfall of more than 1,000 mm (39 in).
Guinea-Bissau Creole, also known as Kiriol or Crioulo, is a creole language whose lexicon derives mostly from Portuguese. It is spoken in Guinea Bissau, Senegal and The Gambia. It is also called by its native speakers as guinensi, kriyol, or portuguis.

Guinea-Bissau–United States relations are bilateral relations between Guinea-Bissau and the United States.
Religion in Guinea-Bissau is diverse, with no particular religion representing an absolute majority. The CIA World Factbook states that around 46% of the population are Muslims, 31% adhere to Folk religions, 19% are Christians, and 4% are non-religious or practice other religions. Meanwhile, the US State Department mentions that estimates vary greatly and cites the Pew Forum data (2010) of 40% Muslim, 31% indigenous religious practices, and 20% Christian. Sunni Islam, including that of Sufi-oriented, are most concentrated in the northern and northeastern parts of the country. Practitioners of traditional indigenous religious beliefs generally live in all but the northern parts of the country. Christians are mostly found along the coastal regions, and belong to the Roman Catholic Church and various Protestant denominations. Christians are concentrated in Bissau and other large towns.
Education in Guinea-Bissau is compulsory from the age of 7 to 13. In 1998, the gross primary enrollment rate was 53.5 percent, with higher enrollment ratio for males compared with females.

Guinea-Bissau–Russia relations are the bilateral foreign relations between Guinea-Bissau and Russia.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) persons in Guinea-Bissau face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Same-sex sexual activity is legal in Guinea-Bissau, but same-sex couples and households headed by same-sex couples are not eligible for the same legal protections available to opposite-sex couples.

Guinea-Bissau–Sweden relations is the bilateral foreign relations between the two countries Guinea-Bissau and Sweden. The ambassador of Sweden to Portugal is accredited to Guinea-Bissau. Guinea-Bissau is accredited to Sweden from its embassy in Brussels and maintains an honorary consulate in Stockholm.
The WHO's estimate of life expectancy for a female child born in Guinea-Bissau in 2008 was 49 years, and 47 years for a boy. in 2016 life expectancy had improved to 58 for men and 61 for women.

The Guinea-Bissau women's national football team represents Guinea-Bissau in international women's football. It is governed by the Football Federation of Guinea-Bissau. It has played in two FIFA-recognised matches, both in 2006 against Guinea. The country also has a national under-17 side which participated in the 2012 Confederation of African Football qualifiers for the FIFA U-17 Women's World Cup. Football is the most popular women's sport in the country. A women's football programme was established in 2004, followed by the creation of a women's national league.

The Athletics Federation of Guinea-Bissau is the governing body for the sport of athletics in Guinea-Bissau. The current president is Renato Moura.
Guinea-Bissau–India relations refers to the international relations that exist between Guinea-Bissau and India. The embassy of India in Dakar, Senegal is concurrently accredited to Guinea-Bissau. India opened an Honorary Consulate in Bissau on 28 May 2010. Guinea-Bissau has no diplomatic mission in India.

Brazil – Guinea-Bissau relations refer to the bilateral relations between the Federative Republic of Brazil and the Republic of Guinea-Bissau. Both nations are members of the Community of Portuguese Language Countries, Group of 77 and the United Nations.
The COVID-19 pandemic in Guinea-Bissau is part of the worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The virus was confirmed to have reached Guinea-Bissau in March 2020.

Bissau-Guinean nationality law is regulated by the Constitution of Guinea-Bissau, as amended; the Bissau-Guinean Nationality Regulation, and its revisions; and various international agreements to which the country is a signatory. These laws determine who is, or is eligible to be, a national of Guinea-Bissau. The legal means to acquire nationality, formal legal membership in a nation, differ from the domestic relationship of rights and obligations between a national and the nation, known as citizenship. Nationality describes the relationship of an individual to the state under international law, whereas citizenship is the domestic relationship of an individual within the nation. Bissau-Guinean nationality is typically obtained under the principle of jus soli, i.e. by birth in Guinea-Bissau, or jus sanguinis, i.e. by birth in Guinea-Bissau or abroad to parents with Bissau-Guinean nationality. It can be granted to persons with an affiliation to the country, or to a permanent resident who has lived in the country for a given period of time through naturalization.