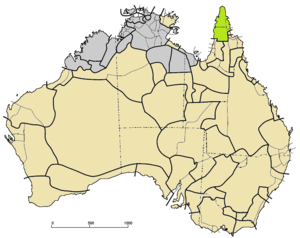
The Pama–Nyungan languages are the most widespread family of Australian Aboriginal languages, containing 306 out of 400 Aboriginal languages in Australia. The name "Pama–Nyungan" is a merism: it derived from the two end-points of the range: the Pama languages of northeast Australia and the Nyungan languages of southwest Australia.
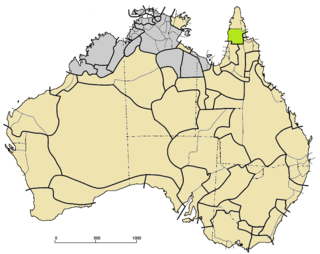
The Wik languages are a subdivision of the Paman languages consisting of sixteen languages, all spoken on the Cape York Peninsula of Queensland, Australia. This grouping was first proposed by R. M. W. Dixon.
Wik-Ngatharr, or Wik-Alken (Wik-Elken), is a Paman language spoken on the Cape York Peninsula of Queensland, Australia, by the Wik-Ngatharr people. It is a co-dialect with Wik-Ngathan, and more distantly related to the other Wik languages. In 1981 there were 86 speakers.
Mpakwithi is an extinct Australian Aboriginal dialect of Queensland.

The Djagaraga or Gudang are an Australian Aboriginal tribe, traditionally lived in the coastal area from Cape York to Fly point, including also Pabaju, in the Cape York Peninsula, Queensland. In the early period of white settlement as the Somerset tribe, after the settlement of Somerset established on their lands in 1863.
Wik-Mungkan, or Wik-Mungknh, is a Paman language spoken on the northern part of Cape York Peninsula of Queensland, Australia, by around 1,650 Wik-Mungkan people, and related peoples including the Wikalkan, Wik-Ngathana, Wikngenchera language groups. Wik Mungkan is healthier than most other languages on the peninsula, and is developing and absorbing other Aboriginal languages very quickly.
Kugu-Muminh (Wik-Muminh), also known as Kugu- or Wik-Nganhcara (Wikngenchera), is a Paman language spoken on the Cape York Peninsula of Queensland, Australia, by several of the Wik peoples. There are multiple dialects, only two of which are still spoken: Kugu-Muminh itself, and Kugu-Uwanh.

The Paman languages are an Australian language family spoken on Cape York Peninsula, Queensland. First noted by Kenneth Hale, Paman is noteworthy for the profound phonological changes which have affected some of its descendants.
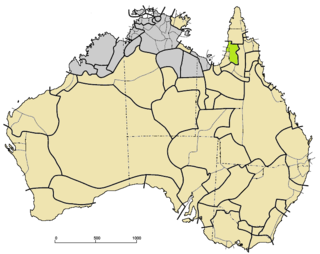
The Southwestern Paman languages are a family of the Paman languages spoken on the western part of the Cape York Peninsula of Queensland, Australia.
Umpila is an Aboriginal Australian language, or dialect cluster, of the Cape York Peninsula in northern Queensland. It is spoken by about 100 Aboriginal people, many of them elderly.
Mpalityan (Mpalitjanh) is an Australian language once spoken in the Cape York Peninsula of Queensland. It and Luthigh are dialects of a single language.
Awngthim is an extinct Australian Aboriginal language formerly spoken in Cape York in Queensland, Australia by the Winduwinda people. The Awngthim language region includes the areas around Weipa and the Cook Shire.
Ndra'ngith (Ntra'angith) is an Australian language once spoken in the Cape York Peninsula of Queensland.
Umpithamu, also spelt Umbindhamu, is an Australian Aboriginal language of the Cape York Peninsula, Queensland, Australia.
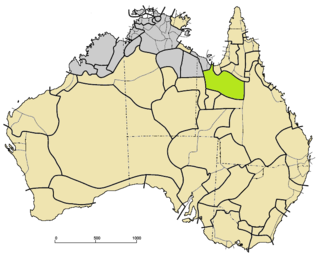
Mayabic, or Mayi, is a small family of extinct Australian Aboriginal languages of Queensland. They were once classified as Paman, but now as a separate branch of Pama–Nyungan.
The Kaantyu are an Indigenous Australian people of the Cape York Peninsula. They live in the area around the present day town of Coen. Most of their traditional tribal land has been taken over for cattle stations. Kaantju refers to the hook of the yuli, their word for woomera.
The Ayapathu people, otherwise known as the Ayabadhu or Aiyaboto, were an Indigenous Australian group, living on the western side of the Cape York Peninsula in northern Queensland.
The Yintyingka, now extinct, were an Indigenous Australian people of central and eastern Cape York Peninsula.
The Umpila are an Indigenous Australian people of the eastern Cape York Peninsula in northern Queensland. The majority of the remnant of the Umpila now live in Lockhart.
The Mbewum were an indigenous Australian people of the Cape York Peninsula of northern Queensland. They were dispossessed and became extinct soon after colonization.