| Type | Public |
|---|---|
| Nasdaq: OPTT | |
| Industry | Renewable Energy, Wave Power, Sustainable Energy |
| Founded | Perth, Western Australia, Australia (1984) |
| Founder | Dr. George W. Taylor |
| Headquarters | Perth, Western Australia, Australia |
Area served | Australia-wide |
Key people | Dr. George Taylor (Chairman) & (CEO) Gilbert George (Director)) Charles F. Dunleavy (Managing Director)) Keith Bowyer (General Manager)) |
| Owner | OPT, Inc (88%) + Woodside Petroleum (12%) |
| Website | (1999 established) |
Ocean Power Technologies Australasia Pty Ltd (OPTA) is an Australian company, a subsidiary of Ocean Power Technologies Inc (OPT) of the United States, a renewable energy company, providing power generation devices, services and related equipment for the extraction of energy from ocean waves.
In 2009 OPTA was part of Victorian Wave Partners formed to develop a 19 megawatt wave power project near Portland, Victoria connected to the grid. [1] The project was to receive an AU$66.46 million grant from the Australia federal government. By 2014, the consortium had abandoned the project, saying it was not commercially viable. OPT had given up on plans to develop the project, which was to cost $232 million for which the Australian government had offered $66.5 million in funding support. [2]

Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC) uses the ocean thermal gradient between cooler deep and warmer shallow or surface seawaters to run a heat engine and produce useful work, usually in the form of electricity. OTEC can operate with a very high capacity factor and so can operate in base load mode.

Wave power is the capture of energy of wind waves to do useful work – for example, electricity generation, water desalination, or pumping water. A machine that exploits wave power is a wave energy converter (WEC).

The Portland wind farm is one of Australia's largest wind farms. Located on the coast of south-western Victoria near the city of Portland, it consists of four separate sites, all of which have been completed as of 2015. Completion of the entire 195 MW project was expected in 2011, at a capital cost of A$330 million.

The Pelamis Wave Energy Converter was a technology that used the motion of ocean surface waves to create electricity. The machine was made up of connected sections which flex and bend as waves pass; it is this motion which is used to generate electricity.

Wind power is one of the main renewable energy sources in Australia and contributed 10% of electricity supplied in 2020, with 37.5% total renewable energy supply. Australia has greatly distinguished conditions for harvesting wind power. Abundant wind resources may be located close to residential areas in the southern parts of the country and on the slopes of the Great Dividing Range in the east.

Solar power in Australia is a fast growing industry. As of June 2022, Australia's over 3.19 million solar PV installations had a combined capacity of 27,167 MW photovoltaic (PV) solar power, of which at least 3,271 MW were installed in the preceding 12 months. In 2019, 59 solar PV projects with a combined capacity of 2,881 MW were either under construction, constructed or due to start construction having reached financial closure. Solar accounted for 9.9% of Australia's total electrical energy production in 2020.

The energy policy of Australia is subject to the regulatory and fiscal influence of all three levels of government in Australia, although only the State and Federal levels determine policy for primary industries such as coal. Federal policies for energy in Australia continue to support the coal mining and natural gas industries through subsidies for fossil fuel use and production. Australia is the 10th most coal-dependent country in the world. Coal and natural gas, along with oil-based products, are currently the primary sources of Australian energy usage and the coal industry produces over 30% of Australia's total greenhouse gas emissions. In 2018 Australia was the 8th highest emitter of greenhouse gases per capita in the world.
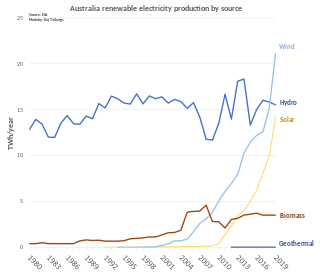
Renewable energy in Australia includes wind power, hydroelectricity, solar PV, heat pumps, geothermal, wave and solar thermal energy.
The Wave Hub is a floating offshore wind and wave power research project. The project is developed approximately 10 miles (16 km) off Hayle, on the north coast of Cornwall, United Kingdom. The hub was installed on the seabed in September 2010, and is a 'socket' sitting on the seabed for wave energy converters to be plugged into. It will have connections to it from arrays of up to four kinds of wave energy converter. A cable from the hub to main land will take electrical power from the devices to the electric grid. The total capacity of the hub will be 20 MWe. The estimated cost of the project is £28 million.

A floating wind turbine is an offshore wind turbine mounted on a floating structure that allows the turbine to generate electricity in water depths where fixed-foundation turbines are not feasible. Floating wind farms have the potential to significantly increase the sea area available for offshore wind farms, especially in countries with limited shallow waters, such as Japan, France and US West coast. Locating wind farms further offshore can also reduce visual pollution, provide better accommodation for fishing and shipping lanes, and reach stronger and more consistent winds.
Pelamis Wave Power designed and manufactured the Pelamis Wave Energy Converter – a technology that uses the motion of ocean surface waves to create electricity. The company was established in 1998 and had offices and fabrication facilities in Leith Docks, Edinburgh, Scotland. It went into administration in November 2014.
Wave power in Australia is being developed as the country has a long and largely deep-water coastline. It is one of several regions of the world where wave power projects are being considered.
Ocean Power Technologies (OPT) is a U.S. publicly owned renewable energy company, providing electric power and communications solutions, services and related for remote offshore applications. The company's PowerBuoy wave energy conversion technology is theoretically scalable to hundreds of megawatts and the generated energy from wave power can be supplied to the grid via submarine cables. Several projects were undertaken around the world, but the economic viability of the theoretical concept has been problematic.
The Oyster is a hydro-electric wave energy device that uses the motion of ocean waves to generate electricity. It is made up of a Power Connector Frame (PCF), which is bolted to the seabed, and a Power Capture Unit (PCU). The PCU is a hinged buoyant flap that moves back and forth with movement of the waves. The movement of the flap drives two hydraulic pistons that feed high-pressured water to an onshore hydro-electric turbine, which drives a generator to make electricity. Oyster was stationed at the European Marine Energy Centre (EMEC) at its Billia Croo site in Orkney, Scotland until the company ceased trading in 2015.

The U.S. state of Massachusetts has vast wind energy resources offshore, as well as significant resources onshore. The 2016 update to the states's Clean Energy and Climate Plan had a goal of reducing 1990 baseline greenhouse gas emissions levels by 25% by 2020. Current goals include installing 3,500 megawatts (MW) of offshore wind power in the state by 2035. However, as of Q4 2021 the state had only 120 MW of wind powered electricity generating capacity, responsible for generating 0.9% of in-state electricity production. The state has awarded contracts to two offshore projects, the 800 MW Vineyard Wind project and 804 MW Mayflower Wind project. Construction began on the Vineyard Wind 1 project on November 18, 2021, after a long fight for approval. Commonwealth Wind was selected for development in 2021.
Wind power in New Jersey is in the early stages of development. As of 2022, New Jersey has just six wind turbines, but the state has plans to develop several major offshore wind projects on the continental shelf of the Atlantic Ocean off the southern Jersey Shore. Legislation has been enacted to support the industry through economic incentives and to permit wind turbines on existing piers.
Solar power in North Carolina has been increasing rapidly, from less than 1 MW (megawatts) in 2007 to 6,152 MW in 2019, and has the second-largest installed PV capacity of all U.S. states. SunEdison built a 17.2-megawatt solar farm in Davidson County.

Wave power in the United States is under development in several locations off the east and west coasts as well as Hawaii. It has moved beyond the research phase and is producing reliable energy for the Grid. Its use to-date has been for situations where other forms of energy production are not economically viable and as such, the power output is currently modest. But major installations are planned to come on-line within the next few years.

The Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA) is an independent agency of the Australian federal government, established in 2012 to manage Australia's renewable energy programs, with the objective of increasing supply and competitiveness of Australian renewable energy sources.