Molecular tweezers, and molecular clips, are host molecules with open cavities capable of binding guest molecules. The open cavity of the molecular tweezers may bind guests using non-covalent bonding, which includes hydrogen bonding, metal coordination, hydrophobic forces, van der Waals forces, π–π interactions, and/or electrostatic effects. These complexes are a subset of macrocyclic molecular receptors and their structure is that the two "arms" that bind the guest molecule between them are only connected at one end leading to a certain flexibility of these receptor molecules.

Chaetoceros is a genus of diatoms in the family Chaetocerotaceae, first described by the German naturalist C. G. Ehrenberg in 1844. Species of this genus are mostly found in marine habitats, but a few species exist in freshwater. It is arguably the common and most diverse genus of marine planktonic diatoms, with over 200 accepted species. It is the type genus of its family.
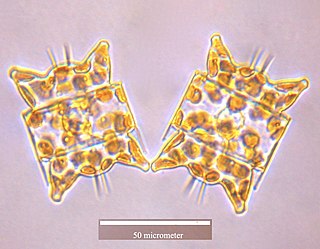
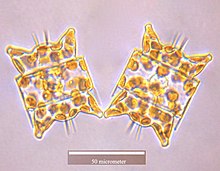
Eupodiscaceae is a diatom family (Bacillariophyceae) present both in marine and freshwater habitats Odontella is the only genera in this family with typical marine species. However, Round et al. (1990) placed Odontella in Triceratiaceae (Schutt) Lemmermann, order Triceratiales Round and Crawford, subclass Biddulphiophycidae Round and Crawford. The taxonomic status of this family is unclear and disputed.

Odontella aurita is a diatom and the type species of genus Odontella. The easiest way to identify this species is by recognizing the very distinct shape of the cells belonging to this genus. Odontella aurita is cultivated industrially for human consumption due to its ability to produce up to 28% of its total lipids as eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), a long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA). PUFAs such as EPA are known to provide a variety of health benefits in humans, and are commonly obtained by fish oil. However, with the increasing concern of over-exploited fisheries, microalgae are a promising source of PUFAs as they can be grown year-round and their fatty acid profile and content are easily manipulated by growth conditions.

Amphora is a major genus of marine and freshwater diatoms. With over 1000 species, it is one of the largest genera of diatoms. These diatoms are recognized by their strongly dorsiventral frustules, which means that their ridges lie close to the ventral margin of the valve, and their girdle is much wider on the dorsal side.
Riedelia is a genus of diatoms known from the fossil record, comprising approximately eight species. Many of the species were originally described under the closely allied genus Hemiaulus. Paleontologists Hans-Joachim Schrader and Juliane Fenner, working with fossil specimens obtained from Leg 38 of the Deep Sea Drilling Program in the Norwegian and Greenland Seas, decided that several previous descriptions of diatoms belonging to Hemiaulus were rightfully placed on Riedelia. Schrader and Fenner note that while Hemiaulus diatoms have polygonal areolated valves, Riedelia valves are punctate with isolated punctae. Additionally, Riedelia typically have two spines, while Hemiaulus have only one. These characteristics were used to justify the placement of these species in Riedelia.
Thalassiosira weissflogii is a species of centric diatoms, a unicellular microalga. It is found in marine environments and also in inland waters in many parts of the world. It is actively studied because it may use C4-plant style strategies to increase its photosynthetic efficiency.

The Cymbellaceae are a diatom family in the order Cymbellales.
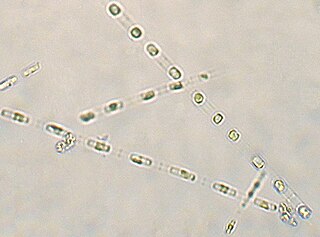
Skeletonema is a genus of diatoms in the family Skeletonemataceae. It is the type genus of its family. The genus Skeletonema was established by R. K. Greville in 1865 for a single species, S. barbadense, found in the Barbados deposit [Jung 2009]. These diatoms are photosynthetic organisms, meaning they obtain carbon dioxide from their surrounding environment and produce oxygen along with other byproducts. Reproduce sexually and asexually [Guiry 2011]. Skeletonema belong to the morphological category referred to as centric diatoms. These are classified by having valves with radial symmetry and the cells lack significant motility [Horner 2002]. Skeletonema are cylindrical shaped with a silica frustule. Cells are joined by long marginal processes to form a filament [Horner 2002]. Their length ranges from 2-61 micrometers, with a diameter ranging from 2-21 micrometers [Hasle 1997]. They are found typically in the neritic zone of the ocean and are highly populous in coastal systems [Jung 2009]. The genus is considered cosmopolitan, showing a wide range of tolerance for salinity and temperature [Hasle 1973]. For example, they have been found in various aquatic environments such as brackish or freshwater. Skeletonema are found worldwide excluding Antarctic waters [Hevia-Orube 2016]. Some harmful effects these diatoms may have on an ecosystem are attributed to large blooming events which may cause hypoxic events in coastal systems. Additionally, they are known to cause water discoloration [Kraberg 2010].
Cymatosira is a genus of diatoms in the family Cymatosiraceae. It is the type genus of its family.

Dictyota is a genus of brown seaweed in the family Dictyotaceae. Species are predominantly found in tropical and subtropical seas, and are known to contain numerous chemicals (diterpenes) which have potential medicinal value. As at the end of 2017, some 237 different diterpenes had been identified from across the genus.
The following index is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the protected areas of South Africa:
Odontella sinensis, also known as the Chinese diatom, is a marine, unicellular species of diatom in the family Triceratiaceae.
Thalassiothrix is a genus of Chromista belonging to the family Thalassionemataceae.

Diploneis is a genus of diatoms belonging to the family Diploneidaceae.

Gomphonema is a genus of diatoms belonging to the family Gomphonemataceae.
Lithodesmium is a genus of diatoms belonging to the family Lithodesmiaceae.
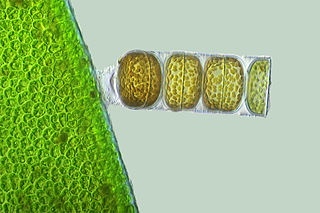
Melosira is a genus of diatoms belonging to the family Melosiraceae.
Stauroneis is a genus of diatoms (Bacillariophyta) with species that occur in fresh and marine water.