Related Research Articles

Tecumseh was a Shawnee chief and warrior who promoted resistance to the expansion of the United States onto Native American lands. A persuasive orator, Tecumseh traveled widely, forming a Native American confederacy and promoting intertribal unity. Even though his efforts to unite Native Americans ended with his death in the War of 1812, he became an iconic folk hero in American, Indigenous, and Canadian popular history.

The Battle of the Thames, also known as the Battle of Moraviantown, was an American victory in the War of 1812 against Tecumseh's Confederacy and their British allies. It took place on October 5, 1813, in Upper Canada, near Chatham. The British lost control of Southwestern Ontario as a result of the battle; Tecumseh was killed, and his confederacy largely fell apart.

Lewis Cass was an American military officer, politician, and statesman. He represented Michigan in the United States Senate and served in the Cabinets of two U.S. Presidents, Andrew Jackson and James Buchanan. He was also the 1848 Democratic presidential nominee. A slave owner himself, he was a leading spokesman for the doctrine of popular sovereignty, which held that the people in each territory should decide whether to permit slavery.

Brevet Brigadier-General James Miller was a senior officer of the United States Army who commanded infantry in the Canadian Theater of the War of 1812. After the war, he served as the first governor of Arkansas Territory from 1819 to 1824. He also served as the superintendent of Indian affairs for the territory. It was during his term as governor, and partly due to his influence, that the territory's capital was moved from Arkansas Post to Little Rock.

William Hull was an American soldier and politician. He fought in the American Revolutionary War and was appointed as Governor of Michigan Territory (1805–13), gaining large land cessions from several American Indian tribes under the Treaty of Detroit (1807). He is most widely remembered, however, as the general in the War of 1812 who surrendered Fort Detroit to the British on August 16, 1812 following the Siege of Detroit. After the battle, he was court-martialed, convicted, and sentenced to death, but he received a pardon from President James Madison and his reputation somewhat recovered.

Duncan McArthur was a military officer and a Federalist and National Republican politician from Ohio. He served as the 11th governor of Ohio.

The Battle of Fort George was a battle fought during the War of 1812, in which the Americans defeated a British force and captured Fort George in Upper Canada. The troops of the United States Army and vessels of the United States Navy cooperated in a very successful amphibious assault, although most of the opposing British force escaped encirclement.

The siege of Fort Meigs took place in late April to early May 1813 during the War of 1812 in northwestern Ohio, present-day Perrysburg. A small British Army unit with support from Indians attempted to capture the recently constructed fort to forestall an American offensive against Detroit, and its Fort Detroit in the Great Lakes region which the British from the north in Canada had captured the previous year. An American sortie and relief attempt failed with heavy casualties, but the British failed to capture the fort and were forced to raise the siege.

The siege of Fort Wayne took place from September 5 – September 12, 1812, during the War of 1812. The stand-off occurred in the modern city of Fort Wayne, Indiana between the U.S. military garrison at Fort Wayne and a combined force of Potawatomi and Miami forces. The conflict began when warriors under the Potawatomi Native American Chiefs Winamac, and Five Medals killed two members of the U.S. garrison. Over the next several days, the Potawatomi burned the buildings and crops of the fort's adjacent village, and launched assaults from outside the fort. Winamac withdrew on 12 September, ahead of reinforcements led by Major General William Henry Harrison.

The siege of Detroit, also known as the surrender of Detroit or the Battle of Fort Detroit, was an early engagement in the War of 1812. A British force under Major General Isaac Brock with indigenous allies under Shawnee leader Tecumseh used bluff and deception to intimidate U.S. Brigadier General William Hull into surrendering the fort and town of Detroit, Michigan, along with his dispirited army which actually outnumbered the victorious British and Indians.

The Battle of Fort Stephenson in August 1813 was an American victory during the War of 1812. American forces successfully defended the fort in August 1813; it guarded an important supply depot. It was located on the west bank of the Sandusky River more than 10 miles upstream from Sandusky Bay in what is now Ohio. The town of Fremont, Ohio developed around the site.

The Battle of Maguaga was a small battle between British troops, Canadian militia and Tecumseh's natives against a larger force of American troops, Ohio Volunteers and Michigan Legion near the Wyandot village of Maguaga which become The Township of Monguagon Township, Michigan in what is now The City of Riverview, Michigan.

James Findlay was an American merchant, politician and veteran of the War of 1812, having served with both the state militia and the United States Army. He was based in Cincinnati, Ohio after migrating there as a young man. He was elected as mayor of Cincinnati to two non-successive terms.
The Battle of Malcolm's Mills was the last battle of the War of 1812 fought in the Canadas. A force of American mounted troops overran and scattered a force of Canadian militia. The battle was fought on November 6, 1814, near the village of Oakland in Brant County, Upper Canada, and was part of a series of battles fought by American Brigadier General Duncan McArthur on an extended raid into Upper Canada, known variously as McArthur's Raid or Dudley's Raid. Marching over 200 miles (320 km) into Canada, the Americans returned to Detroit on November 17 after 11 days of raiding the Ontario Peninsula.
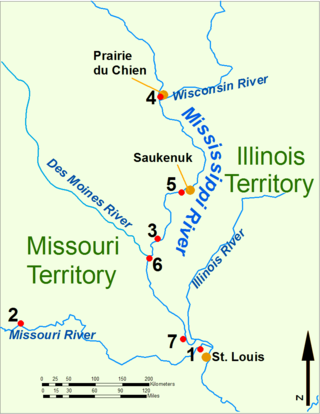
The siege of Prairie du Chien was a British victory in the far western theater of the War of 1812. During the war, Prairie du Chien was a small frontier settlement with residents loyal to both American and British causes. By 1814, both nations were anxious to control the site because of its importance to the fur trade and its strategic location at the intersection of the Mississippi River and the Fox-Wisconsin Waterway, a transportation route linking the Mississippi with the Great Lakes.

Fort Shelby was a military fort in Detroit, Michigan that played a significant role in the War of 1812. It was built by the British in 1779 as Fort Lernoult, and was ceded to the United States by the Jay Treaty in 1796. It was renamed Fort Detroit by Secretary of War Henry Dearborn in 1805.
The Army of the Northwest was a U.S. Army unit formed at the outset of the War of 1812 and charged with control of the state of Ohio, the Indiana Territory, Michigan Territory and Illinois Territory.
Joel Leftwich was an American planter and politician, who also served as brigadier general of the Virginia militia in the War of 1812 and twice represented Bedford County in the Virginia House of Delegates.
The Western theater of the War of 1812 was an theater of war during the War of 1812 between the United States and the United Kingdom. Far from the Atlantic Coast and large cities, logistics and communication were more challenging in the western territories and the United States frontier. For many Native American nations involved, this war was a continuation of the defense of their lands against encroaching settlers.
References
- ↑ Alec R. Gilpin, The War of 1812 in the Old Northwest (Michigan State University Press, 1958, 2012), chapters II and III.
- ↑ "A History of Fort Meigs". Fort Meigs. Retrieved April 29, 2017.
- ↑ "Oliver H. Perry". Ohio History Central. Retrieved April 29, 2017.