Creek mythology is related to a Muscogee tribe who are originally from the southeastern United States, also known by their original name Mvskoke, the name they use to identify themselves today. Mvskoke is their name in traditional spelling. Modern Muscogees live primarily in Oklahoma, Alabama, Georgia, and Florida. Their language, Mvskoke, is a member of the Eastern branch of the Muskogean language family. The Seminole are close kin to the Mvskoke and speak an Eastern Muskogean language as well. The Muscogee were considered one of the Five Civilized Tribes. After the Creek War many of the Muscogee escaped to Florida to create the Seminole.

The Chattahoochee River forms the southern half of the Alabama and Georgia border, as well as a portion of the Florida and Georgia border. It is a tributary of the Apalachicola River, a relatively short river formed by the confluence of the Chattahoochee and Flint rivers and emptying from Florida into Apalachicola Bay in the Gulf of Mexico. The Chattahoochee River is about 430 miles (690 km) long. The Chattahoochee, Flint, and Apalachicola rivers together make up the Apalachicola–Chattahoochee–Flint River Basin. The Chattahoochee makes up the largest part of the ACF's drainage basin.

The Apalachicola River is a river, approximately 160 miles (260 km) long, in the state of Florida. The river's large watershed, known as the Apalachicola, Chattahoochee and Flint (ACF) River Basin, drains an area of approximately 19,500 square miles (50,500 km2) into the Gulf of Mexico. The distance to its farthest head waters in northeast Georgia is approximately 500 miles (800 km). Its name comes from Apalachicola Province, an association of Native American towns located on what is now the Chattahoochee River. The Spanish included what is now called the Chattahoochee River as part of one river, calling all of it from its origins in the southern Appalachian foothills down to the Gulf of Mexico the Apalachicola.

The Flint River is a 344-mile-long (554 km) river in the U.S. state of Georgia. The river drains 8,460 square miles (21,900 km2) of western Georgia, flowing south from the upper Piedmont region south of Atlanta to the wetlands of the Gulf Coastal Plain in the southwestern corner of the state. Along with the Apalachicola and the Chattahoochee rivers, it forms part of the ACF basin. In its upper course through the red hills of the Piedmont, it is considered especially scenic, flowing unimpeded for over 200 miles (320 km). Historically, it was also called the Thronateeska River.

Prospect Bluff Historic Sites is located in Franklin County, Florida, on the Apalachicola River, 6 miles (9.7 km) SW of Sumatra, Florida. The site contains the ruins of two forts.

The Wiregrass region, also known as the Wiregrass plains or Wiregrass country, is an area of the Southern United States encompassing parts of southern Georgia, southeastern Alabama, and the Florida Panhandle. The region is named for the native Aristida stricta, commonly known as wiregrass due to its texture.

Lake Lanier is a reservoir in the northern portion of the U.S. state of Georgia. It was created by the completion of Buford Dam on the Chattahoochee River in 1956, and is also fed by the waters of the Chestatee River. The lake encompasses 38,000 acres (150 km2) or 59 sq mi (150 km2) of water, and 692 mi (1,114 km) of shoreline at normal level, a "full pool" of 1,071 ft (326 m) above mean sea level and the exact shoreline varies by resolution according to the coastline paradox. Named for poet Sidney Lanier, it was built and is operated by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers for flood control and water supplies. Its construction destroyed more than 50,000 acres (20,000 ha) of farmland and displaced more than 250 families, 15 businesses, and relocated 20 cemeteries along with their corpses in the process.

The Walter F. George Lake, named for Walter F. George (1878–1957), a United States senator from Georgia, is formed on the Chattahoochee River along the state line between Alabama and Georgia. It is also widely known by the name, Lake Eufaula – particularly in Alabama, where the state legislature passed a resolution on June 25, 1963, to give the lake that name. The 46,000-acre lake extends north about 85 miles (140 km) from the Walter F. George Lock and Dam and has approximately 640 miles (1,030 km) of shoreline. Popular activities along the lake include camping and trophy fishing.
Hitchiti was a tribal town in what is now the Southeast United States. It was first known as part of the Apalachicola Province, an association of tribal towns along the Chattahoochee River. Shortly after 1690, the towns of Apalachicola Province moved to the central part of present-day Georgia, with Hitchiti joining most of those towns along Ochese Creek. In 1715, most of the towns on Ochese Creek, including Hitchiti, moved back to the Chattahoochee River, where the town remained until its people were forced to move to the Indian Territory as part of the Trail of Tears. Hitchiti was one of several towns whose people spoke the Hitchiti language.

Lake Seminole is a reservoir located in the southwest corner of Georgia along its border with Florida, maintained by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. The Chattahoochee and Flint rivers join in the lake, before flowing from the Jim Woodruff Lock and Dam, which impounds the lake, as the Apalachicola River. The lake contains 37,500 acres (152 km2) of water, and has a shoreline of 376 mi (605 km). The fish in Lake Seminole include largemouth bass, crappie, chain pickerel, catfish, striped bass and other species. American alligators, snakes and various waterfowl are also present in the lake, which is known for its goose hunting.

The tri-state water dispute is a 21st-century water-use conflict among the U.S. states of Georgia, Alabama, and Florida over flows in the Apalachicola-Chattahoochee-Flint River Basin and the Alabama-Coosa-Tallapoosa River Basin. The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers has regulated water flow for the entire Chattahoochee River, from Lake Lanier in Forsyth County, Georgia, to Alabama and Florida.
Fowltown Creek, near modern Albany, Georgia, was where "Neamathla's band of Tuttollossees had lived...before relocating down to modern Decatur and Seminole Counties."

Smith Creek is a stream in White County of the American state of Georgia, and is a tributary of the Chattahoochee River. The creek is approximately 6.65 miles (10.70 km) long.
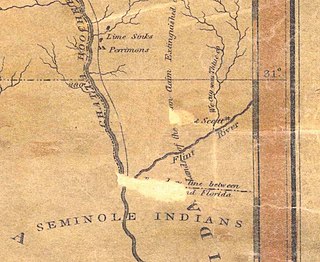
Fort Scott was built in 1816 on the west bank of the Flint River, where it joins the Chattahoochee River to form the Apalachicola, in the southwest corner of Georgia. It was named for Lieutenant Richard W. Scott, who was killed in the Scott Massacre of 1817 and never known to have visited the fort. The need for a fort became evident during the War of 1812, when the British identified the undefended United States border and in 1814 built two forts on the Apalachicola River into which the Flint River flows: a strong fort at Prospect Bluff and a smaller one, Nicolls' Outpost, at the river juncture. This was in Spanish Florida, but Spain had neither the resources nor the inclination to do anything about the fort in a location that was remote.
Nicolls' Outpost was the smaller and more northern of two forts built by British Lt. Col. Edward Nicolls during the War of 1812. (The Americans referred to it as Fort Apalachicola. Built at the end of 1814, together with the larger "British post" or storage depot down the Apalachicola, it was "the northernmost post built by the British during their Gulf Coast Campaign". It was just below the Spanish Florida–Georgia border, where the Flint and Chattahoochee Rivers meet to form the Apalachicola, in River Landing Park in modern Chattahoochee, Florida. Even though what was built was smaller than the much larger British post down the Apalachicola, it was intended to be the base, presumably enlarged, for an English invasion of the United States, and British post was to have been its supply depot. The 1815 end of the War of 1812 aborted this project.

Neamathla (1750s–1841) was a leader of the Red Stick Creek. His name, in the Hitchiti language, means "fat next to warrior", "fat" being a reference to great courage. The Hitchiti language had no written form, but modern scholars agree that Eneah Emathla is the "proper" spelling of his name in English; however, there were two other men also named Eneah Emathla, so the modern convention is to use the spelling Neamathla for the leader.

West Point Lake is a man-made reservoir located mostly in west-central Georgia on the Chattahoochee River and maintained by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (USACE). The Chattahoochee river flows in from the north, before flowing through the West Point Dam, which impounds the lake, and continuing to Columbus, Georgia. Of the four major USACE lakes in the ACF River Basin, West Point Lake is the smallest by area containing 25,864 acres (10,467 ha) of water, and has the second shortest shoreline at 604 mi (972 km). The purposes of the reservoir are to provide flood control, hydroelectric power, and water storage to aid the navigation of the lower Chattahoochee.
Sabacola was a Native American tribal town in what is now the Southeastern United States of America during the 17th, 18th, and early 19th centuries. Usually regarded as belonging to Apalachicola Province, Sabacola had poorly understood connections to the Apalachee people. Although usually described as speaking the Hitchiti language, at least one source stated that the Sabacola spoke another, unidentified language. The town moved to several locations along the Chattahoochee River, sometimes with more than one town including Sabacola in its name at the same time. The town of Sabacola moved to the Ocmulgee River area of central Georgia for about 25 years, before returning to the Chattahoochee River. Sabacola was the only Apalachicola town to have a mission established by the Spanish. The Apalachicola towns, including Sabacola, evolved into the Lower Towns of the Muscogee Confederacy.

Buford Dam is a dam in Buford, Georgia which is located at the southern end of Lake Lanier, a reservoir formed by the construction of the dam in 1956. The dam itself is managed by the United States Army Corps of Engineers.
The Apalachicola band consisted of several Native Americans towns, primarily speakers of the Muscogee language, living along the Apalachicola River in northern Florida in the early 19th century. The 1823 Treaty of Moultrie Creek assigned the Apalachicola band several small reservations along the Apalachicola River, separate from the main reservation created in central and southern Florida for the people collectively called Seminole. The Apalachicola band was allowed to stay on their reservations for only a decade, before being moved to the Indian Territory.














