Related Research Articles

New Kent County is a county in the eastern part the Commonwealth of Virginia. As of the 2020 United States Census, its population was 22,945. Its county seat is New Kent.

Hanover County is a county in the Commonwealth of Virginia. As of the 2020 census, the population was 109,979. Its county seat is Hanover Courthouse.

Dinwiddie County is a county located in the Commonwealth of Virginia. As of the 2020 census, the population was 27,947. Its county seat is Dinwiddie.

Funkstown is a town in Washington County, Maryland, United States. The population was 904 at the 2010 census.

Galeton is a borough in Potter County, Pennsylvania. It is located 50 miles (80 km) southeast of Bradford, Pennsylvania. Light industries, including knitting mills and a tannery have existed in Galeton. The population declined to 993 people in 2020.

Ashland is a town in Hanover County, Virginia, United States, located 16 miles (26 km) north of Richmond along Interstate 95 and U.S. Route 1. As of the 2020 census it had a population of 7,565, up from 7,225 at the 2010 census.

Doswell is an unincorporated community in Hanover County in the Central Region of the U.S. Commonwealth of Virginia. Originally called Hanover Junction, it was located on the Virginia Central Railroad at a crossing of the Richmond, Fredericksburg and Potomac Railroad, a north–south route. Both railroads are now owned by CSX Transportation, although the former Virginia Central line is leased to a short-line carrier, Buckingham Branch Railroad. The area near the Doswell train station is a popular train-watching site for railfans.

The Battle of Hanover Court House, also known as the Battle of Slash Church, took place on May 27, 1862, in Hanover County, Virginia, as part of the Peninsula Campaign of the American Civil War.

The Battle of Totopotomoy Creek, also called the Battle of Bethesda Church, Crumps Creek, Shady Grove Road, and Hanovertown, was a battle fought in Hanover County, Virginia on May 28–30, 1864, as part of Union Lt. Gen. Ulysses Grant's Overland Campaign against Confederate Gen. Robert E. Lee's Army of Northern Virginia.

The Battle of Haw's Shop or Enon Church was fought on May 28, 1864, in Hanover County, Virginia, as part of Union Lt. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant's Overland Campaign against Confederate Gen. Robert E. Lee's Army of Northern Virginia during the American Civil War.

The Bermuda Hundred campaign was a series of battles fought at the town of Bermuda Hundred, outside Richmond, Virginia, during May 1864 in the American Civil War. Union Maj. Gen. Benjamin Butler, commanding the Army of the James, threatened Richmond from the east but was stopped by forces under Confederate Gen. P.G.T. Beauregard.
The Battle of Saint Mary's Church was an American Civil War cavalry battle fought on June 24, 1864, as part of Union Lt. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant's Overland Campaign against Confederate Gen. Robert E. Lee's Army of Northern Virginia.

On the third day of the Battle of Gettysburg during the disastrous infantry assault nicknamed Pickett's Charge, there were two cavalry battles: one approximately three miles (5 km) to the east, in the area known today as East Cavalry Field, the other southwest of the [Big] Round Top mountain.
Elmont is an unincorporated community in Hanover County in the Central Region of the U.S. state of Virginia. It was located on the former Richmond, Fredericksburg and Potomac Railroad, now owned by CSX Transportation. Elmont was located on the old Washington Highway, and was served by an electric trolley car line between Richmond and Ashland.

The Battle of Peebles's Farm was the western part of a simultaneous Union offensive against the Confederate works guarding Petersburg and Richmond, Virginia, during the Siege of Petersburg in the American Civil War.

The Battle of Hatcher's Run, also known as Dabney's Mill, Armstrong's Mill, Rowanty Creek, and Vaughn Road, fought February 5–7, 1865, was one in a series of Union offensives during the siege of Petersburg, aimed at cutting off Confederate supply traffic on Boydton Plank Road and the Weldon Railroad west of Petersburg, Virginia.
The Battle of Meadow Bridge was an engagement on May 12, 1864, in Henrico County, Virginia, during Lt. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant's Overland Campaign of the American Civil War. Following their victory at the Battle of Yellow Tavern on May 11, Union cavalry under Maj. Gen. Philip H. Sheridan advanced in the direction of the Confederate capital of Richmond. Caught in the narrow area between the fortifications of Richmond and the rain-swollen Chickahominy River, the Union troopers were subjected to fire from the artillery of Confederate Maj. Gen. Fitzhugh Lee. Michigan cavalry under Brig. Gen. George A. Custer forced a crossing of a damaged railroad bridge, which was quickly rebuilt by engineers, allowing the troopers to escape to safety and continue their raid.

The First Battle of Deep Bottom, also known as Darbytown, Strawberry Plains, New Market Road, or Gravel Hill, was fought July 27–29, 1864, at Deep Bottom in Henrico County, Virginia, as part of the Siege of Petersburg of the American Civil War. A Union force under Maj. Gens. Winfield S. Hancock and Philip H. Sheridan was sent on an expedition threatening Richmond, Virginia, and its railroads, intending to attract Confederate troops away from the Petersburg defensive line, in anticipation of the upcoming Battle of the Crater. The Union infantry and cavalry force was unable to break through the Confederate fortifications at Bailey's Creek and Fussell's Mill and was withdrawn, but it achieved its desired effect of momentarily reducing Confederate strength at Petersburg.
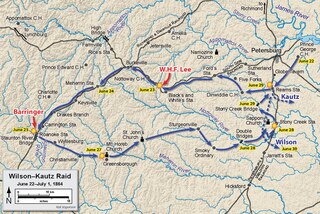
The Wilson–Kautz Raid was a cavalry operation in south central Virginia in late June 1864, during the American Civil War. Occurring early in the Richmond-Petersburg Campaign, the raid was conducted by Union cavalry under Brigadier Generals James H. Wilson and August Kautz, who were ordered to cut railroads between Lynchburg, Virginia, and the vital Confederate rail supply center at Petersburg. While the raid had the intended effect of disrupting Confederate rail communications for several weeks, the raiding force lost much of its artillery, all of its supply train, and almost a third of the original force, mostly to Confederate capture.
Flatwood is an unincorporated community in Shannon County, in the U.S. state of Missouri.
