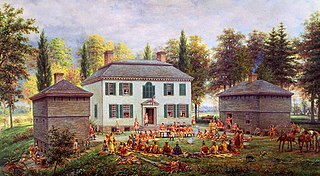Schoharie County is a county in the U.S. state of New York. As of the 2020 census, the population was 29,714, making it the state's fifth-least populous county. The county seat is Schoharie. "Schoharie" comes from a Mohawk word meaning "floating driftwood." Schoharie County is part of the Albany-Schenectady-Troy, NY Metropolitan Statistical Area.

Schoharie is an incorporated town in and the county seat of Schoharie County, New York. The population was 3,299 at the 2000 census.
Fort Orange was the first permanent Dutch settlement in New Netherland; the present-day city of Albany, New York developed at this site. It was built in 1624 as a replacement for Fort Nassau, which had been built on nearby Castle Island and served as a trading post until 1617 or 1618, when it was abandoned due to frequent flooding. Both forts were named in honor of the Dutch House of Orange-Nassau. Due to a dispute between the Director-General of New Netherland and the patroonship of Rensselaerswyck regarding jurisdiction over the fort and the surrounding community, the fort and community became an independent municipality, paving the way for the future city of Albany. After the English reconquered the region they soon abandoned Fort Orange in favor of a new fort: Fort Frederick, constructed in 1676.

Old Fort Johnson is a historic house museum and historic site at 2 Mergner Road in Fort Johnson, New York. It is the site of Fort Johnson, a two-story stone house originally enclosed in fortifications built by Sir William Johnson about 1749. The fort served as Johnson's home, business office and trading center until 1763 when he moved to Johnson Hall in what is now Johnstown, New York. Sir William's son Sir John Johnson owned the house from 1763 until 1776, when it was confiscated by the local Committee of Safety. The house remains and is owned and operated as a museum by the Montgomery County Historical Society. It was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1972.

The Mabee House, on the grounds of the Mabee Farm Historic Site,, is the oldest house still standing in the Mohawk Valley. It is located in the town of Rotterdam, New York, in the hamlet of Rotterdam Junction, New York, along New York State Highway 5S, about six miles (9.7 km) west of the city of Schenectady.

Historic Huguenot Street is located in New Paltz, New York, approximately 90 miles (140 km) north of New York City. The seven stone houses and several accompanying structures in the 10-acre National Landmark Historic District were likely built in the early 18th century by Huguenot settlers fleeing discrimination and religious persecution in France and what's now southern Belgium. After negotiating with the Esopus Indians, this small group of Huguenots settled on a flat rise on the banks of the Wallkill River in 1678. The settlers named the site in honor of Die Pfalz, the region of present-day Germany that had provided them temporary refuge before they came to America. Archaeological finds indicate that the immediate area settled by the Huguenots was occupied by Native Americans prior to European contact. The site is one of the oldest continuously inhabited settlements in the United States.

Dutch barn is the name given to markedly different types of barns in the United States and Canada, and in the United Kingdom. In the United States, Dutch barns represent the oldest and rarest types of barns. There are relatively few—probably fewer than 600—of these barns still intact. Common features of these barns include a core structure composed of a steep gabled roof, supported by purlin plates and anchor beam posts, the floor and stone piers below. Little of the weight is supported by the curtain wall, which could be removed without affecting the stability of the structure. Large beams of pine or oak bridge the center aisle for animals to provide room for threshing. Entry was through paired doors on the gable ends with a pent roof over them, and smaller animal doors at the corners of the same elevations. The Dutch Barn has a square profile, unlike the more rectangular English or German barns. In the United Kingdom a structure called a Dutch barn is a relatively recent agricultural development meant specifically for hay and straw storage; most examples were built from the 19th century. British Dutch barns represent a type of pole barn in common use today. Design styles range from fixed roof to adjustable roof; some Dutch barns have honeycombed brick walls, which provide ventilation and are decorative as well. Still other British Dutch barns may be found with no walls at all, much like American pole barns.

Fort Klock, a fortified stone homestead in the Mohawk River Valley of Upstate New York, was built c.1750 by Johannes Klock, and is a good example of a mid-18th century fortified home and trading post, seeing use during the French and Indian War and the American Revolutionary War The fort is located at 7203 Route 5 roughly two miles (3 km) east of the Village of St. Johnsville, New York. Fort Klock is part of a 30-acre (12 ha) complex that includes the historic homestead, a renovated Colonial Dutch Barn, blacksmith shop, and 19th-century schoolhouse. The site is maintained by Fort Klock Historic Restoration and is open seasonally as a living museum. The fort was declared a National Historic Landmark in 1972.

Mohawk Upper Castle Historic District is a historic district in Herkimer County, New York that was declared a National Historic Landmark in 1993. Located south of the Mohawk River, it includes the Indian Castle Church, built in 1769 by Sir William Johnson, British Superintendent of Indian Affairs, as a missionary church for the Mohawk in the western part of their territory; the Brant Family Barn, a rare surviving example of Dutch colonial barns in the Mohawk Valley; as well as important archaeological site areas revealing life in Nowadaga, as the western part of the Mohawk village of Canajoharie was known. The fortified village was called the Upper Castle by European colonists.

Schoharie Crossing State Historic Site, also known as Erie Canal National Historic Landmark, is a historic district that includes the ruins of the Erie Canal aqueduct over Schoharie Creek, and a 3.5-mile (5.6 km) long part of the Erie Canal, in the towns of Glen and Florida within Montgomery County, New York. It was the first part of the old canal to be designated a National Historic Landmark, prior to the designation of the entire New York State Barge Canal as an NHL in 2017.
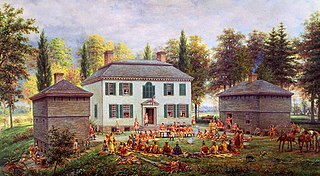
Johnson Hall State Historic Site was the home of Sir William Johnson (1715–1774) an Irish pioneer who became the influential British Superintendent of Indian Affairs in the Province of New York, known for his strong relationship especially with the Mohawk and other Iroquois League nations.

The Senate House State Historic Site is located on Fair Street in Kingston, New York, United States. During the Revolutionary War, New York's First Constitutional Convention met there and on April 20, 1777, adopted the first New York State Constitution. After one month, the Senate fled the British troops who were advancing from Manhattan. The Senate House and much of Kingston was burned in retribution. It has served as a museum from the late 19th century. Currently it is owned and operated by the New York State Office of Parks, Recreation and Historic Preservation.
Fort Hunter is a hamlet in the Town of Florida in Montgomery County, New York, United States, west of the capital at Albany, on the south bank of the Mohawk River and on the northeast bank of Schoharie Creek.

The Stockade Historic District is located in the northwest corner of Schenectady, New York, United States, on the banks of the Mohawk River. It is the oldest neighborhood in the city, continuously inhabited for over 300 years. Union College first held classes in a building within the district, and later it would be one of the termini of an early suspension bridge that was, at the time, the longest in North America. Joseph C. Yates, the 7th Governor of New York and founding trustee of Union College, and Elizabeth V. Gillette, a physician and the first woman from upstate New York elected to the New York State Assembly, were residents of the Stockade.

The First Reformed Church, also known as First Church in Albany or North Dutch Church, is located at North Pearl and Orange streets in Albany, New York, United States. It is a member congregation of the Reformed Church in America. The building was designed by Philip Hooker and built in the period of 1797–1799. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1974.

The Kingston Stockade District is an eight-block area in the western section of Kingston, New York, United States, commonly referred to as Uptown Kingston. It is the original site of the mid-17th century Dutch settlement of Wiltwyck, which was later renamed Kingston when it passed to English control.

Old Lutheran Parsonage is a historic Lutheran church parsonage adjacent to Spring Street in Lutheran Cemetery in Schoharie, Schoharie County, New York. It was built in 1743 and is a 1+1⁄2-story building with basement. It is the oldest building in Schoharie County. And it's one of the oldest religious buildings remaining in New York State.

Van Alstyne Homestead is a historic home located at Canajoharie in Montgomery County, New York. It is a long, low rectangular house with a steeply pitched gambrel roof in the Dutch Colonial style. The original fieldstone house was built before 1730 and has three rooms with a garret under the roof. A 2+1⁄2-story frame addition runs across the rear.
One of New York State's 62 counties, Schoharie County was created with its own borders in 1795. The modern-day area of Schoharie County once fell under the boundaries of the expansive Albany County. Numerous times after the 1683 creation of Albany County, partitions of its area were divided up reassigning parts of the land under new dominions. Partitions that were designated in a 1795 change rendered a parcel to be known as Schoharie County from portions of Albany County's territory.

First Reformed Church of Schenectady is located at 8 North Church Street in the Historic Stockade District of Schenectady, New York and is a member of the Reformed Church in America. The church was first organized in 1680 by Dutch settlers and was the first church established in the Mohawk Valley. The church, along with the Stockade District were added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1973 and again with a boundary increase in 1984 (#73001267).