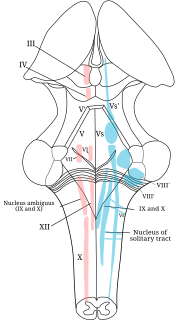Articles related to anatomy include:

The glossopharyngeal nerve, known as the ninth cranial nerve, is a mixed nerve that carries afferent sensory and efferent motor information. It exits the brainstem out from the sides of the upper medulla, just rostral to the vagus nerve. The motor division of the glossopharyngeal nerve is derived from the basal plate of the embryonic medulla oblongata, while the sensory division originates from the cranial neural crest.

The dorsal column–medial lemniscus pathway (DCML) is a sensory pathway of the central nervous system that conveys sensations of fine touch, vibration, two-point discrimination, and proprioception (position) from the skin and joints. It transmits information from the body to the primary somatosensory cortex in the postcentral gyrus of the parietal lobe of the brain. The pathway receives information from sensory receptors throughout the body, and carries this in nerve tracts in the white matter of the dorsal columns of the spinal cord, to the medulla where it is continued in the medial lemniscus, on to the thalamus and relayed from there through the internal capsule and transmitted to the somatosensory cortex. The name dorsal-column medial lemniscus comes from the two structures that carry the sensory information: the dorsal columns of the spinal cord, and the medial lemniscus in the brainstem.

The medial lemniscus, also known as Reil's band or Reil's ribbon, is a large ascending bundle of heavily myelinated axons that decussate in the brainstem, specifically in the medulla oblongata. The medial lemniscus is formed by the crossings of the internal arcuate fibers. The internal arcuate fibers are composed of axons of nucleus gracilis and nucleus cuneatus. The axons of the nucleus gracilis and nucleus cuneatus in the medial lemniscus have cell bodies that lie contralaterally.
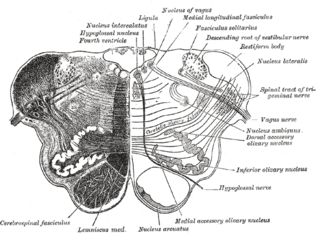
The nucleus ambiguus is a group of large motor neurons, situated deep in the medullary reticular formation named by Jacob Clarke. The nucleus ambiguus contains the cell bodies of nerves that innervate the muscles of the soft palate, pharynx, and larynx which are strongly associated with speech and swallowing. As well as motor neurons, the nucleus ambiguus in its "external formation" contains cholinergic preganglionic parasympathetic neurons for the heart.

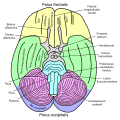
The fourth ventricle is one of the four connected fluid-filled cavities within the human brain. These cavities, known collectively as the ventricular system, consist of the left and right lateral ventricles, the third ventricle, and the fourth ventricle. The fourth ventricle extends from the cerebral aqueduct to the obex, and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).

One of the dorsal column nuclei, the cuneate nucleus is a wedge-shaped nucleus in the closed part of the medulla oblongata, in the brainstem. It contains cells that give rise to the cuneate tubercle, visible on the posterior aspect of the medulla. It lies lateral to the gracile nucleus and medial to the spinal trigeminal nucleus in the medulla.

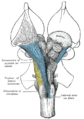
The upper part of the posterior district of the medulla oblongata is occupied by the inferior cerebellar peduncle, a thick rope-like strand situated between the lower part of the fourth ventricle and the roots of the glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves.
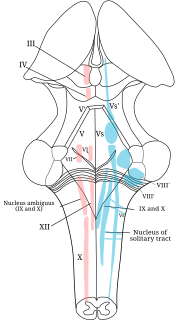
A cranial nerve nucleus is a collection of neurons in the brain stem that is associated with one or more cranial nerves. Axons carrying information to and from the cranial nerves form a synapse first at these nuclei. Lesions occurring at these nuclei can lead to effects resembling those seen by the severing of nerve(s) they are associated with. All the nuclei except that of the trochlear nerve supply nerves of the same side of the body.

In the medulla oblongata, the arcuate nucleus is a group of neurons located on the anterior surface of the medullary pyramids. These nuclei are the extension of the pontine nuclei. They receive fibers from the corticospinal tract and send their axons through the anterior external arcuate fibers and medullary striae to the cerebellum via the inferior cerebellar peduncle.

The cochlear nuclear (CN) complex comprises two cranial nerve nuclei in the human brainstem, the ventral cochlear nucleus (VCN) and the dorsal cochlear nucleus (DCN). The ventral cochlear nucleus is unlayered whereas the dorsal cochlear nucleus is layered. Auditory nerve fibers, fibers that travel through the auditory nerve carry information from the inner ear, the cochlea, on the same side of the head, to the nerve root in the ventral cochlear nucleus. At the nerve root the fibers branch to innervate the ventral cochlear nucleus and the deep layer of the dorsal cochlear nucleus. All acoustic information thus enters the brain through the cochlear nuclei, where the processing of acoustic information begins. The outputs from the cochlear nuclei are received in higher regions of the auditory brainstem.
Cerebellar peduncles connect the cerebellum to the brain stem. There are six cerebellar peduncles in total, three on each side:

The anterior external arcuate fibers vary as to their prominence: in some cases they form an almost continuous layer covering the medullary pyramids and olivary body, while in other cases they are barely visible on the surface.

The anterior median fissure contains a fold of pia mater, and extends along the entire length of the medulla oblongata: It ends at the lower border of the pons in a small triangular expansion, termed the foramen cecum.

In the ventral cochlear nucleus (VCN), auditory nerve fibers enter the brain via the nerve root in the VCN. The ventral cochlear nucleus is divided into the anterior ventral (anteroventral) cochlear nucleus (AVCN) and the posterior ventral (posteroventral) cochlear nucleus (PVCN). In the VCN, auditory nerve fibers bifurcate, the ascending branch innervates the AVCN and the descending branch innervates the PVCN and then continue to the dorsal cochlear nucleus. The orderly innervation by auditory nerve fibers gives the AVCN a tonotopic organization along the dorsoventral axis. Fibers that carry information from the apex of the cochlea that are tuned to low frequencies contact neurons in the ventral part of the AVCN; those that carry information from the base of the cochlea that are tuned to high frequencies contact neurons in the dorsal part of the AVCN. Several populations of neurons populate the AVCN. Bushy cells receive input from auditory nerve fibers through particularly large endings called end bulbs of Held. They contact stellate cells through more conventional boutons.