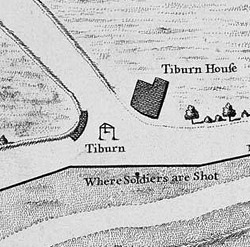
Tyburn was a manor (estate) in London, Middlesex, England, one of two which were served by the parish of Marylebone. Tyburn took its name from the Tyburn Brook, a tributary of the River Westbourne. The name Tyburn, from Teo Bourne, means 'boundary stream'.

Decapitation is the total separation of the head from the body. Such an injury is invariably fatal to humans and most other animals, since it deprives the brain of oxygenated blood by way of severing through the jugular vein and common carotid artery, while all other organs are deprived of the involuntary functions that are needed for the body to function. The term beheading refers to the act of deliberately decapitating a person, either as a means of murder or as an execution; it may be performed with an axe, sword, or knife, or by mechanical means such as a guillotine. An executioner who carries out executions by beheading is sometimes called a headsman. Accidental decapitation can be the result of an explosion, a car or industrial accident, improperly administered execution by hanging or other violent injury. The national laws of Saudi Arabia and Yemen permit beheading. Under Sharia, which exclusively applies to Muslims, beheading is also a legal punishment in Zamfara State, Nigeria. In practice, Saudi Arabia is the only country that continues to behead its offenders regularly as a punishment for capital crimes. Cases of decapitation by suicidal hanging, suicide by train decapitation and by guillotine are known.

Frank Costello was an Italian-American crime boss of the Luciano crime family.

Hanging is killing a person by suspending them from the neck with a noose or ligature. Hanging has been a common method of capital punishment since the Middle Ages, and has been the primary execution method in numerous countries and regions. The first known account of execution by hanging is in Homer's Odyssey. Hanging is also a method of suicide.
A gangster is a criminal who is a member of a gang. Most gangs are considered to be part of organized crime. Gangsters are also called mobsters, a term derived from mob and the suffix -ster. Gangs provide a level of organization and resources that support much larger and more complex criminal transactions than an individual criminal could achieve. Gangsters have been active for many years in countries around the world. Gangsters are the subject of many novels, films, television series, and video games.

A turnstile is a form of gate which allows one person to pass at a time. A turnstile can be configured to enforce one-way human traffic. In addition, a turnstile can restrict passage only to people who insert a coin, ticket, transit pass, security credential, or other method of payment or verification. Modern turnstiles can incorporate biometrics, including retina scanning, fingerprints, and other individual human characteristics which can be scanned. Thus a turnstile can be used in the case of paid access, for example to access public transport, a pay toilet, or to restrict access to authorized people, for example in the lobby of an office building.

Earl J. "Hymie" Weiss, was a Polish-American mob boss who became a leader of the Prohibition-era North Side Gang and a bitter rival of Al Capone. He was known as "the only man Al Capone feared".
Underworld is a 1927 American silent crime film directed by Josef von Sternberg and starring Clive Brook, Evelyn Brent and George Bancroft. The film launched Sternberg's eight-year collaboration with Paramount Pictures, with whom he would produce his seven films with actress Marlene Dietrich. Journalist and screenwriter Ben Hecht won an Academy Award for Best Original Story.

The St. Valentine's Day Massacre is a 1967 American gangster film based on the 1929 mass murder of seven members of Chicago's Northside Gang on orders from Al Capone. The picture was directed by Roger Corman, written by Howard Browne, and starring Jason Robards as Capone, Ralph Meeker as Moran, George Segal as Peter Gusenberg, and David Canary as Frank Gusenberg.
The Irish Mob is a usually crime family–based ethnic collective of organized crime syndicates composed of primarily ethnic Irish members which operate primarily in Ireland, the United States, the United Kingdom, Canada and Australia, and have been in existence since the early 19th century. Originating in Irish-American street gangs – famously first depicted in Herbert Asbury's 1927 book, The Gangs of New York – the Irish Mob has appeared in most major U.S. and Canadian cities, especially in the Northeast and the urban industrial Midwest, including Boston, New York City, Philadelphia, Pittsburgh, Baltimore, Cleveland, and Chicago.
Organised crime in India refers to organised crime elements originating in India and active in many parts of the world. The purpose of organised crime in India, as elsewhere in the world, is monetary gain. Its virulent form in modern times is due to several socio-economic and political factors and advances in science and technology. There is no firm data to indicate the number of organised criminal gangs operating in the country, their membership, their modus operandi, and the areas of their operations. Their structure and leadership patterns may not strictly fall in line with the classical Italian mafia.

Stateville Correctional Center (SCC) is a maximum security state prison for men in Crest Hill, Illinois, United States, near Chicago. It is a part of the Illinois Department of Corrections.

Albert W. Hicks, also known as Elias W. Hicks, William Johnson, John Hicks, and Pirate Hicks, was a triple murderer and one of the last people executed for piracy in the United States. Cultural historian Rich Cohen places him as the first New York City legendary gangster figure, a bridge between the piracy of old and the rise of a new "gangster nation".

The Atlantic City Conference held between 13–16 May 1929 was a historic summit of leaders of organized crime in the United States. It is considered by most crime historians to be the earliest organized crime summit held in the US. The conference had a major impact on the future direction of the criminal underworld and it held more importance and significance than the Havana Conference of 1946 and the Apalachin meeting of 1957. It also represented the first concrete move toward a National Crime Syndicate.

Frank McErlane (1894–1932) was a Prohibition-era Irish-American organized crime figure. He led the Saltis-McErlane Gang, allied with Rusyn American gangster Joseph Saltis and the Johnny Torrio-Al Capone led Chicago Outfit, against rival Irish-American bootleggers, the Southside O'Donnell Gang. He is credited with introducing the Thompson submachine gun to Chicago's underworld. The Illinois Crime Survey called him "the most brutal gunman who ever pulled a trigger in Chicago."

Little Caesar is a 1931 American pre-Code crime film distributed by Warner Brothers, directed by Mervyn LeRoy, and starring Edward G. Robinson, Douglas Fairbanks Jr. and Glenda Farrell. The film tells the story of a hoodlum who ascends the ranks of organized crime until he reaches its upper echelons.
The Spanish Gangster Disciples is a street gang that originated on the south side of Chicago, respectively in the vicinity of 88th & Houston in the South Chicago neighborhood. The gang was founded by Rudy Rios, who was a former member of the Latin Scorpions street gang. It is an offshoot from Gangster Disciples.

Charles Dean O'Banion was an American mobster who was the main rival of Johnny Torrio and Al Capone during the brutal Chicago bootlegging wars of the 1920s. The newspapers of his day made him better known as Dion O'Banion, although he never went by that first name. He led the North Side Gang until 1924, when he was shot and killed, reportedly by Frankie Yale, John Scalise and Albert Anselmi.
This is a glossary of words related to the Mafia, primarily the Sicilian Mafia and Italian American Mafia.
- administration: the top-level "management" of an organized crime family -- the boss, underboss and consigliere.
- associate: one who works with mobsters, but has not been asked to take the vow of Omertà; an almost confirmed, or made guy.
- bagman: a person or paymaster designated to collect or distribute illicitly gained money.
- barone: a baron or landlord.
- books, the: a phrase indicating membership in the family. If there is a possibility for membership, then the books are open. If not, the books are closed.
- boss: the head of the family who runs the operation. The boss also gets points from all family business; also see don, chairman.
- bridge: threat of death; e.g. "our former friend is walking across the bridge".
- button or becoming a button man: a mafia hit man; or someone who has become a made man.
- capo: the family member who leads a crew; short for caporegime or capodecina.
- capo dei capi: "boss of all [the] bosses" is a phrase used mainly by the media, public and the law enforcement community to indicate a supremely powerful crime boss in the Sicilian or American Mafia who holds great influence over the whole organization.
- captain: a capo.
- cement shoes: a method of murder or body disposal, usually associated with criminals such as the Mafia or gangs. It involves weighting down the victim, who may be dead or alive, with concrete and throwing them into water in the hope the body will never be found.
- clip: to murder; also to whack, hit, pop, burn, ice, put a contract out on.
- code of silence: not ratting on one's colleagues once one has been pinched -- no longer a strong virtue in organized crime families. Also, see omertà.
- comare: literally "godmother" in Southern Italian slang, usually pronounced "goomah" or "goomar" in American English: a Mafia mistress.
- confirm: to be made; see made guy.
- connected guy: an associate
- consigliere: the family adviser, who is always consulted before decisions are made.
- Cosa Nostra (Our thing): mob term for the family or Mafia
- crank: speed; in particular, crystal meth.
- crew: the group of soldiers under the capo's command.
- cugine: a young soldier striving to be made.
- don: the head of the family; see boss.
- earner: a member who brings in much money for the family.
- eat alone: to keep for oneself; to be greedy.
- family: an organized crime clan.
- forget about it (often pronounced "fuggedaboutit"): An exclamation; as the title character explains in Donnie Brasco:
"Forget about it" is, like, if you agree with someone, you know, like "Raquel Welch is one great piece of ass. Forget about it!" But then, if you disagree, like "A Lincoln is better than a Cadillac? Forget about it!" You know? But then, it's also like if something's the greatest thing in the world, like, "Minchia! Those peppers! Forget about it!" But it's also like saying "Go to hell!" too. Like, you know, like "Hey Paulie, you got a one-inch pecker?" and Paulie says "Forget about it!" Sometimes it just means "Forget about it."
- friend: "a friend of mine" is an associate, "a friend of ours" is a made man.
- G: a grand; a thousand dollars; also see large.
- garbage business: euphemism for organized crime.
- Golden Age: The days before RICO.
- Goodfella: A member of the Mafia.
- goomar or goomah: Americanized form of comare, a Mafia mistress.
- goombah: an associate, especially a senior member of a criminal gang.
- heavy: packed, carrying a weapon.
- hit: to murder; also see whack.
- initiation or induction: becoming a made man.
- juice: the interest paid to a loan shark for the loan; also see vig.
- kick up: give a part of the income to the next up in the command chain.
- lam: To lay down, go into hiding.
- large: a thousand, a grand, a G.
- LCN: abbreviation for La Cosa Nostra.
- lupara bianca: a journalistic term to indicate a Mafia slaying done in such a way that the victim's body is never found.
- made man: an inducted member of the family.
- make one's bones: gain credibility by killing someone.
- mock execution: to whip someone into shape by frightening them.
- mattresses, going to, taking it to, or hitting the: going to war with a rival clan or family.
- message job: placing the bullet in someone's body such that a specific message is sent to that person's crew or family; see through the eye and through the mouth.
- mob, the: a single organized crime family; or all organized crime families together.
- mobbed up: connected to the mob.
- mobster: one who is in the mob.
- oath: becoming inducted as a made man.
- Omertà: to take a vow of silence in the Mafia, punishable by death if not upheld.
- one-way ride or taking someone for a ride: underworld for an execution method
- outfit: a clan, or family within the Mafia.
- old country: refers to Italy when used by members of the American Mafia
- painting houses: murdering someone
- pass: A reprieve from being whacked.
- paying tribute: giving the boss a cut of the deal.
- pinched: to get caught by the cops or federal agents.
- points: percent of income; cut.
- program, the: The Witness Protection Program.
- rat: someone who turns informant, snitches or squeals after having been pinched.
- RICO: Racketeer Influenced and Corrupt Organizations Act. Passed in 1970 to aid the American government in clamping down on organized crime activities, its scope has since been broadened to prosecute insider traders.
- sent for: to be ordered to a meeting with other mob members and being whacked.
- shakedown: to blackmail or try to get money from someone; also to give someone a scare.
- shy: the interest charged on loans by loan sharks.
- shylock business: the business of loansharking.
- sitdown: a meeting, esp. with another family.
- soldier: the bottom-level member of an organized crime family who is made.
- spring cleaning: cleaning up, hiding or getting rid of evidence.
- straighten out, getting straightened out: becoming a made guy.
- tax: to take a percentage of someone's earnings.
- The Commission and the Sicilian Mafia Commission: two bodies, Italian-American and the Sicilian respectively, of leading Mafia members to decide on important questions concerning the actions of, and settling disputes within the Mafia.
- This Thing of Ours (Cosa Nostra): a mob family, or the entire mob.
- through the eye: a message job through the eye to say "We're watching you!"
- through the mouth: a message job through the mouth to indicate that someone WAS a rat.
- underboss: the second in command to the boss.
- vig: Vigorish abbr. the house's or bookie's take in gambling or the interest paid to a loan shark for the loan; also see juice.
- waste management business: euphemism for organized crime.
- whack: to murder; also clip, hit, pop, burn, put a contract out.
- wiseguy: a made man.
- zips: is a slang term often used as a derogatory slur by Italian American and Sicilian American mobsters in reference to newer immigrant Sicilian and Italian mafiosi.

The ancient Mesopotamian underworld, was the lowermost part of the ancient near eastern cosmos, roughly parallel to the region known as Tartarus from early Greek cosmology. It was described as a dark, dreary cavern located deep below the ground, where inhabitants were believed to continue "a transpositional version of life on earth". The only food or drink was dry dust, but family members of the deceased would pour sacred mineral libations from the earth for them to drink. In the Sumerian underworld, it was initially believed that there was no final judgement of the deceased and the dead were neither punished nor rewarded for their deeds in life.













