
In geometry a quadrilateral is a four-sided polygon, having four edges (sides) and four corners (vertices). The word is derived from the Latin words quadri, a variant of four, and latus, meaning "side". It is also called a tetragon, derived from Greek "tetra" meaning "four" and "gon" meaning "corner" or "angle", in analogy to other polygons. Since "gon" means "angle", it is analogously called a quadrangle, or 4-angle. A quadrilateral with vertices , , and is sometimes denoted as .

A triangle is a polygon with three corners and three sides, one of the basic shapes in geometry. The corners, also called vertices, are zero-dimensional points while the sides connecting them, also called edges, are one-dimensional line segments. The triangle's interior is a two-dimensional region. Sometimes an arbitrary edge is chosen to be the base, in which case the opposite vertex is called the apex.
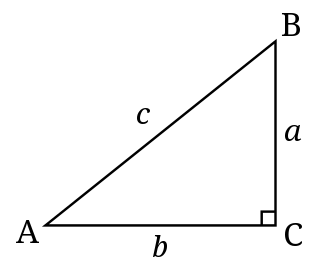
A right triangle or right-angled triangle, sometimes called an orthogonal triangle or rectangular triangle, is a triangle in which two sides are perpendicular, forming a right angle.

In mathematics, a great circle or orthodrome is the circular intersection of a sphere and a plane passing through the sphere's center point.

In geometry, an altitude of a triangle is a line segment through a vertex and perpendicular to a line containing the side opposite the vertex. This line containing the opposite side is called the extended base of the altitude. The intersection of the extended base and the altitude is called the foot of the altitude. The length of the altitude, often simply called "the altitude", is the distance between the extended base and the vertex. The process of drawing the altitude from the vertex to the foot is known as dropping the altitude at that vertex. It is a special case of orthogonal projection.

In geometry, an equilateral triangle is a triangle in which all three sides have the same length. In the familiar Euclidean geometry, an equilateral triangle is also equiangular; that is, all three internal angles are also congruent to each other and are each 60°. It is also a regular polygon, so it is also referred to as a regular triangle.
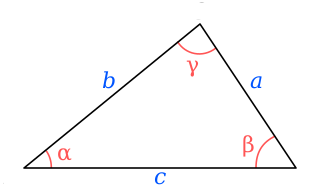
In geometry, Heron's formula gives the area of a triangle in terms of the three side lengths Letting be the semiperimeter of the triangle, the area is

In Euclidean geometry, a cyclic quadrilateral or inscribed quadrilateral is a quadrilateral whose vertices all lie on a single circle. This circle is called the circumcircle or circumscribed circle, and the vertices are said to be concyclic. The center of the circle and its radius are called the circumcenter and the circumradius respectively. Other names for these quadrilaterals are concyclic quadrilateral and chordal quadrilateral, the latter since the sides of the quadrilateral are chords of the circumcircle. Usually the quadrilateral is assumed to be convex, but there are also crossed cyclic quadrilaterals. The formulas and properties given below are valid in the convex case.

In mathematics, the inverse trigonometric functions are the inverse functions of the trigonometric functions. Specifically, they are the inverses of the sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant, and cosecant functions, and are used to obtain an angle from any of the angle's trigonometric ratios. Inverse trigonometric functions are widely used in engineering, navigation, physics, and geometry.

Spherical trigonometry is the branch of spherical geometry that deals with the metrical relationships between the sides and angles of spherical triangles, traditionally expressed using trigonometric functions. On the sphere, geodesics are great circles. Spherical trigonometry is of great importance for calculations in astronomy, geodesy, and navigation.

A cone is a three-dimensional geometric shape that tapers smoothly from a flat base to a point called the apex or vertex.
In geometry, the circumscribed circle or circumcircle of a triangle is a circle that passes through all three vertices. The center of this circle is called the circumcenter of the triangle, and its radius is called the circumradius. The circumcenter is the point of intersection between the three perpendicular bisectors of the triangle's sides, and is a triangle center.

In mathematics, sine and cosine are trigonometric functions of an angle. The sine and cosine of an acute angle are defined in the context of a right triangle: for the specified angle, its sine is the ratio of the length of the side that is opposite that angle to the length of the longest side of the triangle, and the cosine is the ratio of the length of the adjacent leg to that of the hypotenuse. For an angle , the sine and cosine functions are denoted as and .
In mathematics, the Hadwiger–Finsler inequality is a result on the geometry of triangles in the Euclidean plane. It states that if a triangle in the plane has side lengths a, b and c and area T, then
In geometry, the Conway triangle notation, named after John Horton Conway, allows trigonometric functions of a triangle to be managed algebraically. Given a reference triangle whose sides are a, b and c and whose corresponding internal angles are A, B, and C then the Conway triangle notation is simply represented as follows:
In hyperbolic geometry, the "law of cosines" is a pair of theorems relating the sides and angles of triangles on a hyperbolic plane, analogous to the planar law of cosines from plane trigonometry, or the spherical law of cosines in spherical trigonometry. It can also be related to the relativistic velocity addition formula.
Solution of triangles is the main trigonometric problem of finding the characteristics of a triangle, when some of these are known. The triangle can be located on a plane or on a sphere. Applications requiring triangle solutions include geodesy, astronomy, construction, and navigation.
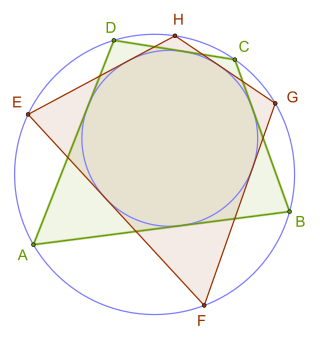
In Euclidean geometry, a bicentric quadrilateral is a convex quadrilateral that has both an incircle and a circumcircle. The radii and centers of these circles are called inradius and circumradius, and incenter and circumcenter respectively. From the definition it follows that bicentric quadrilaterals have all the properties of both tangential quadrilaterals and cyclic quadrilaterals. Other names for these quadrilaterals are chord-tangent quadrilateral and inscribed and circumscribed quadrilateral. It has also rarely been called a double circle quadrilateral and double scribed quadrilateral.
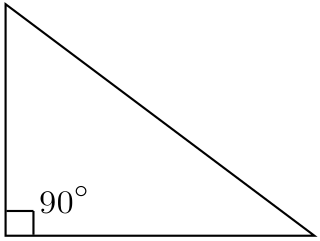
An acute triangle is a triangle with three acute angles. An obtuse triangle is a triangle with one obtuse angle and two acute angles. Since a triangle's angles must sum to 180° in Euclidean geometry, no Euclidean triangle can have more than one obtuse angle. Acute and obtuse triangles are the two different types of oblique triangles — triangles that are not right triangles because they do not have a 90° angle.






















