
Galeon is a discontinued Gecko-based web browser that was created by Marco Pesenti Gritti with the goal of delivering a consistent browsing experience to GNOME desktop environment. It gained some popularity in the early 2000s due to its speed, flexibility in configuration and features.

The Semantic Web, sometimes known as Web 3.0, is an extension of the World Wide Web through standards set by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). The goal of the Semantic Web is to make Internet data machine-readable.
A web browser is an application for accessing websites. When a user requests a web page from a particular website, the browser retrieves its files from a web server and then displays the page on the user's screen. Browsers are used on a range of devices, including desktops, laptops, tablets, and smartphones. In 2020, an estimated 4.9 billion people have used a browser. The most-used browser is Google Chrome, with a 64% global market share on all devices, followed by Safari with 19%.
In connection-oriented communication, a data stream is the transmission of a sequence of digitally encoded signals to convey information. Typically, the transmitted symbols are grouped into a series of packets.
Google Desktop was a computer program with desktop search capabilities, created by Google for Linux, Apple Mac OS X, and Microsoft Windows systems. It allowed text searches of a user's email messages, computer files, music, photos, chats, Web pages viewed, and the ability to display "Google Gadgets" on the user's desktop in a Sidebar.
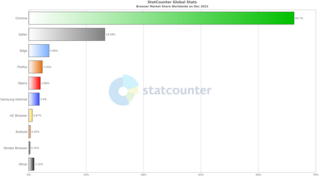
The usage share of web browsers is the portion, often expressed as a percentage, of visitors to a group of web sites that use a particular web browser.

In computing, a news aggregator, also termed a feed aggregator, content aggregator, feed reader, news reader, or simply an aggregator, is client software or a web application that aggregates digital content such as online newspapers, blogs, podcasts, and video blogs (vlogs) in one location for easy viewing. The updates distributed may include journal tables of contents, podcasts, videos, and news items.

The Mozilla Calendar Project was the name for the Mozilla project that led to the development of Sunbird calendar application and the Lightning integrated calendar. Sunbird and Lightning are both free software, released under the Mozilla tri-license: the Mozilla Public License, the GNU General Public License and the GNU Lesser General Public License.
In computer science, the semantic desktop is a collective term for ideas related to changing a computer's user interface and data handling capabilities so that data are more easily shared between different applications or tasks and so that data that once could not be automatically processed by a computer could be. It also encompasses some ideas about being able to share information automatically between different people. This concept is very much related to the Semantic Web, but is distinct insofar as its main concern is the personal use of information.
NEPOMUK is an open-source software specification that is concerned with the development of a social semantic desktop that enriches and interconnects data from different desktop applications using semantic metadata stored as RDF. Between 2006 and 2008 it was funded by a European Union research project of the same name that grouped together industrial and academic actors to develop various Semantic Desktop technologies.
CALO was an artificial intelligence project that attempted to integrate numerous AI technologies into a cognitive assistant. CALO is an acronym for "Cognitive Assistant that Learns and Organizes". The name was inspired by the Latin word "Calo" which means "soldier's servant". The project started in May 2003 and ran for five years, ending in 2008.
EGroupware is free open-source groupware software intended for businesses from small to enterprises. Its primary functions allow users to manage contacts, appointments, projects and to-do lists. The project releases its software under the terms of GNU General Public License (GPL).
O3Spaces is a document management system developed by O3Spaces B.V.. It is built by a team of software engineers based in the Netherlands using OpenOffice.org, StarOffice, and ODF-centric applications as enterprise office and collaboration solutions. The product is written in Java, and based on the Tomcat server with a PostgreSQL backend. O3Spaces works by providing users a single web-based team environment, with built-in search capabilities and an optional Desktop Assistant. Its search functionality is said to work across PDF, ODF, and Microsoft Office document formats. Currently Firefox, Internet Explorer and Safari are supported.

A selection-based search system is a search engine system in which the user invokes a search query using only the mouse. A selection-based search system allows the user to search the internet for more information about any keyword or phrase contained within a document or webpage in any software application on their desktop computer using the mouse.
Collaborative search engines (CSE) are Web search engines and enterprise searches within company intranets that let users combine their efforts in information retrieval (IR) activities, share information resources collaboratively using knowledge tags, and allow experts to guide less experienced people through their searches. Collaboration partners do so by providing query terms, collective tagging, adding comments or opinions, rating search results, and links clicked of former (successful) IR activities to users having the same or a related information need.

Web browsing history refers to the list of web pages a user has visited, as well as associated metadata such as page title and time of visit. It is usually stored locally by web browsers in order to provide the user with a history list to go back to previously visited pages. It can reflect the user's interests, needs, and browsing habits.

Adam Cheyer is a co-founder of Siri Inc. and formerly a director of engineering in the iPhone group at Apple.
Mozilla is a free software community founded in 1998 by members of Netscape. The Mozilla community uses, develops, publishes and supports Mozilla products, thereby promoting exclusively free software and open standards, with only minor exceptions. The community is supported institutionally by the non-profit Mozilla Foundation and its tax-paying subsidiary, the Mozilla Corporation.









