The hacker ethic is a philosophy and set of moral values within hacker culture. Practitioners believe that sharing information and data with others is an ethical imperative. The hacker ethic is related to the concept of freedom of information, as well as the political theories of anti-authoritarianism, anarchism, and libertarianism.
The Open Source Definition (OSD) is a document published by the Open Source Initiative. Derived from Bruce Perens' Debian Free Software Guidelines, the definition is the most common standard for open-source software. The definition has ten criteria, such as requiring freely accessed source code and granting the open-source rights to everyone who receives a copy of the program. Covering both copyleft and permissive licenses, it is effectively identical to the definition of free software, but motivated by more pragmatic and business-friendly considerations. The Open Source Initiative's board votes on proposals of licenses to certify that they are compliant with the definition, and maintains a list of compliant licenses on its website. The definition has been adapted into the Open Knowledge Foundation's Open Definition for open knowledge and into open hardware definitions.

The Open Source Initiative (OSI) is the steward of the Open Source Definition, the most widely used standard for open-source software.
An open standard is a standard that is openly accessible and usable by anyone. It is also a common prerequisite that open standards use an open license that provides for extensibility. Typically, anybody can participate in their development due to their inherently open nature. There is no single definition, and interpretations vary with usage. Examples of open standards include the GSM, 4G, and 5G standards that allow most modern mobile phones to work world-wide.

Open-source software (OSS) is computer software that is released under a license in which the copyright holder grants users the rights to use, study, change, and distribute the software and its source code to anyone and for any purpose. Open-source software may be developed in a collaborative, public manner. Open-source software is a prominent example of open collaboration, meaning any capable user is able to participate online in development, making the number of possible contributors indefinite. The ability to examine the code facilitates public trust in the software.
As an ethic that spans science, engineering, business, and the humanities, transparency is operating in such a way that it is easy for others to see what actions are performed. Transparency implies openness, communication, and accountability.
Openness is an overarching concept that is characterized by an emphasis on transparency and collaboration. That is, openness refers to "accessibility of knowledge, technology and other resources; the transparency of action; the permeability of organisational structures; and the inclusiveness of participation". Openness can be said to be the opposite of closedness, central authority and secrecy.

The open-design movement involves the development of physical products, machines and systems through use of publicly shared design information. This includes the making of both free and open-source software (FOSS) as well as open-source hardware. The process is generally facilitated by the Internet and often performed without monetary compensation. The goals and philosophy of the movement are identical to that of the open-source movement, but are implemented for the development of physical products rather than software. Open design is a form of co-creation, where the final product is designed by the users, rather than an external stakeholder such as a private company.

Open-source hardware consists of physical artifacts of technology designed and offered by the open-design movement. Both free and open-source software (FOSS) and open-source hardware are created by this open-source culture movement and apply a like concept to a variety of components. It is sometimes, thus, referred to as FOSH. The term usually means that information about the hardware is easily discerned so that others can make it – coupling it closely to the maker movement. Hardware design, in addition to the software that drives the hardware, are all released under free/libre terms. The original sharer gains feedback and potentially improvements on the design from the FOSH community. There is now significant evidence that such sharing can drive a high return on investment for the scientific community.
Commons-based peer production (CBPP) is a term coined by Harvard Law School professor Yochai Benkler. It describes a model of socio-economic production in which large numbers of people work cooperatively; usually over the Internet. Commons-based projects generally have less rigid hierarchical structures than those under more traditional business models.

Free and open-source software (FOSS) is software that is available under a license that grants the right to use, modify, and distribute the software, modified or not, to everyone free of charge. The public availability of the source code is, therefore, a necessary but not sufficient condition. FOSS is an inclusive umbrella term for free software and open-source software. FOSS is in contrast to proprietary software, where the software is under restrictive copyright or licensing and the source code is hidden from the users.

Noolaham Foundation is a legally registered, non-profit, non-partisan, secular entity, founded to provide enhanced access to information sources and foster knowledge-based development in Sri Lanka. It maintains an online digital library and archive, facilitates information preservation programs, provides financial assistance and technical guidance for digitization initiatives and actively participates in awareness-raising campaigns. It also co-ordinates a range of fund-raising activities and collaborates with other organizations and individuals.
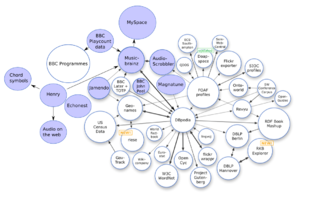
Open data is data that is openly accessible, exploitable, editable and shareable by anyone for any purpose. Open data is licensed under an open license.
The open-source-software movement is a social movement that supports the use of open-source licenses for some or all software, as part of the broader notion of open collaboration. The open-source movement was started to spread the concept/idea of open-source software.

Open educational practices (OEP) are part of the broader open education landscape, including the openness movement in general. It is a term with multiple layers and dimensions and is often used interchangeably with open pedagogy or open practices. OEP represent teaching and learning techniques that draw upon open and participatory technologies and high-quality open educational resources (OER) in order to facilitate collaborative and flexible learning. Because OEP emerged from the study of OER, there is a strong connection between the two concepts. OEP, for example, often, but not always, involve the application of OER to the teaching and learning process. Open educational practices aim to take the focus beyond building further access to OER and consider how in practice, such resources support education and promote quality and innovation in teaching and learning. The focus in OEP is on reproduction/understanding, connecting information, application, competence, and responsibility rather than the availability of good resources. OEP is a broad concept which can be characterised by a range of collaborative pedagogical practices that include the use, reuse, and creation of OER and that often employ social and participatory technologies for interaction, peer-learning, knowledge creation and sharing, empowerment of learners, and open sharing of teaching practices.
The digital commons are a form of commons involving the distribution and communal ownership of informational resources and technology. Resources are typically designed to be used by the community by which they are created.

In R&D management and systems development, open coopetition or open-coopetition is a neologism to describe cooperation among competitors in the open-source arena. The term was first coined by the scholars Jose Teixeira and Tingting Lin to describe how rival firms that, while competing with similar products in the same markets, cooperate which each other in the development of open-source projects in the co-development of WebKit.
InnerSource is the use of open source software development best practices and the establishment of an open source-like culture within organizations for the development of its non-open-source and/or proprietary software. The term was coined by Tim O'Reilly in 2000 in his column.
Internet universality is a concept and framework adopted by UNESCO in 2015 to summarize their position on the internet. The concept recognizes that "the Internet is much more than infrastructure and applications; it is a network of economic and social interactions and relationships, which has the potential to enable human rights, empower individuals and communities, and facilitate sustainable development." The concept is based on four principles agreed upon by UNESCO member states: human rights, openness, accessibility, and multi-stakeholder participation, abbreviated as the R-O-A-M principles.

Open source is source code that is made freely available for possible modification and redistribution. Products include permission to use the source code, design documents, or content of the product. The open source model is a decentralized software development model that encourages open collaboration. A main principle of open source software development is peer production, with products such as source code, blueprints, and documentation freely available to the public. The open source movement in software began as a response to the limitations of proprietary code. The model is used for projects such as in open source appropriate technology, and open source drug discovery.








