
The United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child is an international human rights treaty which sets out the civil, political, economic, social, health and cultural rights of children. The Convention defines a child as any human being under the age of eighteen, unless the age of majority is attained earlier under national legislation.

The Optional Protocol to the Convention on the Rights of the Child on the Involvement of Children in Armed Conflict (OPAC), also known as the child soldier treaty, is a multilateral treaty whereby states agree to: 1) prohibit the conscription into the military of children under the age of 18; 2) ensure that military recruits are no younger than 16; and 3) prevent recruits aged 16 or 17 from taking a direct part in hostilities. The treaty also forbids non-state armed groups from recruiting anyone under the age of 18 for any purpose.
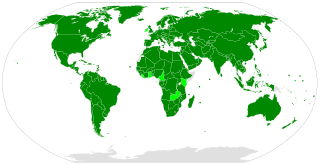
The Optional Protocol on the Sale of Children, Child Prostitution and Child Pornography is a protocol to the Convention on the Rights of the Child and requires parties to prohibit the sale of children, child prostitution and child pornography.

The Committee on the Rights of the Child (CRC) is a body of experts that monitor and report on the implementation of the United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child.

Human rights are largely respected in Switzerland, one of Europe's oldest democracies. Switzerland is often at or near the top in international rankings of civil liberties and political rights observance. Switzerland places human rights at the core of the nation's value system, as represented in its Federal Constitution. As described in its FDFA's Foreign Policy Strategy 2016-2019, the promotion of peace, mutual respect, equality and non-discrimination are central to the country's foreign relations.

The U.S. Department of State's Country Report on Human Rights Practices for São Tomé and Príncipe states that the government generally respects the human rights of its citizens, despite problems in a few areas.

Human rights in Somalia throughout the late 20th-century and early 21st-century were considered dire, but have gradually improved over the following years. Human rights are guaranteed in the Federal Constitution, which was adopted in August 2012. They fall under the Ministry of Human Rights established in August 2013. The central authorities concurrently inaugurated a National Human Rights Day, endorsed an official Human Rights Roadmap, and completed Somalia's first National Gender Policy.

Human rights in Chad have been described as "poor"; for example, Freedom House has designated the country as "Not Free." Chad received a score of 7 for political rights and 6 for civil liberties.

The Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities is an international human rights treaty of the United Nations intended to protect the rights and dignity of persons with disabilities. Parties to the convention are required to promote, protect, and ensure the full enjoyment of human rights by persons with disabilities and ensure that persons with disabilities enjoy full equality under the law. The Convention serves as a major catalyst in the global disability rights movement enabling a shift from viewing persons with disabilities as objects of charity, medical treatment and social protection towards viewing them as full and equal members of society, with human rights. The convention was the first U.N. human rights treaty of the twenty-first century.
The Optional Protocol to the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination against Women (OP-CEDAW) is an international treaty which establishes complaint and inquiry mechanisms for the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW). Parties to the Protocol allow the Committee on the Elimination of Discrimination against Women to hear complaints from individuals or inquire into "grave or systematic violations" of the convention. The Protocol has led to a number of decisions against member states on issues such as domestic violence, parental leave and forced sterilization, as well as an investigation into the systematic killing of women in the Mexican city of Ciudad Juárez, Chihuahua.

The First Optional Protocol to the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights is an international treaty establishing an individual complaint mechanism for the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR). It was adopted by the UN General Assembly on 16/12/1966, and entered into force on 23/03/1976. As of 05/2020, it had 116 state parties and 35 signatories. Two of the ratifying states have denounced the protocol.

Human rights in Madagascar are protected under the national constitution. However, the extent to which such rights are reflected in practice, is subject to debate. The 2009 Human Rights Report by the United States Department of State noted concerns regarding the suspension of democratic electoral processes as the result of recent political unrest. Furthermore, reports of corruption, arbitrary arrest and child labor highlight the prevalence of human rights issues in the country.

Human rights in Botswana are protected under the constitution. The 2009 Human Rights Report by the United States Department of State noted that in general the government of Botswana has respected the rights of its citizens.

Human rights in Cameroon are addressed in the constitution. However, the 2009 Human Rights Report by the United States Department of State noted concerns in regard to election irregularities, security forces torture and arbitrary arrests.

Human rights in Cape Verde are addressed under the national constitution.

Human rights in Burkina Faso are addressed in its constitution, which was ratified in 1991. The 2009 Human Rights Report by the United States Department of State noted concerns regarding restrictions on the press and the operation of the judiciary system. In its 2021 report, Human Rights Watch described the human rights situation in Burkina Faso as being "precarious" in light of ongoing violence committed by Islamists, government security forces, and pro-government militias.
The Committee on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities is a United Nations body of 18 experts that meets two times a year in Geneva to consider the reports submitted by 164 UN member states on their compliance with the Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (CRPD), and to examine individual petitions concerning 94 States Parties to the Optional Protocol.

Human rights are "rights and freedoms to which all humans are entitled". Proponents of the concept usually assert that everyone is endowed with certain entitlements merely by reason of being human.

Equatorial Guinea is known for human rights abuses. Under the current government it has "limited ability of citizens to change their government; increased reports of unlawful murders of civilians by security forces; government-sanctioned kidnappings; systematic torture of prisoners and detainees by security forces; life threatening conditions in prisons and detention facilities; impunity; arbitrary arrest and detention and incommunicado detention; harassment and deportation of foreign residents with limited due process; judicial corruption and lack of due process; restrictions on the right to privacy; restrictions on freedom of speech and of the press; restrictions on the rights of assembly, association, and movement; government corruption; violence and discrimination against women; suspected trafficking in persons; discrimination against ethnic minorities; and restrictions on labor rights."

















