Related Research Articles

An alphabet is a standardized set of basic written graphemes that represent the phonemes of certain spoken languages. Not all writing systems represent language in this way; in a syllabary, each character represents a syllable, and logographic systems use characters to represent words, morphemes, or other semantic units.

The Egyptian language or Ancient Egyptian is a dead Afro-Asiatic language that was spoken in ancient Egypt. It is known today from a large corpus of surviving texts which were made accessible to the modern world following the decipherment of the ancient Egyptian scripts in the early 19th century. Egyptian is one of the earliest written languages, first being recorded in the hieroglyphic script in the late 4th millennium BC. It is also the longest-attested human language, with a written record spanning over 4000 years. Its classical form is known as Middle Egyptian, the vernacular of the Middle Kingdom of Egypt which remained the literary language of Egypt until the Roman period. By the time of classical antiquity the spoken language had evolved into Demotic, and by the Roman era it had diversified into the Coptic dialects. These were eventually supplanted by Arabic after the Muslim conquest of Egypt, although Bohairic Coptic remains in use as the liturgical language of the Coptic Church.

Jean-François Champollion, also known as Champollion le jeune, was a French philologist and orientalist, known primarily as the decipherer of Egyptian hieroglyphs and a founding figure in the field of Egyptology. Partially raised by his brother, the scholar Jacques Joseph Champollion-Figeac, Champollion was a child prodigy in philology, giving his first public paper on the decipherment of Demotic in his mid-teens. As a young man he was renowned in scientific circles, and spoke Coptic, Ancient Greek, Latin, Hebrew and Arabic.
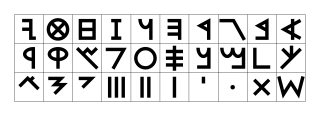
The Phoenician alphabet is an alphabet known in modern times from the Canaanite and Aramaic inscriptions found across the Mediterranean region. The name comes from the Phoenician civilization.

Hieratic is the name given to a cursive writing system used for Ancient Egyptian and the principal script used to write that language from its development in the third millennium BC until the rise of Demotic in the mid-first millennium BC. It was primarily written in ink with a reed pen on papyrus.

Sir Alan Henderson Gardiner, was an English Egyptologist, linguist, philologist, and independent scholar. He is regarded as one of the premier Egyptologists of the early and mid-20th century.

The Paleo-Hebrew script, also Palaeo-Hebrew, Proto-Hebrew or Old Hebrew, is the writing system found in Canaanite inscriptions from the region of biblical Israel and Judah. It is considered to be the script used to record the original texts of the Hebrew Bible due to its similarity to the Samaritan script, as the Talmud stated that the Hebrew ancient script was still used by the Samaritans. The Talmud described it as the "Libona'a script", translated by some as "Lebanon script". Use of the term "Paleo-Hebrew alphabet" is due to a 1954 suggestion by Solomon Birnbaum, who argued that "[t]o apply the term Phoenician to the script of the Hebrews is hardly suitable".
Ayin is the sixteenth letter of the Semitic scripts, including Phoenician ʿayin, Hebrew ʿayinע, Aramaic ʿē, Syriac ʿē ܥ, and Arabic ʿayn ع.

Proto-Sinaitic is considered the earliest trace of alphabetic writing and the common ancestor of both the Ancient South Arabian script and the Phoenician alphabet, which led to many modern alphabets including the Greek alphabet. According to common theory, Canaanites or Hyksos who spoke a Semitic language repurposed Egyptian hieroglyphs to construct a different script. The script is attested in a small corpus of inscriptions found at Serabit el-Khadim in the Sinai Peninsula, Egypt, dating to the Middle Bronze Age.
The history of the alphabet goes back to the conwriting system used for Semitic languages in the Levant in the 2nd millennium BCE. Most or nearly all alphabetic scripts used throughout the world today ultimately go back to this Semitic proto-alphabet. Its first origins can be traced back to a Proto-Sinaitic script developed in Ancient Egypt to represent the language of Semitic-speaking workers and slaves in Egypt. Unskilled in the complex hieroglyphic system used to write the Egyptian language, which required a large number of pictograms, they selected a small number of those commonly seen in their Egyptian surroundings to describe the sounds, as opposed to the semantic values, of their own Canaanite language. This script was partly influenced by the older Egyptian hieratic, a cursive script related to Egyptian hieroglyphs. The Semitic alphabet became the ancestor of multiple writing systems across the Middle East, Europe, northern Africa, and Pakistan, mainly through Ancient South Arabian, Phoenician, Paleo-Hebrew and later Aramaic, four closely related members of the Semitic family of scripts that were in use during the early first millennium BCE.

Ibn Waḥshiyya, died c. 930, was a Nabataean agriculturalist, toxicologist, and alchemist born in Qussīn, near Kufa in Iraq. He is the author of the Nabataean Agriculture, an influential Arabic work on agriculture, astrology, and magic.
Barry John Kemp, is an English archaeologist and Egyptologist. He is Professor Emeritus of Egyptology at the University of Cambridge and directing excavations at Amarna in Egypt. His widely renowned book Ancient Egypt: Anatomy of a Civilisation is a core text of Egyptology and many Ancient History courses.

The writing systems used in ancient Egypt were deciphered in the early nineteenth century through the work of several European scholars, especially Jean-François Champollion and Thomas Young. Ancient Egyptian forms of writing, which included the hieroglyphic, hieratic and demotic scripts, ceased to be understood in the fourth and fifth centuries AD, as the Coptic alphabet was increasingly used in their place. Later generations' knowledge of the older scripts was based on the work of Greek and Roman authors whose understanding was faulty. It was thus widely believed that Egyptian scripts were exclusively ideographic, representing ideas rather than sounds, and even that hieroglyphs were an esoteric, mystical script rather than a means of recording a spoken language. Some attempts at decipherment by Islamic and European scholars in the Middle Ages and early modern times acknowledged the script might have a phonetic component, but perception of hieroglyphs as purely ideographic hampered efforts to understand them as late as the eighteenth century.
Pr is the hieroglyph for 'house', the floor-plan of a walled building with an open doorway.
Miriam Lichtheim was a Turkish-born American-Israeli Egyptologist, known for her translations of ancient Egyptian texts.
Hans Jakob Polotsky was an Israeli orientalist, linguist, and professor of Semitic languages and Egyptology at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem.

Sarah Israelit Groll was an Israeli Egyptologist and linguist.

Wadi el-Hol is a valley on the Farshut Road, north-west of Luxor on the Qena Bend, situated on the west bank of the river Nile in Egypt. Rock inscriptions in the valley appear to show the oldest examples of phonetic alphabetic writing discovered to date.

Karl Richard Lepsius was a pioneering Prussian Egyptologist, linguist and modern archaeologist.

Professor Zipora Cochavi-Rainey born December 1954 in Petach Tikva, Israel, is a linguist and scholar in the Department of Hebrew Language at Beit Berl College, Israel.