
Melting, or fusion, is a physical process that results in the phase transition of a substance from a solid to a liquid. This occurs when the internal energy of the solid increases, typically by the application of heat or pressure, which increases the substance's temperature to the melting point. At the melting point, the ordering of ions or molecules in the solid breaks down to a less ordered state, and the solid melts to become a liquid.
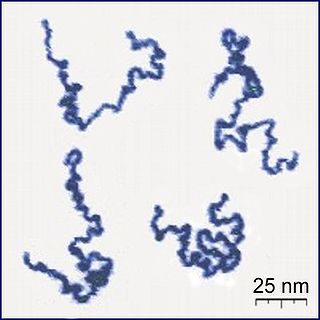
A polymer is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules linked together into chains of repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic and natural polymers play essential and ubiquitous roles in everyday life. Polymers range from familiar synthetic plastics such as polystyrene to natural biopolymers such as DNA and proteins that are fundamental to biological structure and function. Polymers, both natural and synthetic, are created via polymerization of many small molecules, known as monomers. Their consequently large molecular mass, relative to small molecule compounds, produces unique physical properties including toughness, high elasticity, viscoelasticity, and a tendency to form amorphous and semicrystalline structures rather than crystals.

Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula SiO2, commonly found in nature as quartz. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is abundant as it comprises several minerals and synthetic products. All forms are white or colorless, although impure samples can be colored.
In chemistry, a hydrate is a substance that contains water or its constituent elements. The chemical state of the water varies widely between different classes of hydrates, some of which were so labeled before their chemical structure was understood.
In chemistry, a racemic mixture or racemate, is one that has equal amounts of left- and right-handed enantiomers of a chiral molecule or salt. Racemic mixtures are rare in nature, but many compounds are produced industrially as racemates.

Polypropylene (PP), also known as polypropene, is a thermoplastic polymer used in a wide variety of applications. It is produced via chain-growth polymerization from the monomer propylene.

Crystallization is the process by which solids form, where the atoms or molecules are highly organized into a structure known as a crystal. Some ways by which crystals form are precipitating from a solution, freezing, or more rarely deposition directly from a gas. Attributes of the resulting crystal depend largely on factors such as temperature, air pressure, cooling rate, and in the case of liquid crystals, time of fluid evaporation.

Phosphorus pentoxide is a chemical compound with molecular formula P4O10 (with its common name derived from its empirical formula, P2O5). This white crystalline solid is the anhydride of phosphoric acid. It is a powerful desiccant and dehydrating agent.
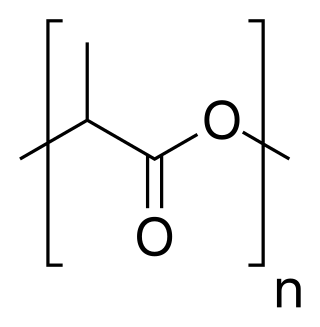
Polylactic acid, also known as poly(lactic acid) or polylactide (PLA), is a thermoplastic polyester with backbone formula (C
3H
4O
2)
n or [–C(CH
3)HC(=O)O–]
n, formally obtained by condensation of lactic acid C(CH
3)(OH)HCOOH with loss of water. It can also be prepared by ring-opening polymerization of lactide [–C(CH
3)HC(=O)O–]
2, the cyclic dimer of the basic repeating unit.

Hot-melt adhesive (HMA), also known as hot glue, is a form of thermoplastic adhesive that is commonly sold as solid cylindrical sticks of various diameters designed to be applied using a hot glue gun. The gun uses a continuous-duty heating element to melt the plastic glue, which the user pushes through the gun either with a mechanical trigger mechanism on the gun, or with direct finger pressure. The glue squeezed out of the heated nozzle is initially hot enough to burn and even blister skin. The glue is sticky when hot, and solidifies in a few seconds to one minute. Hot-melt adhesives can also be applied by dipping or spraying, and are popular with hobbyists and crafters both for affixing and as an inexpensive alternative to resin casting.
In crystallography, polymorphism describes the phenomenon where a compound or element can crystallize into more than one crystal structure. The preceding definition has evolved over many years and is still under discussion today. Discussion of the defining characteristics of polymorphism involves distinguishing among types of transitions and structural changes occurring in polymorphism versus those in other phenomena.
GeSbTe (germanium-antimony-tellurium or GST) is a phase-change material from the group of chalcogenide glasses used in rewritable optical discs and phase-change memory applications. Its recrystallization time is 20 nanoseconds, allowing bitrates of up to 35 Mbit/s to be written and direct overwrite capability up to 106 cycles. It is suitable for land-groove recording formats. It is often used in rewritable DVDs. New phase-change memories are possible using n-doped GeSbTe semiconductor. The melting point of the alloy is about 600 °C (900 K) and the crystallization temperature is between 100 and 150 °C.

Sulfonmethane is a chemical compound first synthesized by Eugen Baumann in 1888 and introduced as a hypnotic drug by Alfred Kast later on, but now superseded by newer and safer sedatives. Its appearance is either in colorless crystalline or powdered form. In United States, it is scheduled as a Schedule III drug in the Controlled Substance Act.

Sucrose octaacetate is a chemical compound with formula C
28H
38O
19or (C
2H
3O
2)
8(C
12H
14O
3), an eight-fold ester of sucrose and acetic acid. Its molecule can be described as that of sucrose C
12H
22O
11 with its eight hydroxyl groups HO– replaced by acetate groups H
3C–CO
2–. It is a crystalline solid, colorless and odorless but intensely bitter.
Crystallization of polymers is a process associated with partial alignment of their molecular chains. These chains fold together and form ordered regions called lamellae, which compose larger spheroidal structures named spherulites. Polymers can crystallize upon cooling from melting, mechanical stretching or solvent evaporation. Crystallization affects optical, mechanical, thermal and chemical properties of the polymer. The degree of crystallinity is estimated by different analytical methods and it typically ranges between 10 and 80%, with crystallized polymers often called "semi-crystalline". The properties of semi-crystalline polymers are determined not only by the degree of crystallinity, but also by the size and orientation of the molecular chains.
In materials science, cocrystals are "solids that are crystalline, single-phase materials composed of two or more different molecular or ionic compounds generally in a stoichiometric ratio which are neither solvates nor simple salts." A broader definition is that cocrystals "consist of two or more components that form a unique crystalline structure having unique properties." Several subclassifications of cocrystals exist.
Berkelium forms a number of chemical compounds, where it normally exists in an oxidation state of +3 or +4, and behaves similarly to its lanthanide analogue, terbium. Like all actinides, berkelium easily dissolves in various aqueous inorganic acids, liberating gaseous hydrogen and converting into the trivalent oxidation state. This trivalent state is the most stable, especially in aqueous solutions, but tetravalent berkelium compounds are also known. The existence of divalent berkelium salts is uncertain and has only been reported in mixed lanthanum chloride-strontium chloride melts. Aqueous solutions of Bk3+ ions are green in most acids. The color of the Bk4+ ions is yellow in hydrochloric acid and orange-yellow in sulfuric acid. Berkelium does not react rapidly with oxygen at room temperature, possibly due to the formation of a protective oxide surface layer; however, it reacts with molten metals, hydrogen, halogens, chalcogens and pnictogens to form various binary compounds. Berkelium can also form several organometallic compounds.

Barium metaphosphate is an inorganic substance with the molecular formula Ba(PO3)2. It is a colourless solid that is insoluble in water, though is soluble in acidic solutions through "slow dissolution". X-ray crystallography shows that this material is composed of Ba2+ cations attached to a polyphosphate ((PO3−)n) anion. A number of hydrated forms are known which are actually cyclic metaphosphates, Ba2(P4O12)·3.5H2O, Ba3(P3O9)2·6H2O.

In organic chemistry, the sulfonamide functional group is an organosulfur group with the structure R−S(=O)2−NR2. It consists of a sulfonyl group connected to an amine group. Relatively speaking this group is unreactive. Because of the rigidity of the functional group, sulfonamides are typically crystalline; for this reason, the formation of a sulfonamide is a classic method to convert an amine into a crystalline derivative which can be identified by its melting point. Many important drugs contain the sulfonamide group.
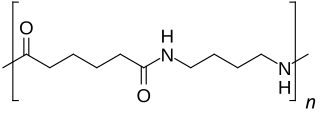
Nylon 46 is a high heat resistant polyamide or nylon. DSM is the only commercial supplier of this resin, which markets under the trade name Stanyl. Nylon 46 is an aliphatic polyamide formed by the polycondensation of two monomers, one containing 4 carbon atoms, 1,4-diaminobutane (putrescine), and the other 6 carbon atoms, adipic acid, which give nylon 46 its name. It has a higher melting point than nylon 6 or nylon 66 and mainly used in applications which must withstand high temperatures.
















