The Flag of Tokelau
The Badge of Tokelau

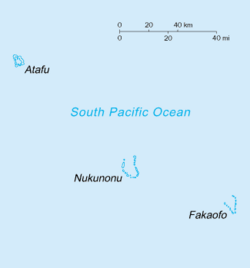
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Tokelau:
Contents
- General reference
- Geography of Tokelau
- Environment of Tokelau
- Populated places of Tokelau
- Demography of Tokelau
- Government and politics of Tokelau
- Branches of the government of Tokelau
- Foreign relations of Tokelau
- Law and order in Tokelau
- Local government in Tokelau
- History of Tokelau
- Culture of Tokelau
- Art in Tokelau
- Sports in Tokelau
- Economy and infrastructure of Tokelau
- Education in Tokelau
- See also
- References
- External links
Tokelau is a territory of New Zealand comprising three tropical coral atolls in the South Pacific Ocean. [1] The United Nations General Assembly includes Tokelau on the United Nations list of non-self-governing territories. [2]
Until 1976 the official name was Tokelau Islands. Tokelau is sometimes referred to by Westerners by the older, colonial name of The Union Islands.


